Finding an alternative for commercial toothpastes is quite a journey with many potholes along the way. Here; s the research I did for the Oils & Herbs Teeth Nourishing Toxin Free Toothpaste.
Why you should not put essential oil in your tooth paste
https://askthedentist.com/essential-oils-toothpaste/
7 vitamins and minerals your mouth needs
Want healthy teeth and gums? Make sure your diet features these key ingredients. These nutritional building blocks are essential for your dental health.
Calcium
No surprises here — calcium is well known as a friend for teeth. Throughout the body, the mineral helps build bones and provide structural support. In your mouth, calcium helps harden your enamel and strengthen your jawbone.
The daily value (DV) for calcium is 1300mg.
What to eat:
Nuts and seeds:
- Sesame seeds raw, 1290.1 mg (97% of daily value)
- Sesame Seeds (Toasted)989mg (76% DV)
- Chia Seeds631mg (49% DV)
- Almonds269mg (21% DV)
- Flax Seeds255mg (20% DV)
- Brazilnuts160mg (12% DV)
- Dry Roasted Hazelnuts123mg (9% DV)
- Almonds269mg (21% DV))
- Dry Roasted Almonds268mg (21% DV)
- Flax Seeds255mg (20% DV)
- Almond Paste172mg (13% DV)
- Dried Lotus Seeds163mg (13% DV)
- Brazilnuts160mg (12% DV)
- Dried Pilinuts145mg (11% DV)
- Dry Roasted Hazelnuts123mg (9% DV)
- Hazelnuts114mg (9% DV)
- Dry Roasted Pistachio Nuts107mg (8% DV)
- Pistachio Nuts105mg (8% DV)
- Walnuts98mg (8% DV)
- Dry-Roasted Mixed Nuts (Salted)87mg (7% DV)
- Macadamia Nuts85mg (7% DV)
- Safflower Seeds78mg (6% DV)
- Dried Sunflower Seeds78mg (6% DV)
- Dried Japanese Chestnuts72mg (6% DV)
- Dry Roasted Pecans72mg (6% DV)
- Dry Roasted Sunflower Seeds70mg (5% DV)
- Hemp Seeds70mg (5% DV)
- Dry Roasted Macadamia Nuts70mg (5% DV)
- Pecans70mg (5% DV)
- Dry Roasted Sunflower Seeds (With Salt)70mg (5% DV)
- Black Walnuts (Dried)61mg (5% DV)
- Dry Roasted Peanuts58mg (4% DV)
- Roasted Squash And Pumpkin Seeds (With Shells)55mg (4% DV)
- Acorns (Dried)54mg (4% DV)
- Butternuts (Dried)53mg (4% DV)
- Roasted Squash And Pumpkin Seeds (Unsalted)52mg (4% DV)
- Roasted Squash And Pumpkin Seeds (Salted)52mg (4% DV)
- Dried Pumpkin And Squash Seeds46mg (4% DV)
- Boiled Chestnuts46mg (4% DV)
- Dry-Roasted Cashews45mg (3% DV)
- Lotus Seeds44mg (3% DV)
- Oil Roasted Cashews43mg (3% DV)
- Cashew Butter43mg (3% DV)
- Cashews (Raw)37mg (3% DV)
- Dried Chinese Chestnuts29mg (2% DV)
- Roasted Chestnuts29mg (2% DV)
- Dried Coconut27mg (2% DV)
- Dried Coconut (Unsweetened)26mg (2% DV)
- Coconut Water24mg (2% DV)
- Dried Ginkgo Nuts20mg (2% DV)
- Roasted Chinese Chestnuts19mg (1% DV)
- Chestnuts19mg (1% DV)
- Chinese Chestnuts18mg (1% DV)
- Coconut Milk18mg (1% DV)
- Pine Nuts (Dried)16mg (1% DV)
- Shredded Coconut Meat15mg (1% DV)
- Boiled Chinese Chestnuts12mg (1% DV)
- Boiled Japanese Chestnuts11mg (1% DV)
- Dried Pine Nuts8mg (1% DV)
- Ginko Nuts2mg (0% DV)
- Dried Beechnuts1mg (0% DV)
- Aloe Vera Gel
Vegetables:
- Dried Chives813mg (63% DV)
- Kanpyo280mg (22% DV)
- Kale254mg (20% DV)
- Collards232mg (18% DV)
- Jute Potherb (Molokhiya) (Cooked)211mg (16% DV)
- Mustard Spinach210mg (16% DV)
- Turnip Greens190mg (15% DV)
- Dandelion Greens raw 187mg (14% DV)
- Garlic181mg (14% DV)
- Freeze-Dried Parsley176mg (14% DV)
- Kelp Seaweed168mg (13% DV)
- Nopales164mg (13% DV)
- Cooked Nopales164mg (13% DV)
- Arugula160mg (12% DV)
- Dried Fungi Cloud Ears159mg (12% DV)
- Cooked Mustard Spinach158mg (12% DV)
- Wakame150mg (12% DV)
- Cooked Kale150mg (12% DV)
- Cooked Tahitian Taro149mg (11% DV)
- Cooked Collards141mg (11% DV)
- Cooked Dandelion Greens140mg (11% DV)
- Parsley138mg (11% DV)
- Cooked Turnip Greens137mg (11% DV)
- Cooked Spinach136mg (10% DV)
- Tahitian Taro129mg (10% DV)
- Wasabi Root128mg (10% DV)
- Cooked Malabar Spinach124mg (10% DV)
- Watercress120mg (9% DV)
- Dried Spirulina Seaweed120mg (9% DV)
- Cooked Mustard Greens118mg (9% DV)
- Cooked Broccoli Raab118mg (9% DV)
- Chrysanthemum117mg (9% DV))
- Chrysanthemum Leaves117mg (9% DV)
- Beet Greens (Raw)117mg (9% DV)
- Mustard Greens115mg (9% DV)
- Cooked Beet Greens114mg (9% DV)
- Sun-Dried Tomatoes110mg (8% DV)
- Vinespinach109mg (8% DV)
- Broccoli Raab (Rapini)108mg (8% DV)
- Bok Choy105mg (8% DV)
- Chinese Broccoli105mg (8% DV)
- Chicory Greens100mg (8% DV)
- Cooked Chinese Broccoli100mg (8% DV)
- Spinach99mg (8% DV)
- Dried Pasilla Peppers97mg (7% DV)
- Pak-Choi (Bok Choy) (Cooked)93mg (7% DV)
- Chives92mg (7% DV)
- Stirfried Soybean Sprouts82mg (6% DV)
- Okra82mg (6% DV)
- Garden Cress81mg (6% DV)
- Cooked Purslane78mg (6% DV)
- Cooked Okra77mg (6% DV)
- Swamp Cabbage77mg (6% DV)
- Cooked Okra (Previously Frozen)74mg (6% DV)
- Irishmoss Seaweed72mg (6% DV)
- Spring Onions72mg (6% DV)
- Laver Seaweed70mg (5% DV)
- Cooked Chrysanthemum69mg (5% DV)
- Cilantro67mg (5% DV)
- Soybean Sprouts67mg (5% DV)
- Purslane65mg (5% DV)
- Citronella (Lemon Grass)65mg (5% DV)
- Sweet Pickled Cucumbers61mg (5% DV)
- Dried Ancho Peppers61mg (5% DV)
- Cooked Garden Cress61mg (5% DV)
- Cooked Soybean Sprouts59mg (5% DV)
- Leeks59mg (5% DV)
- Cooked Podded Peas59mg (5% DV)
- Cooked Swiss Chard58mg (4% DV)
- New Zealand Spinach58mg (4% DV)
- Dill Pickles57mg (4% DV)
- Reduced Sodium Dill Pickles57mg (4% DV)
- Cooked Swamp Cabbage54mg (4% DV)
- Endive52mg (4% DV)
- Swiss Chard51mg (4% DV)
- Radish Sprouts51mg (4% DV)
- Cooked Burdock Root49mg (4% DV)
- Fennel49mg (4% DV)
- Butternut Squash48mg (4% DV
- Cooked Cabbage48mg (4% DV)
- Cooked New Zealand Spinach48mg (4% DV)
- Broccoli47mg (4% DV)
- Cooked Yellow Snap Beans46mg (4% DV)
- Cooked Escarole46mg (4% DV)
- Lotus Root45mg (3% DV)
- Sun-Dried Hot Chile Peppers45mg (3% DV)
- Red Cabbage45mg (3% DV)
- Baked Acorn Squash44mg (3% DV)
- Cooked Green Snap Beans44mg (3% DV)
- Artichokes (Globe Or French)44mg (3% DV)
- Rutabagas (Neeps Swedes)43mg (3% DV)
- Snow Peas43mg (3% DV)
- Taro43mg (3% DV)
- Celeriac43mg (3% DV)
- Morel Mushrooms43mg (3% DV)
- Pumpkin Leaves (Cooked)43mg (3% DV)
- Cooked Celery42mg (3% DV)
- Cooked Snow Peas42mg (3% DV)
- Brussels Sprouts (Raw)42mg (3% DV)
- Cooked Green Beans (Previously Frozen)42mg (3% DV)
- Cooked Red Cabbage42mg (3% DV)
- Chicory Roots41mg (3% DV)
- Cooked Butternut Squash41mg (3% DV)
- Celery40mg (3% DV)
- Broccoli (Cooked)40mg (3% DV)
- Cabbage40mg (3% DV)
- Celtuce39mg (3% DV)
- Pumpkin Flowers39mg (3% DV)
- Pumpkin Leaves39mg (3% DV)
- Baked Sweet Potatoes38mg (3% DV)
- Shallots37mg (3% DV)
- Cooked Parsnips37mg (3% DV)
- Cooked Pumpkin Flowers37mg (3% DV)
- Yellow Snap Beans37mg (3% DV)
- Green Snap Beans (Raw)37mg (3% DV)
- Green Leaf Lettuce36mg (3% DV)
- Green Chili Peppers36mg (3% DV)
- Parsnips36mg (3% DV)
- Pea Sprouts36mg (3% DV)
- Canned Tomato Paste36mg (3% DV)
- Brussels Sprouts (Cooked)36mg (3% DV)
- Savoy Cabbage35mg (3% DV)
- Butterhead Lettuce35mg (3% DV)
- Acorn Squash33mg (3% DV)
- Romaine Lettuce33mg (3% DV)
- Cooked Turnips33mg (3% DV)
- Kimchi33mg (3% DV)
- Carrots33mg (3% DV)
- Green Cauliflower33mg (3% DV)
- Red Leaf Lettuce33mg (3% DV)
- Baby Carrots32mg (2% DV)
- Cooked Green Cauliflower32mg (2% DV)
- Cooked Lima Beans32mg (2% DV)
- Fiddlehead Ferns32mg (2% DV)
- Alfalfa Sprouts32mg (2% DV)
- Sweet Potatoes30mg (2% DV)
- Sauerkraut30mg (2% DV)
- Mashed Sweet Potatoes30mg (2% DV)
- Cooked Savoy Cabbage30mg (2% DV)
- Cooked Carrots30mg (2% DV)
- Turnips30mg (2% DV)
- Cooked Leeks30mg (2% DV)
- Cooked Napa Cabbage29mg (2% DV)
- Canned Lima Beans28mg (2% DV)
- Winter Squash28mg (2% DV)
- Oriental Radishes27mg (2% DV)
- Boiled Sweet Potatoes27mg (2% DV)
- White Icicle Radishes (Daikon)27mg (2% DV)
- Cooked Green Peas (Salted)27mg (2% DV)
- Cooked Green Peas27mg (2% DV)
- Cooked Summer Squash27mg (2% DV)
- Canned Pumpkin26mg (2% DV)
- Cooked Celeriac26mg (2% DV)
- Cooked Acorn Squash26mg (2% DV)
- Stewed Tomatoes26mg (2% DV)
- Cooked Lotus Root26mg (2% DV)
- Radishes25mg (2% DV)
- Peas25mg (2% DV)
- Cooked Kohlrabi25mg (2% DV)
- Lentil Sprouts25mg (2% DV)
- Asparagus24mg (2% DV)
- Kohlrabi24mg (2% DV)
- Onions23mg (2% DV)
- Spaghetti Squash23mg (2% DV)
- Asparagus (Cooked)23mg (2% DV)
- Cauliflower22mg (2% DV)
- Cooked Crookneck Summer Squash22mg (2% DV)
- Cooked Onions22mg (2% DV)
- Cooked Winter Squash22mg (2% DV)
- Crookneck Summer Squash21mg (2% DV)
- Cooked Spaghetti Squash21mg (2% DV)
- Cooked Artichokes (Globe Or French)21mg (2% DV)
- Sweet Onions20mg (2% DV)
- Scallop Squash19mg (1% DV)
- Radicchio19mg (1% DV)
- Witloof Chicory19mg (1% DV)
- Bitter Melon19mg (1% DV)
- Hot Green Chili Peppers18mg (1% DV)
- Cooked Rutabagas (Neeps Swedes)18mg (1% DV)
- Iceberg Lettuce18mg (1% DV)
- Cooked Taro18mg (1% DV)
- Baked Russet Potatoes18mg (1% DV)
- Cooked Zucchini18mg (1% DV)
- Raw Cremini Mushrooms (Exposed To Sunlight Or Uv)18mg (1% DV)
- Canned Tomato Puree18mg (1% DV)
- Cremini Mushrooms18mg (1% DV)
- Cooked Oriental Radishes17mg (1% DV)
- Cooked Hubbard Squash17mg (1% DV)
- Succotash17mg (1% DV)
- Kidney Bean Sprouts17mg (1% DV)
- Cassava16mg (1% DV)
- Ginger16mg (1% DV)
- Zucchini16mg (1% DV)
- Cooked Cauliflower16mg (1% DV)
- Beets (Raw)16mg (1% DV)
- Cooked Beets16mg (1% DV)
- Cucumber16mg (1% DV)
In addition to milk, good sources of calcium include cheese, yogurt, broccoli.
For more on calcium look here.
Vitamin D
Vitamin D helps the body absorb calcium while boosting bone mineral density, so it’s crucial to get an adequate amount of vitamin D to get the most out of your calcium intake.
What to eat: Your body naturally makes vitamin D when it’s exposed to sunlight, but the vitamin can also be found in fatty fish, canned tuna and portobello mushrooms. For more on Vitamin D , look here.
Potassium
What to eat: Bananas are well known sources of potassium, but they’re not alone. Other fruits and vegetables with high levels of the mineral include lima beans, tomatoes, Swiss chard, potatoes, sweet potatoes, avocados and prunes.
Many fresh fruits and vegetables are rich in potassium:
- Bananas, oranges, cantaloupe, honeydew, apricots, grapefruit (some dried fruits, such as prunes, raisins, and dates, are also high in potassium)
- Cooked spinach
- Cooked broccoli
- Potatoes
- Sweet potatoes
- Mushrooms
- Peas
- Cucumbers
- Zucchini
- Pumpkins
- Leafy greens
Juice from potassium-rich fruit is also a good choice:
- Orange juice
- Tomato juice
- Prune juice
- Apricot juice
- Grapefruit juice
Beans or legumes that are high in potassium include:
Other foods that are rich in potassium include:
- Salt substitutes (read labels to check potassium levels)
- Molasses
- Nuts
- Meat and poultry
- Brown and wild rice
- Bran cereal
- Whole-wheat bread and pasta
How Much You Need
You should get 4,700 milligrams (mg) of potassium every day.
Phosphorus
Phosphorus supports calcium in building strong bones and teeth.
What to eat: lentils and pumpkin seeds. You can also find phosphorus in cheese. For more phosphorus sources, look here.
| Food | Serving Size | Phosphorus (mg) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rainbow trout, cooked | 75g (2 ½ oz) | 202 | |||
| Sardines, canned in oil | 75g (2 ½ oz) | 368 | |||
| nuts, seeds and legumes | |||||
| Pumpkin or squash seeds, without shell | 60 mL (1/4 cup) | 676 | |||
| Sunflower seeds, without shell | 60 mL (1/4 cup) | 375-393 | |||
| Beans, adzuki, cooked | 175 mL (3/4 cup) | 286 | |||
| Lentils, cooked | 175 mL (3/4 cup) | 264 | |||
| Chickpeas/garbanzo beans | 175 mL (3/4 cup) | 204 | |||
| Beans (kidney, black-eyed/cowpeas, cranberry/roman), cooked | 175 mL (3/4 cup) | 177-186 | |||
| Egg, cooked | 2 large | 126-157 | |||
| Milk and Alternatives | |||||
| Cheese (cheddar, gruyere, swiss/emmental, gouda, mozzarella, edam, provolone) | 50 g (1 ½ oz) | 232-302 | |||
| Milk (3.3% homo, 2%, 1%, skim, chocolate) | 250 mL (1 cup) | 217-272 | |||
| Cottage cheese | 250 mL (1 cup) | 291-358 | |||
| Yogurt, Greek, all types | 175g (3/4 cup) | 156-246 | |||
| Fortified soy beverage | 250mL (1 cup) | 253 | |||
| Grain Products | |||||
| Bran flakes | 30 g | 344 | |||
| Oatmeal, instant, cooked | 175 mL (¾ cup) | 142 | |||
| Quinoa, cooked | 125 mL (1/2 cup) | 149 |
https://www.unlockfood.ca/en/Articles/Vitamins-and-Minerals/Food-Sources-of-Phosphorus.aspx
Vitamin K
What to eat: Chowing down on leafy greens, such as kale, collards and spinach, can help you increase your vitamin K quota. Other great sources include parsley, broccoli and Brussel sprouts. For more Vitamin K sources look here.
Vitamin C
What to eat: You probably already know that citrus fruits are rich in vitamin C, but you can also find it in potatoes and leafy greens. For more Vitamin C sources, look here.
Bèta Carotene
What to eat: For strong gums and teeth, load up on leafy green vegetables like spinach, kale and collard greens, or in orange-colored fruits and oranges: think apricots, cantaloupe, pumpkin, carrots and sweet potatoes. For more Bèta Carotene sources, look here.
https://www.deltadentalins.com/oral_health/vitamins-and-minerals.html
Secret of Tibetan monks
In mountainous districts of Tibet, where there were no dentists at all, local aboriginals didn’t even hear of such a disease, like caries. And that’s because Tibetans have been using a special tooth-paste, which helps keeping teeth healthy till old age, for centuries. Receipt of a wonder-working remedy is quite simple, Tibetans make no secret of it.pain
Take half a glass of coarse salt, pour with cold boiled water and mix with a spoon intensively during a minute. Remove foam. Draw some quantity of crystals from the bottom with a tooth-brush and brush teeth with them after meal in the morning and evening, and rinse mouth with “pickle”. Of course, firstly you will feel discomfort because of taste of salt in places, where sensibility of your teeth is especially heightened, but in about a week you will get used and unpleasant sensations will be over. Saline tooth-paste works wonders: kills microbes, strengthens enamel, covers mouth cavity, cracks and splits with thin disinfectant layer.
Gymnastics for teeth
Wise Chinese people learned struggling with various diseases using the simplest and cunning methods since great antiquity. They also know how to struggle with caries. Simple Chinese preventive measures against this disease are effective not less, than popular boosted remedies.
In the morning during washing you need to take a big gulp of cold boiled water and keep it in your mouth for 3 minutes, and then swallow slowly, in 3 doses. This method is considered to strengthen teeth and contribute to salivation.
After meal you should definitely rinse your mouth – not only Chinese people know about this simple rule, we also know about it since childhood. Besides common profit, rinsing – is a wonderful exercise not only for teeth: it strengthens muscles of lips and cheeks greatly.
White teeth without paste
It’s not a secret that many special whitening pastes cannot remove unattractive film from teeth, as advertising promises. And procedure of bleach in a dentist’s cabinet, according to doctors’ confessions, is efficient, but has lots of nuances. For example, such unpleasant consequences, like increase of sensitivity of teeth to changes of temperatures and also the fact, that you will have to pass through this procedure regularly. If you are prejudiced against modern “wonder-remedies” and chemicals they contain, you can also gain desirable effect easily with help of folk remedies.
It is recommended to use herbal powder for brushing to whiten teeth. To cook it you will need a powder of tormentil rhizome – 2 parts, powder of calamus root – 2 parts and powder of birch coal – 1 part. You will find all necessary components in a drug store. Mix them, dilute with slightly warm water till thick sour cream consistence and use like a usual tooth-paste. Don’t take food during an hour after this procedure.
For most tolerant home “pharmaceutics”, which have no objection of working thoroughly to cook an effective remedy for keeping their teeth healthy, we can offer such method.
Burn egg-plants (cut in small circles) in an oven or an oiled frying pan till carbonization. Dip your finger in this black powder and brush your teeth for about 3 minutes, the longer, the better. This powder not only whitens, but also strengthens teeth. It’s desirable that you would not take food for about an hour. Don’t worry about your finger, this egg-plant “coal” can be rinsed with water easily. Of course, cooking this remedy will require time of you, so it is better to put it by, counting on several doses.
Everyone knows about whitening characteristics of lemon juice and baking soda. Try to use such simple receipt: it is recommended to brush teeth with lemon juice once a week, to keep them white. To remove yellowness, you will also need to add 1-2 drops of lemon juice and some salt to your tooth-paste or powder. Remember, you should not use lemon juice and soda more than once a week!
Tips to please
Of course, you kiss with your lips, but teeth also take an active part in this process. Make them attractive! Achieve beautiful and natural condition of your health. Don’t delay your visits to a dentist, don’t be lazy to search and use receipts of efficient remedies for strengthening beauty and health of your teeth, and, thus, your charming and confident smile. Use methods of care of your 32 “pearls”, tested by many generations of women, more often.
http://www.womanspassions.com/articles/166.html
De Julia Roberts van het Stenen Tijdperk
12:49 uur
Archeologen hebben een bijzonder skelet -9.000 jaar oud- gevonden: het had nog een perfect gebit. Daarom hebben ze het skelet “Julia Roberts” genoemd.
De tanden van de oude dame waren allen nog geheel intact en bovendien prachtig recht. De archeologen zijn van mening dat mensen in het Stenen Tijdperk een vorm van tandpasta moeten hebben ontwikkeld. Vondsten rondom het skelet gaven aan dat haar dieet gelijk was aan ieder ander in het Stenen Tijdperk, hoewel haar gebit er vele malen beter uitzag dan dat in menig ander skelet uit dezelfde periode.
Het skelet werd aangetroffen in Bulgarije, en wordt algemeen aangenomen als het oudste in Europa.
De vinder: “Ze moet een bijzondere schoonheid zijn geweest en had de concurrentie aan kunnen gaan met de Hollywood-figuren van tegenwoordig. Ze is de Julia Roberts van het Stenen Tijdperk: ze moet een perfecte glimlach hebben gehad. Maar voor ons is het vooral een groot mysterie.
Vorig jaar berichtten Weense historici dat ze een bijzondere ontdekking hadden gedaan in het oude Egypte: een manier om tandpasta te maken, en het zag ernaar uit dat het om massaproductie ging.
In oude Egyptische geschriften wordt gewag gemaakt van een ‘poeder voor witte en perfecte tanden’ dat, gemengd met speeksel, een ‘schoonmaakpasta’ vormde.
Volgens het recept heb je ervoor nodig: een halve gram zout, 1 gram munt, een kwart gram iris en 20 peperkorrels. Deze allen moeten worden geplet en vermengd met speeksel om het perfecte gebit te bewerkstelligen. [Bron: Ananova]
http://www.missgien.net/weblog/archieven/00002314.html
In general, baking soda would need to be used correctly to protect the enamel of the teeth from damage. Ideally, the soda should not be used too much because it can damage the enamel due to repeated usage. Generally, it can only be used only once a week and at a time for two minutes.
Put the rhizome on a cutting board and slice it into thin strips using a sharp knife. An alternative is to grate the rhizome because that gives you smaller chips that are easier to powder. Once the rhizome is in small pieces, lay it out on a drying screen to dry
- Water – In addition to being the best way to quench your thirst, it’s the smartest way to avoid stained teeth. See, water rinses away the sugars, acids, and hidden food particles that can wear away enamel and result in tooth discoloration.
- Sugar-Free Drinks – If plain water won’t do, then opt for sugar-free drinks since they also rinse away the substances that can attack your teeth over time.
- Fish and Flax Seeds –These choices are full of omega-3 fatty acids, which are the strongest anti-inflammatory nutrients. And foods that reduce inflammation may protect you from gum disease.
- Cocoa – Research shows that cocoa can also lessen inflammation, while protecting you from tooth decay and enamel erosion.
- Cheeses and Milk – Along with neutralizing acids in the mouth by increasing your saliva flow, all of the protein and calcium in these dairy sources can strengthen teeth and prevent the erosion of their white enamel.
See the Light on which Foods Cause the Discoloration of Teeth Too many people are in the dark about the clear link between your diet and the discoloration of teeth. Eating the wrong foods can destroy your tooth enamel and leave you with darker, stained teeth. To maintain the brightest smile, stay away from these dental dangers:
- Sweets – Most candies and gums are all sugar, which can attack teeth and remove their white enamel.
- Starchy Foods – Starchy items like white breads, rice, potatoes, pastas, and cereals are full of sneaky sugars that can deplete tooth enamel.
- Sugary Beverages – Sugary drinks such as carbonated beverages, fruit juices, and sports drinks are brimming with simple sugars and acids that can eat away at enamel, which makes teeth appear much darker.
- Darker Drinks – Drinking dark beverages like coffee, tea, and red wine will almost always cause tooth discoloration, as well as weaken tooth enamel due to their harmful acids.
https://www.dentalcarepalmcoast.com/blog/chew-over-the-foods-that-can-cause-or-curb-stained-teeth/https://www.dentalcarepalmcoast.com/blog/chew-over-the-foods-that-can-cause-or-curb-stained-teeth/
If you use salt or baking soda to whiten your teeth, here’s why you should stop
By Lisa Drayer, CNN
Updated 1150 GMT (1950 HKT) October 3, 2019 Of all the ways to whiten your teeth, brushing with salt is not one of them.
Of all the ways to whiten your teeth, brushing with salt is not one of them.
(CNN)If you regularly enjoy coffee, tea, red wine and pastas with marinara sauce, you might be aware that these foods and beverages leave behind stains on your teeth well after they are consumed.But if you think you’ve found a whitening solution in the form of table salt (sodium chloride) or baking soda (another type of salt, sodium bicarbonate), think again.”I see no clinical reason why someone would brush their teeth with salt,” said Dr. Matt Messina, an Ohio-based dentist and assistant professor at the Ohio State University College of Dentistry. “There is no scientific evidence that brushing with salt has any sort of whitening effect on teeth.”
The same can be said for baking soda, although there is more of a scientific basis to the value of using sodium bicarbonate to brush your teeth, Messina explained. It’s a mild abrasive, and chemically also a mild bleach, which can neutralize cavity-causing acids. So when commercially available toothpaste didn’t exist, he said, baking soda made sense for its ability to polish teeth and reduce acidity.

Not everyone uses a toothbrush to clean their teeth — here’s what science says about the alternativesBut that was then; today, you’ve got better options. In fact, exposing teeth to salt or baking soda could erode the tooth’s surface enamel over time. Enamel is like the finished surface of a floor: It’s a thin, hard outer layer that protects each tooth. When enamel is worn away by an irritant, such as salt, decay can occur as bacteria in plaque are able to penetrate teeth more quickly, where they produce acids that can lead to cavities.Nerve damage can occur as well, and gums may become more sensitive, explained Dr. Gerald Grossman, a New York-based cosmetic dentist and diplomate of the American Board of Aesthetic Dentistry.
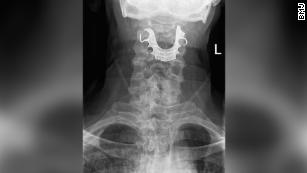
A man’s false teeth got stuck in his throat during a surgery. It was eight days before anyone noticed.Since salt and baking soda are abrasive they could remove stains from teeth, but that’s like trying to lighten your floors by sanding them down, said Messina, who is also a spokesperson for the American Dental Association. It’ll work — but eventually you’d sand away the floor’s entire surface.ADVERTENTIE”You might see short-term whitening with an abrasive, as it will remove surface stains and teeth may get whiter quickly, but the long-term damage is in no way worth that,” Messina said. The erosion of enamel can also cause teeth to become more yellow over the long-term, as the yellow-colored dentin, the inner layer of tooth, is exposed.There’s no way to know how much is too much scrubbing with salt, because everybody’s case is different, Messina explained. “But enamel doesn’t grow back … once it’s gone, it’s gone.”
The best way to whiten teeth
To keep your teeth as white as possible, it’s important to brush and clean between your teeth and floss on a regular basis with a toothpaste approved by the American Dental Association. “Clean teeth are whiter and healthier,” Messina said.The ADA seal of acceptance indicates the toothpaste has been independently tested and is safe and effective when used as directed, Messina explained.
Mouthwash after exercise may counter a workout’s blood-pressure-lowering benefits, study findsSodium chloride — aka salt — might be used as an ingredient in toothpaste, but if it is, “the percent in the toothpaste would be very, very small,” Grossman said. “It’s not like taking a ¼ tsp of salt and putting it into your paste and brushing your teeth,” he added. “It would be in solution. There is nothing there that would be abrasive.”
If regular brushing and flossing isn’t giving you the results you want, both Grossman and Messina recommend a personalized, in-office consultation with a dentist. “There are safe and effective whitening techniques, but they will be different for each individual person,” Messina said.Grossman recommends a bleaching system with a light-activated technology, as well as custom home trays that can help maintain whiter teeth as you continue to eat and drink your favorite foods and beverages — you know, your morning Joe, that glass of red wine, and that tasty pasta with tomato sauce.
https://edition.cnn.com/2019/10/03/health/salt-baking-soda-teeth-whitening-wellness/index.html
Best teas for oral health
https://www.greatoralhealth.com/blogs/news/here-are-some-of-the-best-teas-for-oral-health
Tandjes , de pareltjes van het gezicht.
Een stralende lach is een visitekaartje van jezelf.
Op het eerste gezicht word er eerst naar de tanden gekeken als je ergens binnen komt. Tanden worden vaak vergelijkt met pareltjes.
En om die pareltjes glanzend en gezond te houden, is een goede verzorging nodig.
Melktandjes
De vormen van tanden en kiezen begint al in de baarmoeder.
De eerste elementen ontstaan in de zesde week van de zwangerschap. Tijdens de zesde maand beginnen deze elementen hard te worden.
De baby heeft bij de geboorte nog geen zichtbare tandjes. De eerste tandjes komen pas vanaf de zesde maand na de geboorte door, eerst de snijtanden in de onderkaak en daarna die van de bovenkaak.
Als laatste verschijnen de melkkiezen. De meeste kinderen hebben rond hun derde levensjaar een compleet melkgebit.
Wisselen.
Het melkgebit bestaat uit twintig elementen: tien boven en tien onder.
Deze melktanden zijn een beetje blauwwit van kleur, omdat het glazuur minder hard is. Ondertussen vormt zich in het kaakbeen een nieuw, volwassen gebit.
Dit blijvende gebit duwt, wanneer het element klaar is, het melkgebit eruit. Dit zorgt er voor dat de melktanden en kiezen om de beurt los te zitten en vallen uiteindelijk eruit.
Ongeveer rond het zesde levensjaar begint een kind te wisselen van de melktanden, dit kan ook eerder zijn. Een melkelement valt zes maanden voor het tevoorschijn komen van het blijvende element uit.
Ieder melkelement wordt één-op-één vervangen door een volwassen tand of kies. Het kan een aantal jaren duren voordat het wisselproces voltooit is.
Rond het viertiende levensjaar is het volwassen gebit volledig doorgekomen.
Doorkomen en wisselen.
Het kan aardig pijnlijk zijn als de tandjes doorkomen en uiteindelijk gaan wisselen. Baby’s en kinderen zijn dan soms koortsig, hangerig en huilerig en hebben pijn.
Doormiddel van een (verkoelende) bijtring en speciale pijnstillende druppeltjes helpen de baby door deze periode heen te komen. Een kinderparacetamolletje is goed voor kinderen met koorts en pijn.
Maak van het wisselen van de tandjes geen drama,maar juich met het kind mee wanneer de tand uit de mond is en maak er iets speciaals van, zoals een leuke kaart of een ketting.
Volwassen.
Kleine kinderen zijn vaak maar wat trots op hun grote nieuwe voortanden, waar het wisselproces mee begint. Een voltooide volwassen, blijvend gebit bestaat uit 28 elementen.
Rond de twintigste levensjaar kunnen er nog vier verstandskiezen bijkomen, maar dit is niet altijd het geval. Als de verstandskiezen doorgekomen zijn kan het voorkomen dat er weinig plek in de mond is, als gevolg kan het zijn dat deze verstandkiezen eruit worden getrokken.
Hygiëne.
Hygiëne is zeer belangrijk, het maakt niet uit of je een babytand in je mond hebt staan of 28 perfecte tanden.
Om je tanden in goede staat te houden kan je het beste minimaal tweemaal daags poetsen met een fluoridenhoudende tandpasta.
Verstandig.
Het doorkomen van de verstandskiezen heeft niet direct met je verstand te maken.
De naam verwijst naar het feit dat deze kiezen omstreeks de jongvolwassen leeftijd tevoorschijn komen. Zo rond je twintigste mag men aanmenen dat je verstandiger bent geworden.
http://www.babybrabbel.org/tandjes/tandjes.html
Tandartsen beschrijven de perfecte lach
Amerikaanse tandartsen springen in op de omstreden trend om een zo ideaal mogelijk uiterlijk te hebben: ze hebben een heuse standaard bedacht voor dé perfecte glimlach.
Tandartsen beschrijven de perfecte lach
Volgens hen heeft iemand een perfecte glimlach als deze voldoet aan drie ‘eisen’: Zo min mogelijk zichtbaar tandvlees, geen onnatuurlijk witte tanden en de onderste rij tanden ietsjes verborgen achter de bovenste.
Wat volgens hen ook belangrijk is als je een perfecte glimlach wilt, is dat de middelste twee boventanden iets langer zijn dan de tanden ernaast. De bovenlip en onderlip moeten symmetrisch zijn en tanden mogen zeker niet te wit zijn.
Volgens tandarts Nicholas Davis wil iedereen in Amerika de perfecte glimlach. Vrouwen die bij hem hun tanden laten ‘doen’ willen het liefst lachen als Jessica Simpson.
Volgens hen heeft iemand een perfecte glimlach als deze voldoet aan drie ‘eisen’: Zo min mogelijk zichtbaar tandvlees, geen onnatuurlijk witte tanden en de onderste rij tanden ietsjes verborgen achter de bovenste.
Wat volgens hen ook belangrijk is als je een perfecte glimlach wilt, is dat de middelste twee boventanden iets langer zijn dan de tanden ernaast. De bovenlip en onderlip moeten symmetrisch zijn en tanden mogen zeker niet te wit zijn.
Volgens tandarts Nicholas Davis wil iedereen in Amerika de perfecte glimlach. Vrouwen die bij hem hun tanden laten ‘doen’ willen het liefst lachen als Jessica Simpson.
http://www.gezondheidsnet.nl/uiterlijk/nieuws/1562/tandartsen-beschrijven-de-perfecte-lach
Vitamines en Mineralen
Vitamines en Mineralen
De volgende informatie geeft antwoord op de volgende vragen. Wat is het nut van vitamines en mineralen? In welke voedingsmiddelen komen ze voor en wanneer is het belangrijk om extra vitaminen en mineralen in te nemen.
Onmisbaar
Vitaminen en mineralen zorgen ervoor dat we gezond blijven. Ze zijn nodig voor de groei en voor herstel na ziekte. De hoeveelheid die we dagelijks nodig hebben noemen we ADH (Aanbevolen Dagelijkse Hoeveelheid). Ons lichaam kan niet alle vitamines zelf maken. Daarom halen we deze stoffen uit onze voeding. Er zijn 13 verschillende vitamines die belangrijk zijn voor ons lichaam. Toch horen we vaak over andere vitamines maar deze worden zelf aangemaakt door ons lichaam of zijn helemaal niet belangrijk zoals bv. Lecithine, vitamine Q. De belangrijkste vitamines zijn: A, B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, B7, B11, B12, C, D, E, K.
Mineralen zin net zo belangrijk als vitamines voor het functioneren van het lichaam. Ook deze stoffen halen we uit onze voeding. Bekende mineralen zijn: natrium, kalium, fosfor, calcium, ijzer, zink, jodium. Het is belangrijk om gevarieerd te eten aangezien niet alle voedingsmiddelen alle mineralen en vitamines bevatten. Eet sowieso elke dag vers fruit, groente en volkoren producten.
Vitamines
Vitamine A (=retinol): Deze vitamine is aanwezig in lever (veel), boter, groene en gele groentes (bv. wortel, spinazi, broccoli). Vitamine A voorkomt nachtblindheid en is belangrijk voor de gezondheid van huid, gebit en haren. In het algemeen is het niet nodig om extra vitamine A in te nemen aangezien de dagelijkse voeding genoeg vitamine A bevat. Teveel vitamine A kan schadelijk zijn. Zwangere vrouwen mogen geen lever eten.
Vitamine B1(=thiamine): Zit vooral in volkorenprodukten, vlees, eieren, erwten, bonen, noten en aardappelen. Het zorgt voor een goede werking van het hart en zenuwstelsel.
Vitamine B2(=riboflavine): Zit in brood en jonge groene groente. Het stimuleert de energievoorziening van het lichaam en is goed voor huid en haar.
Vitamine B3(=nicotinezuur): Is aanwezig in vlees, noten en volkorenproducten. Het is goed voor de energievoorziening en zenuwstelsel.
Vitamine B5 (=pantotheenzuur): Zit vooral in vlees, noten, melk en brood. Het is van belang voor de energievoorziening, voor de vorming van bepaalde hormonen en voor de opbouw en afbraak van vetten.
Vitamine B6(=pyridoxine): Komt voor in vlees, bruin brood, groente en melkproducten. Het is onmisbaar voor de bloedaanmaak, zenuwstelsel en groei.
Vitamine B7(=biotine, =vitamine H): Zit in paddestoelen, cacao, noten bloemkool en bonen. Het verzorgt de energiestofwisseling en de vorming van vetzuren. Het is ook goed voor huid en haar.
Vitamine B11(=acidum folicum): Zit in vlees, groente, graanproducten en noten. Deze vitamine is nodig voor de aanmaak van rode bloedcellen en ook voor de groei van het lichaam.
Vitamine C(=ascorbinezuur): Zit in bijna alle groenten en fruit. Vitamine C zorgt voor een goede wondgenezing, verhoogt de weerstand en houdt deze op peil en verbetert de opname van ijzer uit de voeding.
Vitamine D(=colcalciferol): Zit in vis, eieren, boter en lever. Bovendien maakt het lichaam zelf vitamine D aan onder invloed van zonlicht. Deze vitamine is goed voor de botten en verbetert de opname van calcium en fosfor uit voedsel.
Vitamine E (=tocoferol): Is aanwezig in vetten en oliën, eieren, boter, graanproducten en groente vooral groene. Het zorgt voor een gezonde huid en rode bloedcellen. Vitamine K (=fytomenadion):zit veel in groene groenten en wordt ook in de darmen zelf gemaakt door bacteriën. Het is belangrijk voor de bloedstolling.
Mineralen
Natrium: Komt voor in bijna alle voedingsmiddelen. Het is een bestanddeel van keukenzout en zorgt voor het evenwicht in vocht van het lichaam. Samen met kalium is natrium nodig voor het goed functioneren de zenuwen en spieren.Teveel natrium is slecht voor de nieren en vergroot de kans op hoge bloeddruk. Kijk daarom uit wanneer je zout bij het eten gebruikt. Bv. Ketjap, maggi en all-seasoning kruiden bevatten al zout en dus hoef je geen extra zout toe te voegen. Gebruik ook geen zout wanneer je water kookt voor bv. rijst, spaghetti etc.
Calcium(=kalk): Kalk zit vooral in melkproducten maar ook in groente en noten. Kalk is nodig voor gezonde botten en tanden.
Ijzer: Zit in vlees, graanproducten, aardappelen en groente. Ijzer uit dierlijke producten wordt beter in het lichaam opgenomen dan ijzer uit plantaardige producten. Ijzer zorgt indirect voor het zuurstoftransport door het lichaam.
Fluor(=fluoride): Fluoride komt in zeer kleine hoeveeldheden voor in bijna alle voedingsmiddelen. In thee en in zeevis zit relatief veel fluoride. Het is belangrijk voor de stevigheid van botten en beschermt je tanden. Omdat onze voeding te weinig fluoride bevat om een goede bescherming te geven tegen tandbederf, is extra fluoride nodig in de vorm van tandpasta. Dit is belangrijk voor volwassen en ook voor kinderen.
Jodium: Wordt toegevoegd aan bijna alle soorten zout. Het zit in brood en ook in zeevis. Het is belangrijk voor de schildklierhormonen. Deze hormonen zijn onmisbaar voor de groei, zenuwstelsel en voor een goede stofwisseling. Mensen die weinig of geen brood eten, hebben kans op een jodiumtekort. De schildklier gaat dan trager werken en zwelt op. Dit noemen we struma. Teveel jodium is ook schadelijk. De schildklier gaat dan te snel werken. Dit leidt o.a. tot hartproblemen. Gebruik daarom geen Kelp tabletten want deze bevattten veel jodium.
Wie moeten er EXTRA vitaminen en mineralen gebruiken?
Baby’s
Baby’s hebben kans op een tekort aan vitamine K. Zeker bij baby’s die alleen borstvoeding krijgen. Aan flesvoeding is al vitamine K toegevoegd. Indien de baby alleen borstvoeding krijgt, heeft de baby elke dag en 3 maanden lang 3 druppels vitamine K (0.25mg/g) nodig.
Baby’s die alleen borstvoeding krijgen hebben extra vitamine D nodig voor de opbouw van botten en tanden.
Kinderen
Kinderen hebben vitamine A nodig voor de groei en de ontwikkeling van het gebit, nagels, haar en botten / voor het gezichtsvermogen & om het weerstandsvermogen van de huid en de slijmvliezen te verhogen. Voedingsmiddelen die rijk zijn aan vitamine A: boter / margarine / halvarine / lever / melk / vette vis / wortelen / spinazie / bloemkool. Zorg dus dat uw kind hier voldoende van binnen krijgt. Lukt dit niet dan kan het worden aangevuld met vitamine AD druppeltjes of tabletjes speciaal voor kinderen.
Kinderen in de groei hebben extra vitamine D nodig voor de opbouw van botten en tanden. Vitamine D druppeltjes of tabletjes worden aanbevolen voor: kinderen van 1 tot 4 jaar het hele jaar door
Kinderen met een donkere huidskleur van 4-7 jaar hebben ook extra vitamine D nodig. Vrouwen die zwanger zijn (vanaf de derde maand zwangerschap) en vrouwen die borstvoeding geven hebben ook extra vitamine D nodig.
Vrouwen
Vrouwen in de vruchtbare leeftijd hebben vaak een licht ijzertekort door ijzerverlies bij de menstruatie. Advies: eet wat meer ijzerrijke voeding, zoals volkorenproducten, vlees, groente en aardappelen. Bij een groot ijzertekort is er kans op bloedarmoede. De eerste verschijnselen zijn moeheid en duizeligheid. Ga met deze klachten naar de huisarts. Want een groot ijzertekort is met voeding niet aan te vullen.
Vrouwen die zwanger willen worden moeten vitamine B11 (foliumzuur) nemen tot en met de achtste week van de zwangerschap. Foliumzuur vermindert de kans op een “open ruggetje” bij de baby.
Senioren
Senioren hebben extra vitamine D nodig om botafbraak tegen te gaan.
Vraag advies aan uw huisarts. Voor sterke botten neem je voeding met genoeg calcium. Voor volwassenen 1000 mg per dag. Deze hoeveelheid wordt bereikt met 2 plakken kaas en bij elke maaltijd melk, vla of yoghurt. De calciumbehoefte loopt op met de leeftijd: mensen tussen 51 en 70 jaar hebben 1100 mg calcium nodig en 70-plussers 1200mg. Wie met de voeding genoeg calcium binnenkrijgt, heeft geen kalktabletten nodig. Soms krijgen oudere mensen niet genoeg vitamines en mineralen binnen. Vooral als ze weinig in de buitenlucht komen, minder eten of/en als ze medicijnen gebruiken. Vraag advies aan de huisarts.
Dieetgebruikers
Wie een speciaal dieet volgt, of wie bepaalde voedingsmiddelen niet wil of mag gebruiken, kan een vitamine- of mineralenpreparaat nodig hebben. Overleg met huisarts of diëtist. Mensen die een extreem dieet volgen of zelfs vasten om af te vallen, krijgen soms niet alle noodzakelijke vitamines en mineralen binnen. Dan kan een vitamine- of mineralenpreparaat nodig zijn. Overleg met huisarts of diëtist.
Patiënten
Extra vitamines en mineralen kunnen nuttig zijn voor mensen met bepaalde ziekten, zoals darmziekten, en bij herstel na een zware ziekte of operatie. Bijvoorbeeld na een darmoperatie kan de opname van vitamines en mineralen verstoord zijn en dan is het belangrijk om extra vitamines en mineralen te nemen. Overleg met huisarts of diëtist. Medicijngebruik kan de opname van vitamines en mineralen uit voeding verminderen.
Mensen die specifieke geneesmiddelen gebruiken, mensen die een bepaalde operatie hebben gehad en bij bepaalde aandoeningen. Deze mensen moeten aan de dokter vragen welke vitamines en mineralen ze extra moeten in nemen. Vraag advies aan de huisarts.
Kijk uit, teveel vitamines en mineralen kunnen schadelijk zijn!
Link:
Vitamine-info
http://www.democrazy.nl/culuit/index.php?module=pagemaster&PAGE_user_op=view_page&PAGE_id=867
Fluor – Fluoride
Natuurlijke bronnen:
Andijvie, bieten, bloemkool, chinese kool, groene kool, peterselie, rode kool, spruiten, uien, waterkers, zuurkool. Avocado’s, jenever-bessen, paardekastanjes, vlierbessen. Nieren. Haver en volkoren tarwe. Eidooiers, geitekaas, melk, roquefort. Alsem, kamille, karwei, knoflook, maagdenpalm, peterselie, zouthout. Natuurlijk hard water en calciumfluoride.
Eigenschappen:
Een van de bekendste functies van fluor is de bescherming van tanden en kiezen tegen gaatjes. Fluor verlaagt de zuurgraad in de mondholte tijdens de consumptie van koolhydraten. Voorts lijkt het dat fluor in samenwerking met calcium de botten versterkt.
Deficiëntie-symptomen:
Belangrijke toename van caries. Tandverval.
Kan gunstig werken op/bij:
Aandoeningen van tanden en tandvlees (rottende tanden), osteoporose (atrofie van het skelet).
Wisselwerking met medicijnen, vitaminen of mineralen:
Aluminiumhydroxide,
Calciumsupplementen: vermindert de resorptie van fluoride.
Wisselwerking met andere stoffen:
Melk: vermindert de resorptie van fluoride. Neem uw dosis twee uur voor u melk drinkt of twee uur erna.
Dosering:
De normale (minimale) dagelijkse behoefte is niet vastgesteld, maar men denkt dat de gemiddelde opname tussen 0,25 en 0,35 mg ligt.
Waarschuwing:
2 tot 8 mg kan tot fluorvergiftiging leiden (verkleuring van het tand-emaille). Een dosis van 8 tot 20 delen fluor per miljoen delen water kan de oorzaak zijn van osteosclerose. Kreupelmakende fluorvergifti-ging wordt gekenmerkt door verkalking van de spierligamenten en ongecontroleerde nieuwe botgroei, gewoonlijk van de lange, platte botten.
Vergiftiging kan voorkomen bij 500 delen fluor op 1 miljoen delen water, dat is bij een dosis die 2500 maal zo groot is als de aanbevo-len hoeveelheid.
http://www.andersgezond.org/2007/09/mineralen-en-hun-toepassing.html
Jodium
Natuurlijke bronnen:
Aardappelschillen, artisjokken, asperges, bloemkool, broccoli, champignons, groene peper, prei, rode kool, savooiekool, sla, snijbiet, spinazie, spruitjes, tomaten, uien, waterkers. Aardbeien, appels, avocado’s, Bartlett-peren, bosbessen, sinaasappelen, zonnebloemzaadjes. Garnalen, heilbot, kabeljauw, kammosselen, makreel, mosselen, oesters, schelvis, zalm, zeeforel, zeekreeft en in mindere mate ander zeevoedsel. Blaaswier, Iers mos (parelmos), IJslands mos. Agar-agar, kelp, zeewier, zeezout.
Eigenschappen:
Betrokken bij de synthese van schildklierhormonen. Essentieel voor het behoud van gezonde huid, haar en nagels.
Deficiëntie-symptomen:
Vergrote schildklier, droge huid en haar, verlies van fysieke en mentale vitaliteit; kropziekte bij kinderen die geboren worden indien de moeder lijdt aan jodium-deficientie.
Voor relevante producten bij deze publicatie : surf naar http://www.herbsofcourse.eu
Geplaatst door Anders Gezond op 0:03
Labels: mineraal, mineraalhuishouding, mineralen, minera
Calcium
Natuurlijke bronnen:
andijvie, bloemkool, broccoli, groen van bieten, groene bonen, kekers, kievitsbonen, kool, koolrabi, koolraap, lijnzaad, linzen, luzernespruiten, okra, pastinaak, rabarber, selderij, sla, snijbiet, soja-bonen, spinazie, tomaten, uien, waterkers, wortels. Amandelen, ananas, avocado’s, bananen, citroenen, dadels, frambozen, gedroogde abrikozen, gedroogde pruimen, grapefruit, krenten, kokosnoten, perziken, pruimen, lemmetjes, rozijnen, vijgen, zure bosbes, zwarte walnoten. Gegrilde kip, lever; garnalen, kreeft, oesters. Sojameel. De meeste kaassoorten, gecondenseerde melk, karnemelk, taptemelk. Bieslook, geitenbaard, guichelheil, herderstasje, kamille, kleefkruid, klein hoefblad, lijnzaad, maretak, netel, paardebloemwortels, paardestaart, parelmos (Iers mos), pijlwortel, stalkruid, vlasleeuwebek, weegbree, zilverschoon, zuring. Beendermeelcalcium, calcium uit eierschalen of uit oesterschelpen, calciumgluconaat, calciumlactaat, dolomiet (bitterkalk), kelp.
Eigenschappen:
Van belang bij bot- en tandvorming, bloedstolling, spiercontractie en hartfunctie. Een cofactor van veel enzymen.
Deficiëntie-symptomen:
Osteoporose (late symptomen): veelvuldig breuken in de wervelkolom en andere botten, de rug wordt krom, de wortels van ruggemergzenuwen raken bekneld, chronische pijn, gewichtsverlies. Osteomalacie: veelvuldige breuken.Spierkrampen, stuipaanvallen, pijn onder in de rug. Tetanie, weke botten, broze botten, rug en beenpijnen; slapeloosheid, depressie; geirriteerdheid.
Kan gunstig werken op/bij:
Aambeien, aandoeningen van tanden en tandvlees, acne, allergien, anemie (bloedarmoede), arteriosclerose, artritis, atherosclerose, been of voetkramp, botbreuk, cataract (grijze staar), coeliakie (inheemse spruw), constipatie (verstopping), diabetes (suikerziekte), diarree, dikkedarmontsteking, duizeligheid, epilepsie, ettering van de tandkassen, psychische klachten, gewone verkoudheid, hemofilie, hypertensie (hoge bloeddruk), koorts, maagzweer (peptisch), nagelproblemen, nefritis (nierontsteking), osteomalacie (beenverweking), osteoporose (atrofie van het skelet), ouder worden, overgewicht en zwaarlijvigheid, pernicieuze anemie (behoort tot auto-immuun ziekten), rachitis (engelse ziekte), slapeloosheid, spierkrampen in het algemeen, syndroom van Meniere, tetanie voorbijgaande wondkramp), tuberculose, wormen, ziekte van Parkinson, zonnebrand.
Gebruik:
Calcium is effectiever als het wordt ingenomen met vitamine A en C (helpen bij de absorptie), vitamine D (helpt in de reabsorptie van calcium in de nierbuisjes en bij het vasthouden en benutten van calcium), onverzadigde vetzuren (helpen calcium beschikbaar te maken voor de weefsels), ijzer (helpt bij absorptie), magnesium (de delen calcium op 1 deel magnesium), mangaan, fosfor, hydrochloor zuur.
Antagonisten zijn o.a. aspirine, antibiotica, aluminiumbevattende antacida.
Een verandering in de eiwit-inname beinvloedt het calcium-metabolisme.
Wisselwerking met medicijnen, vitaminen of mineralen:
Preparaten met digitalis: onregelmatige hartslag.
IJzersuppleties: vermindert de resorptie van ijzer, tenzij men tegelijkertijd vitamine C neemt.
Magnesium bevattende medicijnen of supplementen verhoogt de gehalten van deze stoffen in het bloed.
Orale voorbehoedsmiddelen (de pil) en oestrogeen: kan de calciumresorptie vergroten.
Kaliumsupplementen: grotere kans op een onregelmatige hartslag.
Tetracyclines (oraal): vermindert de resorptie van tetracycline.
Vitamine A (megadoses): versnelt botverzwakking.
Vitamine D (megadoses): veroorzaakt een zeer sterkte verhoging van de resorptie van calciumsupplementen.
Wisselwerking met andere stoffen:
Tabak,
Alcohol,
Thee,
Koffie: vermindert de resorptie.
Neem calcium niet met melk of andere zuivelprodukten, zodat het lichaam zowel calcium kan opnemen uit het voedsel als uit calcium-supplementen.
Voedsel: Eet liever geen spinazie, rabarber, zemelen, volkorenprodukten, vers fruit of verse groenten tegelijkertijd met calcium. Ze kunnen een efficiente resorptie van calcium verhinderen.
Dosering:
Slechts 20 tot 30% van de inname wordt geabsorbeerd in de twaalfvingerige of dunne darm; de rest wordt via ontlasting e.d. verwijderd.
Om nu het evenwicht in het lichaam op peil te houden wordt de normale (minimale) dagelijkse behoefte aan calcium volgens sommigen gesteld op 800 mg, volgens anderen op 1800 mg. Zwangere vrouwen hebben 400 mg. meer nodig, en zogende moeders 500 mg meer.
Waarschuwing:
De giftige hoeveelheid is nog niet vastgesteld, maar een aantal symptomen van calciumvergiftiging zijn te onderkennen; calciumneerslag in de nieren of andere organen en een trage werking van deze organen.
Als de calcium-inname hoog is, dient de magnesium-inname dit ook te zijn. Te weinig magnesium resulteert in calcium ophoping in spieren, hart en nieren (veroorzaakt zo nierstenen).
http://www.andersgezond.org/2007/09/mineralen-en-hun-toepassing.html
Chloor – Chloride
Natuurlijke bronnen:
Aardappelen, asperges, kool, pastinaak, sla, spinazie, tomaten, uien, wortels. Ananas, bananen, citroenen, dadels, druiven, kokosnoten, sinaasappelen. Dierlijke organen. Vis in het algemeen; oesters, zalm. Volkoren tarwe. Eidooiers, het wit van eieren, kaas, melk. Alle planten bevatten meer of minder chloor in de vorm van natriumchloride.
Eetbaar zeewier, hui (wei), kelp, natriumchloride (of keukenzout).
Eigenschappen:
Handhaaft osmotische waarde en zuurgraad. Essentieel in maagsappen extracellulair volume.
Deficiëntie-symptomen:
Kan het zuur-base-evenwicht in de lichaamsvloeistoffen verstoren (zeldzaam).
Verlies van haar en tanden, slechte spiersamentrekking, verzwakte spijsvertering, misselijkheid, (voortdurend) braken, verwardheid, slapte, coma.
Als opzettelijk wordt verzuimd chloride aan babyvoeding toe te voegen, ontwikkelt zich bij de baby alkalose (alkalivermeerdering), hypovolemie (te gering bloedvolume) en belangrijk urineverlies. Ook kunnen er psychomotorische storingen, geheugenverlies en vertraging in de groei optreden.
Kan gunstig werken op/bij:
Braken, diarree.
Wisselwerking met medicijnen, vitaminen of mineralen:
Kalium,
Natrium: handhaaft het normale zuur-base-evenwicht in het lichaam.
Dosering:
De normale (minimale) dagelijkse behoefte is niet vastgesteld, doch ons eten bevat voldoende zout om 3 tot 9 gram chloor per dag binnen te krijgen.
Waarschuwing:
Buitengewoon zoutgebruik (= natriumchloride) verhoogt de kans op hoge bloeddruk.
Er is geen giftige dosis vastgesteld, maar elke hoeveelheid chloor groter dan 14 gram wordt als overmatig beschouwd.
Allergische reacties zoals astma en netelroos kunnen het gevolg zijn van zwaar gechloreerd drinkwater. Bovendien wordt er van uit gegaan dat chloor in sommige gevallen de oorzaak is van functionele olitis.
Andere vergiftigingsverschijnselen kunnen zijn atherosclerose, het snakken naar adem, duizeligheid en het blauw worden ten gevolge van zuurstofgebrek.
http://www.andersgezond.org/2007/09/mineralen-en-hun-toepassing.html
Fosfor – Fosfaat
Natuurlijke bronnen:
Bonen, groen van de paardebloem, kekers, limabonen, linzen, mais, okra, pastinaak, sojabonen, spinazie, spruitjes, waterkers. Appels, amandelen, avocado’s, citroen, druiven, grapefruit, kersen, lemmetjes, passievrucht, pecannoten, pompoenen, pruimen, rozijnen, walnoten.
Kalfsvleesgehakt, mager vlees, runderlever. Heilbot, oesters.
Havermout. Eidooier, kaas, melk. Bloemen van de goudsbloem en geitenbaard, kalamus, karweizaadjes, knoflook, muur, sesam, zoethoutwortel, zuring. Beendermeel.
Eigenschappen:
Onderdeel van botten, tanden en een cofactor voor verschillende hormonen en B-vitamines. Tevens betrokken bij het vrijmaken van energie uit voeding, handhaven zuurgraad, glucoseabsorptie, vettransport en calciummetabolisme.
Deficiëntie-symptomen:
Pijnlijke botten, verlies van gewicht en eetlust, slapte, botten die makkelijk breken, onregelmatige ademhaling, vermoeidheid, stoornissen in zenuwstelsel, ettering van de tandkassen.
Kan gunstig werken op/bij:
Aandoeningen van tanden en tandvlees, arteriosclerose, artritis, atherosclerose, been of voetkramp, belemmerde groei, botbreuk, dikkedarmontsteking, psychische klachten, kanker, osteomalacie (beenverweking), osteoporose (atrofie van het skelet), rachitis (engelse ziekte), rugpijn, stress, zwangerschap.
Gebruik:
Fosfor is effectiever als het wordt ingenomen met vitamine A, vita-mine D, onverzadigde vetzuren, calcium (1 deel fosfor op 2,5 delen calcium), ijzer, mangaan, proteine.
Antagonisten zijn o.a. alcohol, aspirine, diuretica.
Aluminiumbevattende antacida verhogen de fosfor-behoefte.
Wisselwerking met medicijnen, vitaminen of mineralen:
Captopril,
Preparaten met digitalis, Diuretica, kaliumconserverend (amiloride, spironeclacteen, triamtereen),
Emalapril: geeft meer kans op een te grote hoeveelheid kalium (hypokalemie).
Anabole steroiden,
Testosteron: geeft meer kans op oedeem.
Anti-maagzuurmiddelen met aluminium of magnesium:
kan de resorptie van fosfaten verhinderen.
Supplementen met calcium en anti-maagzuurmiddelen: vergroot het risico van calciumafzetting in de zachte weefsels. Vermindert de resorptie van fosfor.
Geneesmiddelen met cortison of ACTH: verhoogt serumnatriumgehalte.
Salicylaten: kan de plasmaconcentratie van salicylaten verhogen.
Vitamine D: hindert de fosforresorptie, maar kan ook meer kans geven op te veel fosfor in het bloed en de lichaamscellen.
Wisselwerking met andere stoffen:
Alcoholische dranken: verminderen de voor de vitale lichaamsfuncties beschikbare fosfor.
‘Soft drinks’: een buitensporige consumptie kan een schadelijke uitwerking hebben op de resorptie van fosfor en calcium.
Voedsel:
Een buitensporige consumptie van rabarber, spinazie en zemelen kan de resorptie van kaliumfosfaten verminderen.
Een buitensporige consumptie van vlees en kant-en-klaar voedsel kan een schadelijke uitwerking hebben op de resorptie van fosfor
en calcium.
Dosering:
De normale (minimale) dagelijkse behoefte is ongeveer 800 mg, al spreken andere bronnen van 1800 mg. Voor zwangere vrouwen en zogende moeders ligt de behoefte op resp. 1200 en 2200 mg.
Waarschuwing:
De hoeveelheid welke giftige effecten geeft is onbekend, maar buiten gewoon grote hoeveelheden fosfor zonder een evenredige hoeveelheid calcium kunnen tot het begin van een fosfordeficientie leiden.
http://www.andersgezond.org/2007/09/mineralen-en-hun-toepassing.html
IJzer
Natuurlijke bronnen:
Bieten, bladgroenten, broccoli, champignons, erwten, gedroogde bonen, kool, linzen, luzerne, olijven, prei, sojabonen, spinazie, uien, waterkers. Aardbeien, amandelen, appels, avocado’s, bramen, dadels, gedroogde pruimen, johannesbrood, kersen, krenten, loganbessen, peren, perziken, pruimen, sesamzaad, walnoten, watermeloen, zonnebloemzaadjes. Kippevlees, lamsvlees, lever, nieren, rundvlees. Bruine rijst, volkoren granen. Eidooiers. Blad van de koningskaars, bladeren van de aardbei en vlasleeuwebek, brandnetel, geitenbaard, gele veldzuring (bevat 40% ijzer), jalapwortel, peterselie, stalkruid, zilverschoon. Eetbaar zeewier, gedroogde lever, gist, kelp, melasse.
Eigenschappen:
Onderdeel van hemoglobine, myoglobine en andere enzymen.
Deficiëntie-symptomen:
Anemie, zwakte, lusteloosheid, vermoeidheid, bleke huid, men voelt zich niet in orde, hartkloppingen na inspanning, prikkelbaarheid, kloofjes in lippen en tong, moeilijkheden bij het slikken.
Kan gunstig werken op/bij:
Aandoeningen van tanden en tandvlees, alcoholisme, anemie, coeliakie (inheemse spruw), diabetes (suikerziekte), diarree, dikkedarmontsteking, gastritis (maagcatarre), jicht, kanker, kneuzingen, leukemie, maagzweer (peptisch), menstruatie, nagelproblemen, nefritis (nierontsteking), ouder worden, pernicieuze nemie (hoort bij auto-immuun ziekten), scheurbuik, tuberculose, wormen, zwangerschap, zweren.
Gebruik:
IJzer is effectiever als het wordt ingenomen met vitamine B12 (helpt de ijzer-functie in het lichaam), foliumzuur, vitamine C (helpt bij de absorptie), calcium, fosfor, hydrochloride zuur (nodig bij de assimilatie van ijzer), kobalt, koper.
Antagonisten zijn o.a. aspirine, EDTA (voedingsconserveringsmiddel) en vitamine E.
Vitamine C verhoogt de ijzerabsorptie. Antacida en sommige laxeermiddelen verlagen de ijzer-absorptie, evenals thee, koffie en grote hoeveelheden melk.
Penicilline verhoogt de ijzer-behoefte.
Wisselwerking met medicijnen, vitaminen of mineralen:
Cholestyramine,
Sulfasalazine: vermindert de uitwerking van ijzer.
Pancreatine,
Zink (grote hoeveelheden): vermindert de ijzerresorptie.
Allopurinol: kan een te grote ijzerafzetting in de lever veroorzaken.
Anti-maagzuurmiddelen: kan een slechte ijzerresorptie veroorzaken.
Calcium: de combinatie is noodzakelijk voor een efficiente calcium-resorptie.
Koper helpt bij de koperresorptie.
IJzersupplementen (andere): kan een te grote ijzerafzetting in de lever veroorzaken.
Penicillamine: vermindert de uitwerking van penicillamine.
Tetracyclines: vermindert de uitwerking van tetracycline. Neem het ijzer drie uur voor of twee uur na gebruik van tetracycline.
Vitamine C: versterkt de uitwerking van ijzer. Is nodig voor de vorming van rode bloedcellen en hemoglobine.
Vitamine E: versterkt de uitwerking van ijzer.
Wisselwerking met andere stoffen:
Alcohol: door alcohol gaat het lichaam meer ijzer gebruiken. Hierdoor kunnen organen beschadigd worden. Gebruik het niet of met mate.
Dranken: Melk vermindert de ijzerresorptie. Thee vermindert de ijzerresorptie. Koffie vermindert de ijzerresorptie.
Dosering:
De normale (minimale) dagelijkse behoefte is 10 mg voor mannen en 8 mg voor vrouwen. Tijdens de menstruatie, zwangerschap en lactatieperiode is sprake van een verhoogde ijzerbehoefte, en vandaar dat vrouwen tussen 18 en 59 een hogere dosis kunnen overwegen.
Waarschuwing:
De giftige hoeveelheid ijzer bedraagt bij kinderen ongeveer 900 mg. Voor volwassenen varieert deze dosis. De normale signalen van een ijzervergiftiging zijn opspelend maagzuur, misselijkheid, constipatie, diarree en andere spijsverteringsstoornissen. Wordt er niet corrigerend ingegrepen dan kunnen de lever en pancreas worden beschadigd.
http://www.andersgezond.org/2007/09/mineralen-en-hun-toepassing.html
Calcium
Natuurlijke bronnen:
andijvie, bloemkool, broccoli, groen van bieten, groene bonen, kekers, kievitsbonen, kool, koolrabi, koolraap, lijnzaad, linzen, luzernespruiten, okra, pastinaak, rabarber, selderij, sla, snijbiet, soja-bonen, spinazie, tomaten, uien, waterkers, wortels. Amandelen, ananas, avocado’s, bananen, citroenen, dadels, frambozen, gedroogde abrikozen, gedroogde pruimen, grapefruit, krenten, kokosnoten, perziken, pruimen, lemmetjes, rozijnen, vijgen, zure bosbes, zwarte walnoten. Gegrilde kip, lever; garnalen, kreeft, oesters. Sojameel. De meeste kaassoorten, gecondenseerde melk, karnemelk, taptemelk. Bieslook, geitenbaard, guichelheil, herderstasje, kamille, kleefkruid, klein hoefblad, lijnzaad, maretak, netel, paardebloemwortels, paardestaart, parelmos (Iers mos), pijlwortel, stalkruid, vlasleeuwebek, weegbree, zilverschoon, zuring. Beendermeelcalcium, calcium uit eierschalen of uit oesterschelpen, calciumgluconaat, calciumlactaat, dolomiet (bitterkalk), kelp.
Chloor – Chloride
Natuurlijke bronnen:
Aardappelen, asperges, kool, pastinaak, sla, spinazie, tomaten, uien, wortels. Ananas, bananen, citroenen, dadels, druiven, kokosnoten, sinaasappelen. Dierlijke organen. Vis in het algemeen; oesters, zalm. Volkoren tarwe. Eidooiers, het wit van eieren, kaas, melk. Alle planten bevatten meer of minder chloor in de vorm van natriumchloride.
Eetbaar zeewier, hui (wei), kelp, natriumchloride (of keukenzout).
Fluor – Fluoride
Natuurlijke bronnen:
Andijvie, bieten, bloemkool, chinese kool, groene kool, peterselie, rode kool, spruiten, uien, waterkers, zuurkool. Avocado’s, jenever-bessen, paardekastanjes, vlierbessen. Nieren. Haver en volkoren tarwe. Eidooiers, geitekaas, melk, roquefort. Alsem, kamille, karwei, knoflook, maagdenpalm, peterselie, zouthout. Natuurlijk hard water en calciumfluoride
Fosfor – Fosfaat
Natuurlijke bronnen:
Bonen, groen van de paardebloem, kekers, limabonen, linzen, mais, okra, pastinaak, sojabonen, spinazie, spruitjes, waterkers. Appels, amandelen, avocado’s, citroen, druiven, grapefruit, kersen, lemmetjes, passievrucht, pecannoten, pompoenen, pruimen, rozijnen, walnoten.
Kalfsvleesgehakt, mager vlees, runderlever. Heilbot, oesters.
Havermout. Eidooier, kaas, melk. Bloemen van de goudsbloem en geitenbaard, kalamus, karweizaadjes, knoflook, muur, sesam, zoethoutwortel, zuring. Beendermeel.
IJzer
Natuurlijke bronnen:
Bieten, bladgroenten, broccoli, champignons, erwten, gedroogde bonen, kool, linzen, luzerne, olijven, prei, sojabonen, spinazie, uien, waterkers. Aardbeien, appels, avocado’s, bramen, dadels, gedroogde pruimen, johannesbrood, kersen, krenten, loganbessen, peren, perziken, pruimen, sesamzaad, walnoten, watermeloen, zonnebloemzaadjes. Kippevlees, lamsvlees, lever, nieren, rundvlees. Bruine rijst, volkoren granen. Eidooiers. Blad van de koningskaars, bladeren van de aardbei en vlasleeuwebek, brandnetel, geitenbaard, gele veldzuring (bevat 40% ijzer), jalapwortel, peterselie, stalkruid, zilverschoon. Eetbaar zeewier, gedroogde lever, gist, kelp, melasse.
http://www.andersgezond.org/2007/09/mineralen-en-hun-toepassing.html
Chemische samenstelling
Macro-elementen:
eiwitten 7 – 35 %,
koolhydraten 15 – 35 %,
vetten 2 – 15 %,
water 5 – 40 %
Micro-elementen:
mineralen: kalium, magnesium, calcium, ijzer, fosfor, zwavel, mangaan, silicium, koper
vitamines: B1 (thiamine), B2 (riboflavine), B3 (nicotinamide), B6 (pyridoxide), B8 (biotine), B9 (foliumzuur), B12), nicotinezuur, C (ascorbinezuur), pantoteenzuur, in mindere mate A (retinol), D (ergosterol) E (tocoferol), K (fytomenadion) en rutine
aminozuren: van de 22 gekende aminozuren werden er een twintigtal in stuifmeel aangetoond.
antibiotische stoffen
enzymen en hormonen
http://nl.wikipedia.org/wiki/Stuifmeel
Zelf Tandpasta Maken
Wanneer je de hoeveelheden vermeld in het onderstaande recept aanhoudt, krijg je uiteindelijk 80 gram tandpasta. Deze hoeveelheid komt ongeveer overeen met de inhoud van een tube.
De hoofdbestanddelen van een tube Tandpasta
| Actieve stoffen |
| Bindmiddel |
| SchuimMiddel |
| Water |
| middel |
| Waterbindersmiddel |
| stoffen |
| Polijst |
| Middel |
geprecipiteerd krijt
Puur, kunstmatig calciumcarbonaat, vaak een afvalproduct bij de vervaardiging van medicijnen en chemische producten. Het wordt in de industrie gebruikt als een inert pigment of in gesso onderlagen en pastelkrijt.
Categorie: Materialen > krijt (materiaal).
Gevonden op http://www.aat-ned.nl/wwwopac.exe?databa
Calciumcarbonaat
Uit Wikipedia, de vrije encyclopedie
| Calciumcarbonaat | |
| Structuurformule en molecuulmodel | |
Structuur | |
| Algemeen | |
| Molecuulformule | CaCO3 |
| Andere namen | kalksteen, aragoniet, calciet, aeromatt, akadama, albacar, albafil, albaglos, atomite, AX 363, BF 200, brilliant 15, brilliant 1500, britomya, calcene, calcicoll, calcidar 40, calcilit, calmos, calmote, calofil, calofort, calopake, calseeds, caltec, carbium, durkal |
| Molmassa | 100,1 g/mol |
| SMILES | C([O-])(=O)[O-].[Ca+2] |
| CAS-nummer | 471-34-1 |
| EG-nummer | 207-439-9 |
| Beschrijving | wit poeder |
| Vergelijkbaar met | calciumbicarbonaat, calciumoxide, gips, natriumbicarbonaat, natriumcarbonaat |
| Waarschuwingen en veiligheidsmaatregelen | |
| Risico (R) en veiligheid (S) | R-zinnen: R37, R38, R41 S-zinnen: S26, S36 |
| LD50 (ratten) | 6450 mg/kg |
| Fysische eigenschappen | |
| Aggregatietoestand | vast |
| Kleur | wit |
| Dichtheid | 2,93 g/cm³ |
| Smeltpunt | (ontleedt bij 899°C) 1339 °C |
| Onoplosbaar in | water |
| Geometrie en kristalstructuur | |
| Kristalstructuur | tetrahedraal |
| Waar mogelijk zijn SI-eenheden gebruikt. Tenzij anders vermeld zijn standaardomstandigheden gebruikt (298,15 K of 25 °C, 1 bar) |
Calciumcarbonaat (chemische formule: CaCO3) is het koolzure zout van calcium.
[bewerk] Voorkomen
Calciumcarbonaat komt in de natuur zeer verbreid voor als het mineraal calciet. Het sedimentaire gesteente kalksteen en de metamorfe vorm hiervan, marmer, zijn grotendeels uit calciet opgebouwd. In de natuur is calciet meestal gedeeltelijk vervuild met magnesium-ionen, dat in het kristalrooster van calciet calcium-ionen kan vervangen. Een instabiele polymorf van calciet is aragoniet, dit wordt door veel zeedieren gebruikt om hun skeletten uit op te bouwen. Nadat organismen met aragoniet-skeletten sterven, zal de aragoniet sedimenteren en door rekristallisatie naar calciet omvormen.
Wordt calciumcarbonaat in een zuur gebracht, zoals ethaanzuur of een oplossing van waterstofchloride, dan gaat het snel net als alle andere carbonaat-zouten een zuur-base reactie aan onder ontwikkeling van, CO2.
De schaal van eieren van vogels en de schelp van slakken en schelpdieren bestaat grotendeels uit calciumcarbonaat. Het is ook een versterkend mineraal in de schalen van krabben, kreeften, andere schaaldieren en veel insecten. Chemisch gezien zijn de natuurlijke voorkomens verontreinigd met allerlei andere stoffen.
In het huishouden kent men calciumcarbonaat als ketelsteen.
[bewerk] Eigenschappen
Calciumcarbonaat is een zout en dus een polaire stof. In zuivere toestand is het een witte vaste stof, die slecht oplosbaar is in water. In zuren is de stof wel oplosbaar.
Het lage ontledingspunt (899°C) in vergelijking met het smeltpunt (1339°C) heeft te maken met het feit dat bij de ontledingstemperatuur de evenwichtsdruk van CO2 boven CaCO3 standaarddruk bereikt. De verbinding wordt dan omgezet in calciumoxide, (CaO). Door te zorgen dat het gasvormige kooldioxide niet kan ontsnappen kan het smeltpunt van calciumcarbonaat bereikt worden.
[bewerk] Gebruik
[bewerk] Bouwmateriaal
Calciumcarbonaat wordt veel als bouwmateriaal gebruikt. Zowel als structureel element(tand) als om de bij sommige soorten kalksteen en marmer hoge decoratieve waarde. Kalksteen bevat vaak goed herkenbare fossielen (de kalk in kalksteen is afkomstig van de schalen van grote of kleine schelpdieren).
[bewerk] Landbouw
In de landbouw wordt calciumcarbonaat onder de naam kalk gebruikt als bodemverbeteraar. De kalk neutraliseert de aanwezige zuren doordat het het basische carbonaat-ion bevat, en verhoogt zo de pH. Meestal wordt koolzure magnesiakalk (Dolokal) of schuimaarde (Betacal) gebruikt. Dolokal bevat zo’n 80% kalk (CaCO3) en 19% magnesiumcarbonaat (MgCO3); Dolomiet respectievelijk 60% en 8%.
Het ionrooster van calciumcarbonaat heet kubisch vlakgecentreerd.
Calciumcarbonaat is ook het voornaamste bestanddeel van maagtabletten.
Het wordt ook gebruikt voor de witte “schimmel” bij verschillende soorten droge worsten.
http://nl.wikipedia.org/wiki/Calciumcarbonaat
Calcium
Uit Wikipedia, de vrije encyclopedie
Calcium is een scheikundig element met symbool Ca en atoomnummer 20. Het is een zilverwit aardalkalimetaal.
| Inhoud[verbergen]1 Ontdekking2 Toepassingen3 Opmerkelijke eigenschappen4 Voorkomen5 Isotopen6 Toxicologie en veiligheid7 Calcium als mineraal8 Externe links |
[bewerk] Ontdekking
Calciumoxide (CaO) werd al door de Romeinen gebruikt, maar pas in 1808 werd het als element ontdekt en door middel van elektrolyse geïsoleerd door Humphry Davy. De naam is afkomstig van het Latijnse Calx, dat “kalksteen” betekent.
[bewerk] Toepassingen
Calciumverbindingen vormen de basis van botten en tanden, daarom is het voor veel organismen belangrijk om er voldoende van binnen te krijgen. Teveel van calcium binnen krijgen kan bij jonge dieren leiden tot Wobbler.
Toepassingen van calcium in de industrie zijn:
- Reductor bij extractie van andere metalen zoals uranium, zirkonium en thorium
- In de vorm van calciumoxide is het de grondstof van veel bouwmaterialen zoals cement
- De-oxidator voor allerlei legeringen
Daarnaast wordt calcium als metaal ook wel in legeringen gebruikt, vooral in combinatie met aluminium, beryllium, koper, lood en magnesium
[bewerk] Opmerkelijke eigenschappen
Calcium is het op vijf na meest voorkomende element in de aardkorst en van essentieel belang voor het leven op aarde. Het reageert met water onder vorming van calciumhydroxide. Bij verbranding van element geeft het een roodgele vlam, Calciumchloride-xhydraat (x staat bijvoorbeeld voor di-, tri-, of mono-) brand echter steenrood.
[bewerk] Voorkomen
Calcium is een lithofiel element, dat in de Aarde vooral in de korst voorkomt, die ongeveer voor 4,15 gewichtsprocent uit calcium bestaat. Door de reactieve eigenschappen komt het niet in ongebonden toestand voor. Bekende mineralen waarin calcium voorkomt zijn calciet (calciumcarbonaat), gips (calciumsulfaat) en fluoriet (calciumfluoride). Meestal wordt calcium geïsoleerd met behulp van elektrolyse van calciumchloride en calciumfluoride.
Opgelost calcium in de oceanen wordt door diverse organismen gebruikt om hun skelet uit op te bouwen in de vorm van de mineralen calciet en aragoniet. Als deze organismen sterven bezinken hun skeletjes naar de bodem om daar sediment te vormen. Door hoge hydrostatische druk is in de bathyale zone (op meer dan 4,5 km diepte) de oplosbaarheid van calciumcarbonaat groter, waardoor het oplost. Calciumrijke sedimenten worden daarom alleen in ondiepere zeeën, zoals op het continentaal plat, gevormd. Als kalksediment lithificeert wordt het kalksteen.
Dieper in de korst kan calcium in diverse metamorfe mineralen voorkomen. Voorbeelden zijn dolomiet, calciet, hornblende, grossulaar (Ca-granaat), plagioklaas en orthopyroxeen. Door metasomatisme en retrograde metamorfose kunnen deze mineralen in bijvoorbeeld talk, epidoot of tremoliet worden omgezet.
[bewerk] Isotopen
| Meest stabiele isotopen | |||||
| Iso | RA (%) | Halveringstijd | VV | VE (MeV) | VP |
| 40Ca | 96,941 | stabiel met 20 neutronen | |||
| 41Ca | syn | 1,03×105 j | EV | 11,140 | 41K |
| 42Ca | 0,647 | stabiel met 22 neutronen | |||
| 43Ca | 0,135 | stabiel met 23 neutronen | |||
| 44Ca | 2,086 | stabiel met 24 neutronen | |||
| 45Ca | syn | 162,61 d | β | 4,204 | 45Sc |
| 46Ca | 0,004 | stabiel met 26 neutronen | |||
| 47Ca | syn | 4,536 d | β | 1,992 | 47Sc |
| 48Ca | 0,187 | 6×1018 j | 2β | 4,.272 | 48Ti |
Van calcium zijn meerdere stabiele isotopen bekend, waarvan 40Ca en 44Ca in aanzienlijke hoeveelheden in de natuur voorkomen.
Bepaalde micro-organismen (radiolaria) fractioneren afhankelijk van de temperatuur de twee stabiele isotopen van calcium bij het onttrekken uit het zeewater. In de geochemie wordt de verhouding 44Ca/40Ca in kalkskeletjes uit marien sediment daarom gebruikt om de vroegere temperatuur van zeewater te berekenen. Dit kan echter alleen voor niet te diep begraven sedimenten, omdat diagenetische reacties de verhouding veranderen als het sediment te diep begraven wordt en onder te hoge druk komt te staan.
[bewerk] Toxicologie en veiligheid
elementair metalisch Calcium is brandbaar.
[bewerk] Calcium als mineraal
Calcium is nodig voor de opbouw en het onderhoud van de botten en de tanden, bij de werking van zenuwen en spieren, bij de bloedstolling en bij het transport van stoffen in de lichaamscellen. Een gevarieerde voeding met melkproducten zorgt voor voldoende opname van kalk door het lichaam, zoals melk en melkproducten, groente, noten en peulvruchten. Een calciumtekort kan leiden tot botontkalking (osteoporose) en bij kinderen verschijnselen van Engelse ziekte (rachitis) en spierkrampen.
[bewerk] Externe links
Wikimedia Commons heeft meer afbeeldingen die bij dit onderwerp horen: Calcium.
- PeriodiekSysteem.com over: Calcium
- Lenntech over: Calcium
- (en) EnvironmentalChemistry.com over: Calcium
- (en) WebElements.com over: Calcium
- Voedingscentrum over calcium als mineraal
http://nl.wikipedia.org/wiki/Calcium
Wobbler is een aandoening die te maken heeft met de regulatie van calcium in het lichaam. Doordat er minder osteoclasie plaatsvindt, vernauwt de ruggengraat dicht bij de nek. De zenuwen kunnen er niet goed doorheen. Deze aandoening komt bijvoorbeeld voor bij een te hoge inname van calcium bij jonge dieren.
http://nl.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wobbler
Letterlijke tekst uit de clip
In Limburg bestaat de ondergrond voor een groot gedeelte uit mergel. Mergel is lang geleden ontstaan. Toen was een groot gedeelte van Nederland nog zee. En in die zee leefden een hele boel dieren… Als die dood gingen zakten ze naar de zeebodem. Daar losten ze op en zo ontstond een dikke laag kalk. ater kwam er zand en klei overheen. Zo werd de kalklaag samengeperst. Er ontstond een dikke aardlaag die we nu kalksteen of mergel noemen. En die mergel vind je nu in de grond van Limburg.
http://www.schooltv.nl/beeldbank/clip/20071031_mergel01
Ontstaan van kalksteen
Eigenlijk zijn het schelpjes
Voor:
PO, groep 4 – VO, klas 1
Lengte:
0:58 minuten
Vakgebied:
PO: Aardrijkskunde > Energiebronnen en stoffen > Kalk
VO: Aardrijkskunde > Energiebronnen en grondstoffen > Kalk
Doorsturen Voeg toe aan favorieten
URL
Wat is dit?
Dit is een link naar de pagina waar deze clip op staat. Deze kan je kopiëren en in een presentatie, digitale les of website plaatsen.
EMBED
Wat is dit?
Dit is een stukje code waarmee je de speler met clip in een webpagina kan opnemen. Copieer de code en plak het exact zo in de HTML-code van de pagina.
POPUP
Wat is dit?
Deze link is om de clip in een pop-up te tonen, een kleiner venster boven je pagina. Handig als je de clip niet in de pagina wilt zetten met EMBED.
Ongeveer 70 miljoen jaar geleden lag het grootste deel van wat nu Nederland is, op de bodem van een binnenzee, de Krijtzee. Alle schelpen uit die zee zijn op de bodem terechtgekomen en vormden een laag kalksteen. Deze kalksteen komt bijna overal in Nederland voor, maar alleen in Zuid-Limburg zit deze niet zo diep onder de grond en is dus gemakkelijk te winnen.
Trefwoorden
Letterlijke tekst uit de clip
Soms zie je in kalksteen nog hele schelpen zitten. Ook vind je er fossielen van andere zeediertjes. Dat komt omdat kalksteen uit schelpen en skeletten is ontstaan. Miljoenen jaren geleden was een groot deel van wat we nu Nederland noemen, nog zee. En in die zee leefden een heleboel kleine diertjes en schelpen. Als die dood gingen zakten ze naar de zeebodem. Zo ontstond er een dikke laag kalk van schelpen en skeletten op die oude zeebodem. Later kwam er zand en klei, aangevoerd door de rivieren, over de kalklaag heen. Deze nieuwe zeebodem persten de kalklaag samen en dekte deze af. De schelpen en skeletten braken en verpulverden. Langzaam ontstond er een massieve aardlaag die we nu kalksteen noemen. En deze ligt heel diep onder de grond van nu.
ttp://www.schooltv.nl/beeldbank/clip/20030623_kalksteen02
In Zuid-Limburg zie je kalksteenafgravingen. Kalksteen wordt niet meer gebruikt om direct van te bouwen, maar in verpulverde vorm hebben we het nog wel nodig als een grondstof. De kalk gaat naar de fabriek om verder te worden verwerkt. Daar wordt het eerst flink gemalen en gezeefd. En wordt het kalksteenpoeder. Dit wordt bijvoorbeeld toegevoegd aan onze voeding. Want mensen hebben kalk nodig voor hun botten. Dat geldt ook voor dieren. Dus in diervoeder wordt ook kalkpoeder gestopt. Ook bomen en planten hebben kalk nodig. Van nature zit dit in de bodem, maar door de zure regen is de kalk opgelost. Daarom wordt er gesproeid met kalkpoeder om het tekort weer aan te vullen. Tenslotte gebruiken we kalksteenpoeder ook nog als bouwmateriaal. Er kan namelijk heel goed cement van worden gemaakt. Van cement maken we beton om bijvoorbeeld bruggen te bouwen. Of de muren van huizen te metselen.
http://www.schooltv.nl/beeldbank/clip/20030623_kalksteen03
| looneylover |
| Bekijk openbaar profiel |
| Bekijk de fotoboekpagina van looneylover |
| Zoek meer berichten van looneylover |
| 06-11-2006, 22:28 | |
| looneyloverV – Lid | bij 1 ben ik er ongeveer uit. alleen weet ik niet of het wel klopt: gidspoeder, CaSO4 (s) kalksteenpoeder, CaCO3 (s) bij welke stof komt er een neerslag? en bij welke stof is dat dan? bij Cu2+ –> CaSO4 –> reageert goed –> CaCO3 –> reageert slecht –> dus neerslag |
| __________________life sucks but it beats the alternative | |
| looneylover |
| Bekijk openbaar profiel |
| Bekijk de fotoboekpagina van looneylover |
| Zoek meer berichten van looneylover |
| 07-11-2006, 03:16 | |
| Amoa22V – Lid | Je eigen oplossing1 ziet er goed uit voor zover ik kan zien zonder binas. in Binas staat een tabelletje wat aangeeft welke stoffen met elkaar reageren en welke niet, en of je dan vloeistof neerslag of gas krijgt, is zeer handig bij die vragen. wat vraag 2 betreft, gips en kalksteen bevatten allebei Ca, dus zoek een stof uit die neerslag vormt met het CO3 van calciumcarbonaat, en met SO4 niet. (of juist andersom en omgekeerd principe gebruiken). Weeg van te voren je krijtje. Zeef de nieuw ontstane vaste stof uit, weeg deze. Haal uit je tabel welke atomen er in het nieuwe molecuulsoort zitten. De atoomgewichten zijn opzoekbaar, zoek dus het gewicht op van C,O en reken uit hoeveel CaCO3 er nodig was om de nieuwe hoeveelheid C,O te verkrijgen. Deel dit gewicht door het begingewicht van het krijtje en zet er % achter. tis al laat dus beetje wazige uitleg, succes iig! |
| __________________..:Look straight into the sun until she breaks your face and you’ll start smiling:.. | |
| 07-11-2006, 07:14 | |
| looneyloverV – Lid | hartelijk dank voor je uitleg.. ik snap in iedergeval hoe het nou allemaal in elkaar zit.. ondanks je zo laat gereageerd hebt |
| looneylover |
| Bekijk openbaar profiel |
| Bekijk de fotoboekpagina van looneylover |
| Zoek meer berichten van looneylover |
| 07-11-2006, 09:40 | |
| sdekivit20M – Lid | je kunt ook gewoon de Ca-concentratie uitrekenen door een titratie met Na-EDTA uit te voeren, maar aangezien de ts 16 is en dus in de 4e klas waarschijnlijk zit, hebben ze dit nog niet gehad. |
| 07-11-2006, 18:05 | |
| looneyloverV – Lid | Citaat:sdekivit schreef op 07-11-2006 @ 09:40 : je kunt ook gewoon de Ca-concentratie uitrekenen door een titratie met Na-EDTA uit te voeren, maar aangezien de ts 16 is en dus in de 4e klas waarschijnlijk zit, hebben ze dit nog niet gehad.ik zit in de 5de maar uh ik had vandaag dat practicum en het klopte wel zo ongeveer hoe ik het moest doen. dus bedankt ik dacht trouwens dat ik dat practicum morgen pas had, maar bleek niet zo te zijn. |
| __________________life sucks but it beats the alternative | |
http://forum.scholieren.com/showthread.php?t=1498909
Kalksteen Schooltv (1): het ontstaan van kalksteen.
Schooltv (2): Kalksteen als bouwmateriaal.
Schooltv (3): kalksteenpoeder.
Universiteit van Amsterdam: met azijn onderzoeken of een steen kalksteen is.
Suzy e.a.: kijken wat er gebeurd als je kalksteen of schelpen in azijn doet.
http://www.encyclopedoe.nl/index.php?onderwerp_id=161
deze plant groeit in het wild in kalkvolle grond, wat zeldzaam is bij vep. In de pot, voeg een glas dolomie (kalksteen poeder) per liter in de grond.
http://www.geocities.com/d_vandermarel/pinguicula_winterhard.html
Daarnaast worden verkennende experimenten uitgevoerd naar de mogelijkheid
tot het herstel en de bescherming van mortel- en betonoppervlakken door CaCO3-precipitatie
Gips is eigenlijk één van de drie verschijningsvormen van de stof calciumsulfaat (CaSO4):
- gips, CaSO4·2H2O of calciumsulfaatdihydraat, het uitgeharde gips;
- half hydraat, 2CaSO4·H2O of calciumsulfaathemihydraat, een gipspoeder dat door toevoeging van water hard wordt;
- anhydriet, CaSO4, de watervrije vorm. Wordt onder andere in de bouw als vulstof gebruikt.
Bij het verhitten van het gips boven 150°C dehydrateert het mineraal gedeeltelijk (een verlies van water uit zijn chemische structuur) en wordt het halfhydraat gevormd:
CaSO4·2H2O + energie (warmte) → CaSO4·½H2O + 1½H2O (stoom)
Wordt het halfhydraat verder verwarmd (180°C), ontstaat het anhydraat.
Verder komt gips in de natuur ook voor in kristallijne vorm als seleniet en als albast. Deze vormen hebben watermoleculen in de kristalstructuur (CaSO4·2H2O).
Gips is zacht. Op de hardheidsschaal van Mohs is het hardheid twee. Met een vingernagel kan men een kras maken in het gips, wat aangeeft dat gips zachter is dan nagel. Gips komt ook in de natuur voor en er kunnen dikke afzettingen in gesteentelagen aanwezig zijn. Doordat gips van nature erg zacht is zal het snel eroderen. Meestal als gips in de formatie van een bergen aanwezig is, zullen de gipslagen onder gesteentelagen van minder erosiegevoelige gesteenten als zandsteen en kalksteen. Een voorbeeld van een berg die gedeeltelijk uit gips bestaat is de Dent du Villard.
Doordat gips kristalwater bevat kan het worden gebruikt als brandvertrager. Mede hierdoor wordt gips veel toegepast in de bouw. Het wordt dus ingezet als een vlamvertrager, bijvoorbeeld in verf of plafondelementen. Het mechanisme van de vlamvertraging gaat als volgt. De energie van de brand wordt gebruikt om het kristalwater te verwijderen. Daarbij ontstaat eerst CaSO4·½H2O en bij voldoende hoge temperatuur tenslotte CaSO4.
Gips zet bij verharding iets uit (0,5%).
Gezien de productie kan het gips onderverdeeld worden in drie types:
- Natuurgips wordt gedolven in sites uit de natuur, vooral in Frankrijk, in het bekken rond Parijs. De eerste gipslagen ontstonden zo’n 100 tot 200 miljoen jaar geleden door verdamping van het zeewater in de ondiepe wateren van de aarde.
- Fosfo-gips ontstaat bij de recyclage van fosfaten uit de kunstmeststoffen-industrie. Dit gips bevat zeer veel radon, een radio-actief gas dat permanent ontsnapt uit het gips, en voor een verhoogde radio-activiteit zorgt. In bepaalde landen is dit gipstype verboden.
- Sulfo-gips ontstaat bij de recyclage uit de met steenkool aangedreven elektriciteitscentrales. Dit is beter bekend als RO-gips (rookgasontzwaveling-gips). Simpel gezegd worden de rookgassen door een kalkemulsie gevoerd en dan geoxideerd, waardoor het zwavel uit de steenkool zich bindt aan de kalk. Door er nog eens flink zuurstof doorheen te blazen verandert het calciumsulfiet in sulfaat en hebben we gips met een hoge zuiverheidgraad.
- Afgietsels van beelden worden ook van gips gemaakt. Vandaar dat zo’n beeld ook een gips wordt genoemd
- Schoolbordkrijt
- Vulstof in verf en in tandpasta
- Calciumsulfaat is ook toegelaten als Voedingsadditief voor voedingsmiddelen. Het E-nummer van calciumsulfaat is E516
- Grondverbeteraar
- CaSO4 word in zijn watervrije toestand soms gebruikt in vuurwerk als Hoge-temperatuur oxidator zoals in rode sterren of sommige flash composities.
- Archeologisch conservatie- en restauratiewerk
http://nl.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gips
Introductie
Woon ik wel gezond?
Doe de test!
Radon is een radioactief edelgas dat vrijkomt uit bouwmaterialen en uit de bodem. In woningen (en vooral kruipruimtes) kan radon zich in de lucht ophopen. Volgens de Gezondheidsraad leidt blootstelling aan radon binnenshuis in Nederland tot naar schatting 800 extra gevallen van longkanker. Toch zijn de radonconcentraties in woningen in Nederland ten opzichte van de ons omringende landen relatief laag. Dit komt doordat daar veel meer radon uit de bodem komt en vervolgens de woning binnentreedt.
In Nederland zijn minerale bouwmaterialen, zoals beton, cellenbeton en kalkzandsteen, de belangrijkste bron van radon in de woning. Daarom hebben de producenten de verplichting op zich genomen ervoor te zorgen dat de uitstoot van radongas uit deze bouwmaterialen niet zal toenemen. Ook kunt u zelf door uw woning goed te ventileren ervoor zorgen dat de radonconcentratie in de woning niet onnodig hoog wordt.
http://www.vrom.nl/pagina.html?id=12339
7. Wat is radon?
Radon is een natuurlijk voorkomend radioactief edelgas. Bij kamertemperatuur is radon kleur- en geurloos. Het kan vrijkomen uit de bodem en uit bouwmaterialen die hun oorsprong hebben in de aardkorst, zoals beton, gips, cement en baksteen.
In bijna alle bodemtypen komt radium voor. Radon wordt gevormd uit radium dat van nature in de bodem voorkomt. De vorming van radon uit radium verloopt via een radioactief proces. Dat betekent dat radium ‘vervalt’ tot radon, waarbij er straling vrijkomt. Radon komt via uitdamping vrij uit de bodem. Kleigrond geeft meer radon af dan andere bodemtypen, zoals zandgrond.
Het radon dat uit de bodem opstijgt, dringt via minuscule kieren en gaten in de vloer de woning binnen. Het radon dat uit bouwmaterialen ontstaat, komt rechtstreeks in de woning terecht. In tegenstelling tot een groot aantal regio’s in het buitenland is in Nederland
Vanuit de kruipruimten kan radon via openingen tussen de kruipruimte en de begane grond de woning binnendringen. In Nederland is de bijdrage van de bodem aan de radonconcentratie in de woning beperkt (voor nieuwbouwwoningen gemiddeld 15 procent). Bouwmaterialen vormen in Nederland de belangrijkste bron van straling in de woning (70 procent). De overige 15 procent komt uit de buitenlucht.
Radon vervalt weer verder tot de zogenaamde radondochters. Ook bij dit proces komt straling vrij. Deze straling is verantwoordelijk voor de gezondheidseffecten van radon.
8. Kan ik ziek worden van radon?
De belangrijkste wijze waarop het lichaam in aanraking komt met radon is door het gas in te ademen. Het radon zelf geeft geen gezondheidsproblemen, men ademt het net zo makkelijk weer uit als in. De gezondheidsproblemen worden veroorzaakt door de radondochters, deze ontstaan door het verval van radon.
De dochters kunnen zich aan hele fijne deeltjes in de lucht hechten. Wanneer deze deeltjes vervolgens ingeademd worden komen de radondochters in de longen terecht. Zij kunnen dan op de wanden van de luchtwegen achterblijven of via het bloed verder verspreid worden door het lichaam. Ook de radondochters vervallen op een gegeven moment en zenden daarbij straling uit. Wanneer de dochters in het lichaam vervallen kan deze straling veel meer schade aanrichten dan wanneer het lichaam van buitenaf aan de straling wordt blootgesteld.
Uit onderzoek onder mijnwerkers blijkt dat radon longkanker kan veroorzaken. Naarmate de blootstelling aan radon hoger is, neemt de kans op longkanker toe. De Gezondheidsraad (een onafhankelijk adviesorgaan voor de overheid op het gebeid van volksgezondheid) leidde in 1993 uit Nederlandse blootstellingsgegevens en gegevens uit mijnwerkersonderzoek af, dat radon in Nederland jaarlijks ongeveer 900 dodelijke longkankerslachtoffers maakt.
Om de concentratie radon in uw woning zo laag mogelijk te houden kunt u de volgende maatregelen nemen:
– maak openingen rond leidingen in de vloer van de begane grond geheel dicht; doe dit ook met openstaande kieren en naden in uw vloer;
– zorg voor een goede ventilatie van de kruipruimte en de woning.
Voor meer informatie over radon kijk op de website van het ministerie van VROM: www.vrom.nl/radon
Radon gas – verhoogd risico op longkanker voor rokers en niet-rokers
Dit was even schrikken voor mij. Radon gas in woningen is de nummer 1 reden van longkanker bij niet-rokers (*). En de nummer 2 reden van longkanker bij rokers. Rook je dus en zit er veel radon gas in je woning dan loop je nog meer kans om longkanker te krijgen.
In Amerika overlijden ieder jaar zo’n 21.000 mensen door dit radioactief gas dat in steenachtige bouwmaterialen zoals bakstenen en cement zit. Radon ontstaat uit radium. Radium komt van nature in alle bodemsoorten voor, maar in sommige bodemsoorten zit meer radium en in andere minder.
Even goed lezen dus……
Ron
(*) Bron : Epa.gov
Radon is een natuurlijk voorkomend, radioactief edelgas. Het element komt vrij bij het radioactief verval van radium, dat in sporen in de bodem en steenachtige bouwmaterialen aanwezig is. In woningen en andere verblijfs- en werkruimten kan radon zich in de lucht ophopen, waardoor de concentratie er hoger is dan buiten. Naar veronderstelling draagt het inademen van de eveneens radioactieve vervalproducten van radon bij aan het optreden van longkanker.
Radon is een kleurloos, geurloos en natuurlijk voorkomend radioactief gas. Radon ontstaat uit radioactief verval van uranium dat in de grond en in bouwmaterialen voorkomt. Radon uit de grond, dringt via kieren en gaten in kruipruimtes en kelders van woningen.
Welke woningen bevatten veel Radon?
In oudere woningen (van voor 1970) is Radon in de binnenlucht vooral uit de kruipruimte onder de woning afkomstig. In nieuwe woningen (vanaf 1970) is Radon vooral afkomstig uit de bouwmaterialen. Woningen gebouwd en of verbouwd vanaf de jaren zeventig zijn kierdichter dan de oudere woningen, waardoor Radon zonder goede ventilatie nauwelijks nog uit zichzelf kan afnemen of verdwijnen.
Woningen die weinig of slecht geventileerd worden bevatten over het algemeen meer Radon dan soortgelijke woningen die goed geventileerd worden.
* Verblijf in gebouwen is verantwoordelijk voor ongeveer de helft van de gemiddelde stralingsdosis in Nederland.
* Radon in huis komt voort uit de bodem onder en rondom de woning, uit de bouwmaterialen en uit de buitenlucht.
* De radonconcentratie in de Nederlandse woning bedraagt gemiddeld ca. 23 à 24 becquerel per m3 (Bq/m3) lucht. In nieuwbouwwoningen ligt de gemiddelde concentratie hoger, namelijk rond 30 Bq/m3.
* Voor bestaande woningen kan de radonconcentratie worden teruggedrongen door het afdichten van de begane grondvloer ten opzichte van de kruiprumte (o.a. kruipluik, meterkast, leidingdoorvoeren) en het voldoende ventileren van de woning
[Bron: NRG]
In 1993 besprak de Gezondheidsraad in een advies over het Basisdocument Radon de risico’s verbonden aan radonblootstelling. Dat advies berustte in belangrijke mate op een rapport van een commissie van de Academie van Wetenschappen in de VS, het zogeheten BEIR-IV-rapport (BEIR: Biological Effects of Ionizing Radiation). Onlangs heeft de Amerikaanse Academie opnieuw over radon gepubliceerd: het BEIR-VI-rapport. Op verzoek van de Voorzitter van de Gezondheidsraad heeft een werkgroep van de Raad het nieuwe rapport bestudeerd en nagegaan of een bijstelling van het eerdere advies van de Gezondheidsraad op zijn plaats zou zijn.
In het BEIR-VI-rapport worden het risico verbonden aan radonblootstelling, net als eerder, afgeleid uit resultaten van epidemiologisch onderzoek onder mijnwerkers. De conclusie — die door de werkgroep wordt onderschreven — is dat de centrale schatting van het risico iets is toegenomen, namelijk van 4 tot 5 per 10 000 per WLM (WLM is een maat voor de blootstelling aan radon). Gezien de onzekerheidsmarges is dit geen wezenlijke verandering. Voor Nederland leiden de nieuwe inzichten, rekening houdend met de meest recente gegevens over de blootstelling, tot de schatting dat 100 tot 1200 gevallen van longkanker per jaar aan radonblootstelling zijn toe te schrijven. De centrale schatting bedraagt 800.
Vooral rokers lopen een risico omdat roken en blootstelling aan radon elkaar lijken te versterken bij het teweegbrengen van longkanker. De analyses in het Amerikaanse rapport en die van de werkgroep zijn gebaseerd op een lineair verband tussen blootstelling aan de straling van ingeademde radonvervalproducten en de kans op longkanker. Daarbij wordt een drempel van de blootstelling waaronder geen gevolgen optreden afwezig geacht. De werkgroep meent dat deze veronderstelling het meest plausibel is en het hanteren ervan de minste kans op een onderschatting van het risico geeft.
[Bron: Gezondheidsraad]
Meting laten verrichten?
Wanneer u wilt weten hoe hoog de radonconcentratie in uw woning is, kan worden overwogen om een radonmeting in één of meer kamers uit te voeren. De kosten per radonmeter bedragen EUR 55,=. Zodra het bedrag is ontvangen, zult u binnen een maand de bestelde radonmeter(s) per post ontvangen. Tevens is een gebruiksaanwijzing en een adreslabel voor de retourzending ingesloten. Doordat de radonconcentratie kan variëren in de tijd, dient deze minimaal drie maanden op een vaste plek in de door u gewenste ruimte te blijven staan. Na afloop van de meetpereiode zendt u de radonmeter retour en zullen we u binnen enkele weken de resultaten van de meting schriftelijk doen toekomen.
NRG/RE
Postbus 9034
6800 ES ARNHEM
telefoon : 026 – 356 30 55
fax : 026 – 445 07 87
e-mail : info.im@nrg-nl.com
internet : NRG Radiation & Environment
http://www.fonteine.com/radon.html
HARDNESS: Hard water simply means that the water is ‘hard to use’. Hard water has dissolved limestone in it. Limestone is mostly calcium carbonate. Calcium carbonate is everywhere, and of which, teeth, bones, seashells, pearls, mother of pearl. Stalactites and stalagmites, the “White Cliffs of Dover”, marble and the “Carlsbad Caverns”, for example, are made. When hard water is heated, it causes scale to form inside pipes, causing constriction. Hard water reacts with soap causing soap scum, the stuff of which bathtub rings are made. It coats your skin, your hair, your appliances, your dishes and flatware. It can cause dry skin, rashes and acne. Correction is recommended for any reading over 3.5 grains per gallon, and pays for itself in cost savings.
Snail_diagram-en_edit1.svg (SVG file, nominally 751 × 370 pixels, file size: 498 KB)
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Image:Snail_diagram-en_edit1.svg
http://herborist.web-log.nl/herborist/2006/02/salie_salvia_of.html
http://www.herbasanitas.nl/Zwangerschap%20en%20kruiden.htm
eruit:
salie oestrogeen
peterselie
erin
karwij
kamille
paardebloem
oregano
Plantaardige oestrogenen
Plantaardige oestrogenen
Fyto-oestrogenen (fyto betekent plant) zijn van nature in voedsel voorkomende stoffen. Bijna alle groenten, vruchten en granen bevatten fyto-oestrogenen in wisselende sterkte en samenstelling, maar de isaflavonen (een van de soorten fyto-oestrogenen) zijn het heilzaamst. Deze komen voor in peulvruchten als soja, linzen en kikkererwten. Bacteriën in onze darmen zetten isaflavonen om in stoffen die een oestrogeen-effect hebben, al zijn het zelf geen hormonen. De volgende voedingsmiddelen zijn bronnen van fyto-oestrogenen, enkele met een hoog gehalte aan isaflavonen:
- peulvruchten als sojabonen, linzen, kikkererwten, kidneyboontjes, erwten
- knoflook
- selderij
- zaden als lijnzaad, sesamzaad, pompoenpitten, maanzaad, zonnebloempitten
- lijnolie
- granen als rijst, haver, gerst, rogge, tarwe
- fruit als appels, peren, pruimen, kersen, cranberry’s, citroenen en grapefruits
- groenten als broccoli, wortelen, rabarber, aardappelen
- kiemspruiten als alfalfa en taugé
- bepaalde kruiden en specerijen als kaneel, salie, rode klaver, hop, venkel, peterselie,paardebloem
peterselie eruit:oestrogeen
Karwij Karwij (Carum carvi) is een schermbloemige plant met aromatische zaadjes, die soms ook kummel genoemd worden. Karwij wordt in diverse keukens gebruikt, waaronder de Nederlandse. Traditionele recepten van bijvoorbeeld kool zoals zuurkool maken vaak gebruik van karwijzaad. Het heeft een sterke, wat anijsachtige smaak, niet te verwarren met komijnzaad, wat milder van smaak is.
Karwijzaad kent een lange geschiedenis van traditioneel gebruik. Zo werd het ingezet bij spijsverteringsproblemen zoals dyspepsie en flatulentie, als laxeermiddel en bijvoorbeeld ook bij menstruatieproblemen.
In farmacologische toepassingen wordt vooral de aromatische olie van karwijzaad gebruikt. Deze olie bevat verschillende actieve componenten, waaronder carveol, carvone en thymol. Carvone lijkt carcinogenese tegen te gaan door glutathion-s-transferase te stimuleren. Ook lijkt karwij antihistamine en antibacteriële eigenschappen te hebben. Maar het onderzoek hiernaar is in een beginnend stadium en dat betekent dat deze studies nu nog geen waarde voor de klinische praktijk hebben.
karwij kan erin blijven
paardebloem
De paardebloem (taraxacum officinale) is een plant die tot de composietenfamilie behoort en die iedereen kent.
Vroeger stonden de weilanden er vol mee. Tegenwoordig, nu boeren hun weilanden bespuiten, zie je ze al veel minder.
En dat is heel erg jammer, want behalve dat hij er mooi uitziet, is het ook nog eens een geneeskrachtige plant.
Als gevolg van overbemesting loopt de diversiteit van plantensoorten terug, en daardoor gaan o.a. planten als de brandnetel, kleefkruid, vogelmuur, paardebloem, akkerdistel, e.a. beter groeien, zodat men weer geneigd is daar weer iets tegen te doen, met alle gevolgen van dien.
Dus …… boeren, burgers en buitenlui, let op uw zaak !
De paardebloem wordt ook wel pissebloem genoemd vanwege de diuretische oftewel vochtafdrijvende werking.
Andere namen zijn nog molsla, paardesla, hondsbloem, en konijnen lusten het ook erg graag.
In het Frans zegt men Pissenlit of Dent de Lion, in het duits Löwenzahn en in het engels heet hij Dandelion.
Het kruid heeft een gunstige werking op de gal- en leverfunctie, en dat is wetenschappelijk bewezen.
Daarnaast heeft het een gunstige werking op de celfunctie in de vorm van een betere ademhalingscapaciteit (dus meer zuurstof) van de bloedcellen en de weefsels.
Ook zijn er nog andere kruiden die tot de composietenfamilie behoren en die eveneens als levermiddel worden toegepast.
Dit zijn mariadistel, artisjok en cichorei.
Andere planten die b.v nog tot de composietenfamilie behoren zijn absint, andijvie, guldenroede, dragon, kamille, sla, witlof, maar ook de zonnebloem, en andere planten. Over de mariadistel kunt u ook al een stuk lezen bij de onderwerpen.
De belangrijkste inhoudstoffen van de paardebloemwortel zijn bitterstoffen.
Verder tot 18 % suikers (fructose), waarvan de hoogste concentratie in de lente wordt aangetroffen in het kruid.
Tot 40% inuline, waarvan de hoogste concentratie in de herfst wordt aangetroffen, terwijl de inuline in het voorjaar slechts 1 tot 2 % bedraagt en in de zomer 15 tot 24 %.
Paardebloemwortel bevat ook nog vele enzymen.
En verder nog flavonoïden ( zie ook: quercetine en citroen).
Bitterstoffen bevorderen de afscheiding in de spijsverteringsorganen.
Dat is de reden dat het helpt bij een verlaagd zuurgehalte van het maagsap (subacide gastritis), eetlustgebrek en in het algemeen bij allerlei spijsverteringsstoornissen.
Bitterstoffen werken naar beide kanten, zodat het ook kan worden ingezet bij verhoogd zuurgehalte van het maagsap.
Het verschil zit hierin, en dit is belangrijk, dat bitterstofplanten een half uur vóór de maaltijd worden ingenomen in geval van verlaagd zuurgehalte en eetlustgebrek (hypoaciditeit en anorexie) en omgekeerd een half uur tot een uur ná de maaltijd bij teveel maagzuur en kramp (hyperaciditeit en spasmus).
Paardebloemwortel heeft een gunstige werking op de gal- en leverfunctie, en de uitscheiding van gal neemt door het gebruik ervan toe. Mensen die aanleg hebben voor het vormen van galstenen kunnen de paardebloemwortel (een preparaat hiervan) preventief gebruiken. In dit geval zal men het een lange periode moeten gebruiken, zodat de algemene stofwisseling gunstig wordt beïnvloed. Let wel, paardebloemwortel heeft geen galsteenoplossend vermogen !
Paardebloemwortel is een cholagogum.
Een cholagogum is een stof die de galstroom van de galblaas naar de darm bevordert.
Daarnaast is het een cholereticum en dat is een stof die de galvorming bevordert.
Het kruid wordt dan ook gebruikt voor ziekten van de galblaas en onvoldoende werking van de lever.
Ook heeft de paardebloemwortel een lichte ontsteking-bestrijdende invloed. Dit noemt men een antiflogistische werking. Hierdoor is het ook goed inzetbaar bij reumatische aandoeningen (jicht, artritis).
Zowel het kruid zelf als de wortel van de plant hebben een sterke urinedrijvende werking, en daarnaast heeft het kruid ook invloed op de uitscheiding van natrium, chloor en water.
Dit noemt men respectievelijk een diureticum en een sali-diureticum (het kruid zelf zou een sterkere urinedrijvende werking hebben dan de wortel). Dit is de reden dat het kruid vaak wordt gebruikt in afslankkuren. Ook heeft paardebloemwortel in lichte mate een laxerende werking.
Men heeft hier dus te maken met een veelzijdig kruid, bloedzuiverend en een algemeen versterkend middel. Van ouds her wordt het middel dan ook gebruikt als voorjaarskuur, maar ook ter ondersteuning bij reuma, jicht en chronisch eczeem en het heeft een stimulerend effect op de bloedvorming.
In de volksgeneeskunde heeft de paardebloem al een heel lange traditie, zowel in Europa als in Azië.
In China gebruikt men de paardebloem (traditionele toepassing) bij borstkanker.
Eén van de inhoudstoffen in het blad van het kruid is coumestrol, welke stof een oestrogene factor heeft (borstkanker is een oestrogeen-gevoelige kanker).
Wanneer plantaardig oestrogeen gegeten wordt, neemt het natuurlijk oestrogeen in het lichaam af.
Men weet niet of dit een relatie heeft met een effect dat het kruid tegen borstkanker zou hebben.
Meer onderzoek is dus op zijn plaats.
De stof coumestrol is dus een plantaardig oestrogeen (phyto-oestrogeen).
Men vindt het ook in andere planten, waarvan de coumestrol in alfalfa het meest krachtig is van de plantaardige oestrogenen. Uit de zaadjes van alfalfa kweekt men, net zoals men dat met tuinkers doet, spruitgroente. Ook vindt men het in Witte klaver, erwten, bonen, spruitjes, kool, spinazie en soyabonen.
Omdat wetenschappers phyto-oestrogenen hebben teruggevonden in urine en bloed, weet men dat het in het menselijk lichaam wordt opgenomen.
Sommige studies in verschillende landen suggereren dat phyto-oestrogenen kunnen helpen beschermen tegen bepaalde vormen van kanker, zoals borst, uterus- en prostaatkanker.
Ook soja-eiwit, dat veel isoflavonen bevat zou bijdragen op vermindering van de kans op borstkanker. In Zuid-Oost Azië waar men dagelijks 50 tot 100 mg. isoflavonen met het eten binnenkrijgt, komt borstkanker minder voor. In onze streken krijgt men gemiddeld slechts 1 mg. van de isoflavonen binnen. Dit is geen bewijs, echter het wijst in de richting van een mogelijk verband. Door het intikken van +oestrogeen +borstkanker kan er via de zoekmachines allerlei informatie op dit gebied gevonden worden.
Terug naar de paardebloem.
De paardebloem kan men ook gewoon als gezonde voeding nuttigen. De blaadjes kun je in het voorjaar als sla gebruiken, die in deze periode minder bitter zijn, terwijl het vitaminegehalte hoog is in deze periode. Het werkt dan bloedreinigend en het stimuleert de bloedvorming. Zelfs de bloemen kunnen door de sla gegeten worden, en deze zijn rijk aan carotenoïden. Er bestaan wel 500 verschillende carotonoïden, en sommige daarvan worden als kleurstoffen in levensmiddelen verwerkt, de zogenaamde E-nummers, zoals in dit geval E160-161.
Beta-caroteen of ook wel pro-vitamine A is de grondstof voor vitamine A.
Het zijn de oranje-rode kleurstoffen in planten zoals paprika, tomaten, wortelen, meloen, abrikozen, kersen, pompoenen, maar men vindt het ook in broccoli, spinazie, groene kool en de paardebloem, welke laatste een zeer hoog gehalte aan beta-caroteen bevat.
Molsla noemt men de paardebloemen die onder een molshoop groeien en daardoor bleek van kleur blijven. Ook dit wordt als sla gegeten en in Frankrijk en Engeland zelfs gekweekt. We kennen allemaal Brussels lof, familie van de paardebloem, die op grote schaal in het donker wordt gekweekt en als groente wordt verkocht. Paardebloembladeren kan men als bloedzuiverende thee gebruiken en de wortels van de paardebloem kunnen in geroosterde vorm verwerkt worden als koffiesurrogaat.
Verder bevat het paardebloemblad vitamine B, C, en zelfs vitamine D en E. Dat paardebloem (zowel blad als wortel) vitamine D bevat, is best wel bijzonder, omdat het weinig voorkomt in planten. Men treft het ook nog aan in peterselie, alfalfa (spruitgroente !), avocado, paddestoelen en brandnetels.
Ook zijn er allerlei mineralen vertegenwoordigd in de paardebloem. In het blad en de wortel treft men vooral kalium aan, maar ook natrium, magnesium, silicium, ijzer, mangaan, zink, koper en fosfor. Ook treft men in de paardebloem een relatief hoog gehalte aan choline aan (onderdeel van vitamine B-complex).
Volgens het groot vitaminen boek van Mindell is choline één van de weinige stoffen die door de bloed-hersenbarrière heen kunnen dringen. Volgens Mindell helpt choline mee bij het onder controle houden van de cholesterolvorming, helpt mee met het verzenden van prikkels naar de hersenen (geheugen, Alzheimer), helpt bij het afbreken van giftige stoffen en geneesmiddelen in de lever, en heeft ook nog een kalmerend effect.
Dan heeft men nog het melksap, dat zich bevindt in het blad, de stengel en de wortel. Ook dit bevat weer bepaalde stoffen zoals o.a. suikers, vetten, bitterstoffen en inuline. Het melksap wordt vanouds wel uitwendig toegepast op wratten.
En de bloem bevat behalve pro-vitamine A nog wat monoterpenen (zie ook: sinaasappelschilletjes). Inuline is een koolhydraat dat ook in aardperen voorkomt. Bij de vertering van inuline komt geen glucose vrij en er is zodoende ook geen insuline nodig om dit koolhydraat te verwerken.
Een inventarisatie van de werking en toepassingen van de paardebloem:
antidiabeticum (ondersteuning bij suikerziekte)
aperativum (eetlustopwekkend)
cholagogum (galdrijvend)
cholereticum (galproduktie-bevorderend)
depurativum (bloed- en lymfezuiverend)
digestivum (spijsverteringsbevorderend)
diureticum (urinedrijvend)
stimulerend voor de alvleesklier (pancreas)
versterkend voor lever en gal
licht antiflogistisch (ontstekingsremmend)
mild laxerend.
De toepassingen van de paardebloem kunnen dan zijn:
Lever- en galaandoeningen (onvoldoende werking van de lever en gal, ter voorkoming van galstenen, galkoliek, leverstuwing, ter ondersteuning bij geelzucht, poortaderstuwing)
Klierziekten (bloedreinigend)
Reumatische aandoeningen, jicht, artritis (diuretisch en licht ontstekingsremmend)
Huidaandoeningen (wratten, eczeem, acne, bladeren als papje op de huid, vitamine D !)
Zweren, abcessen, eczeem (zie boven: papje op de huid aanbrengen)
Cellulitis
Slechte nierwerking en vochtophopingen/oedeem (urinedrijvend)
Bloedarmoede (via stimulering van de lever werkt het kruid normaliserend op de bloedvorming)
Voorjaarsmoeheid (bloedreinigend)
Constipatie(licht laxerend)
Slechte spijsvertering (spijsverteringsbevorderend i.v.m. de bitterstoffen)
Suikerziekte (inuline)
Stoornissen van de buikspeekselklieren en de milt.
Ook bij katten, honden en paarden e.a. kan men paardebloem toepassen. Ook voor dieren is het vochtafdrijvend, leverstimulerend, helpt bij gewrichtsaandoeningen, huidproblemen, leverkwalen en het geeft een glanzende vacht. Denk ook aan al die dieren die de paardebloem graag lusten.
Contra-indicaties zijn er niet, behalve dat er mensen zijn die bij aanraking allergisch reageren (contactdermatitis).
Vermeldenswaard is nog dat paardebloembladeren zo verschillend van vorm kunnen zijn.
Dit heeft te maken met de standplaats en de omstandigheden waarin de plant groeit.
Als de plant veel licht krijgt zijn de bladeren scherper ingesneden, terwijl de bladeren rond en gladder van vorm zijn, als de plant op een vochtige plaats groeit.
http://www.paradijsvogel.nl/paardebloem.htm
kamille erin
http://herborist.web-log.nl/herborist/2006/02/salie_salvia_of.html
http://www.herbasanitas.nl/Zwangerschap%20en%20kruiden.htm
eruit:
salie oestrogeen
peterselie
erin
karwij
kamille
paardebloem
oregano
Plantaardige oestrogenen
Plantaardige oestrogenen
Fyto-oestrogenen (fyto betekent plant) zijn van nature in voedsel voorkomende stoffen. Bijna alle groenten, vruchten en granen bevatten fyto-oestrogenen in wisselende sterkte en samenstelling, maar de isaflavonen (een van de soorten fyto-oestrogenen) zijn het heilzaamst. Deze komen voor in peulvruchten als soja, linzen en kikkererwten. Bacteriën in onze darmen zetten isaflavonen om in stoffen die een oestrogeen-effect hebben, al zijn het zelf geen hormonen. De volgende voedingsmiddelen zijn bronnen van fyto-oestrogenen, enkele met een hoog gehalte aan isaflavonen:
- peulvruchten als sojabonen, linzen, kikkererwten, kidneyboontjes, erwten
- knoflook
- selderij
- zaden als lijnzaad, sesamzaad, pompoenpitten, maanzaad, zonnebloempitten
- lijnolie
- granen als rijst, haver, gerst, rogge, tarwe
- fruit als appels, peren, pruimen, kersen, cranberry’s, citroenen en grapefruits
- groenten als broccoli, wortelen, rabarber, aardappelen
- kiemspruiten als alfalfa en taugé
- bepaalde kruiden en specerijen als kaneel, salie, rode klaver, hop, venkel, peterselie,paardebloem
peterselie eruit:oestrogeen
Karwij Karwij (Carum carvi) is een schermbloemige plant met aromatische zaadjes, die soms ook kummel genoemd worden. Karwij wordt in diverse keukens gebruikt, waaronder de Nederlandse. Traditionele recepten van bijvoorbeeld kool zoals zuurkool maken vaak gebruik van karwijzaad. Het heeft een sterke, wat anijsachtige smaak, niet te verwarren met komijnzaad, wat milder van smaak is.
Karwijzaad kent een lange geschiedenis van traditioneel gebruik. Zo werd het ingezet bij spijsverteringsproblemen zoals dyspepsie en flatulentie, als laxeermiddel en bijvoorbeeld ook bij menstruatieproblemen.
In farmacologische toepassingen wordt vooral de aromatische olie van karwijzaad gebruikt. Deze olie bevat verschillende actieve componenten, waaronder carveol, carvone en thymol. Carvone lijkt carcinogenese tegen te gaan door glutathion-s-transferase te stimuleren. Ook lijkt karwij antihistamine en antibacteriële eigenschappen te hebben. Maar het onderzoek hiernaar is in een beginnend stadium en dat betekent dat deze studies nu nog geen waarde voor de klinische praktijk hebben.
karwij kan erin blijven
paardebloem
De paardebloem (taraxacum officinale) is een plant die tot de composietenfamilie behoort en die iedereen kent.
Vroeger stonden de weilanden er vol mee. Tegenwoordig, nu boeren hun weilanden bespuiten, zie je ze al veel minder.
En dat is heel erg jammer, want behalve dat hij er mooi uitziet, is het ook nog eens een geneeskrachtige plant.
Als gevolg van overbemesting loopt de diversiteit van plantensoorten terug, en daardoor gaan o.a. planten als de brandnetel, kleefkruid, vogelmuur, paardebloem, akkerdistel, e.a. beter groeien, zodat men weer geneigd is daar weer iets tegen te doen, met alle gevolgen van dien.
Dus …… boeren, burgers en buitenlui, let op uw zaak !
De paardebloem wordt ook wel pissebloem genoemd vanwege de diuretische oftewel vochtafdrijvende werking.
Andere namen zijn nog molsla, paardesla, hondsbloem, en konijnen lusten het ook erg graag.
In het Frans zegt men Pissenlit of Dent de Lion, in het duits Löwenzahn en in het engels heet hij Dandelion.
Het kruid heeft een gunstige werking op de gal- en leverfunctie, en dat is wetenschappelijk bewezen.
Daarnaast heeft het een gunstige werking op de celfunctie in de vorm van een betere ademhalingscapaciteit (dus meer zuurstof) van de bloedcellen en de weefsels.
Ook zijn er nog andere kruiden die tot de composietenfamilie behoren en die eveneens als levermiddel worden toegepast.
Dit zijn mariadistel, artisjok en cichorei.
Andere planten die b.v nog tot de composietenfamilie behoren zijn absint, andijvie, guldenroede, dragon, kamille, sla, witlof, maar ook de zonnebloem, en andere planten. Over de mariadistel kunt u ook al een stuk lezen bij de onderwerpen.
De belangrijkste inhoudstoffen van de paardebloemwortel zijn bitterstoffen.
Verder tot 18 % suikers (fructose), waarvan de hoogste concentratie in de lente wordt aangetroffen in het kruid.
Tot 40% inuline, waarvan de hoogste concentratie in de herfst wordt aangetroffen, terwijl de inuline in het voorjaar slechts 1 tot 2 % bedraagt en in de zomer 15 tot 24 %.
Paardebloemwortel bevat ook nog vele enzymen.
En verder nog flavonoïden ( zie ook: quercetine en citroen).
Bitterstoffen bevorderen de afscheiding in de spijsverteringsorganen.
Dat is de reden dat het helpt bij een verlaagd zuurgehalte van het maagsap (subacide gastritis), eetlustgebrek en in het algemeen bij allerlei spijsverteringsstoornissen.
Bitterstoffen werken naar beide kanten, zodat het ook kan worden ingezet bij verhoogd zuurgehalte van het maagsap.
Het verschil zit hierin, en dit is belangrijk, dat bitterstofplanten een half uur vóór de maaltijd worden ingenomen in geval van verlaagd zuurgehalte en eetlustgebrek (hypoaciditeit en anorexie) en omgekeerd een half uur tot een uur ná de maaltijd bij teveel maagzuur en kramp (hyperaciditeit en spasmus).
Paardebloemwortel heeft een gunstige werking op de gal- en leverfunctie, en de uitscheiding van gal neemt door het gebruik ervan toe. Mensen die aanleg hebben voor het vormen van galstenen kunnen de paardebloemwortel (een preparaat hiervan) preventief gebruiken. In dit geval zal men het een lange periode moeten gebruiken, zodat de algemene stofwisseling gunstig wordt beïnvloed. Let wel, paardebloemwortel heeft geen galsteenoplossend vermogen !
Paardebloemwortel is een cholagogum.
Een cholagogum is een stof die de galstroom van de galblaas naar de darm bevordert.
Daarnaast is het een cholereticum en dat is een stof die de galvorming bevordert.
Het kruid wordt dan ook gebruikt voor ziekten van de galblaas en onvoldoende werking van de lever.
Ook heeft de paardebloemwortel een lichte ontsteking-bestrijdende invloed. Dit noemt men een antiflogistische werking. Hierdoor is het ook goed inzetbaar bij reumatische aandoeningen (jicht, artritis).
Zowel het kruid zelf als de wortel van de plant hebben een sterke urinedrijvende werking, en daarnaast heeft het kruid ook invloed op de uitscheiding van natrium, chloor en water.
Dit noemt men respectievelijk een diureticum en een sali-diureticum (het kruid zelf zou een sterkere urinedrijvende werking hebben dan de wortel). Dit is de reden dat het kruid vaak wordt gebruikt in afslankkuren. Ook heeft paardebloemwortel in lichte mate een laxerende werking.
Men heeft hier dus te maken met een veelzijdig kruid, bloedzuiverend en een algemeen versterkend middel. Van ouds her wordt het middel dan ook gebruikt als voorjaarskuur, maar ook ter ondersteuning bij reuma, jicht en chronisch eczeem en het heeft een stimulerend effect op de bloedvorming.
In de volksgeneeskunde heeft de paardebloem al een heel lange traditie, zowel in Europa als in Azië.
In China gebruikt men de paardebloem (traditionele toepassing) bij borstkanker.
Eén van de inhoudstoffen in het blad van het kruid is coumestrol, welke stof een oestrogene factor heeft (borstkanker is een oestrogeen-gevoelige kanker).
Wanneer plantaardig oestrogeen gegeten wordt, neemt het natuurlijk oestrogeen in het lichaam af.
Men weet niet of dit een relatie heeft met een effect dat het kruid tegen borstkanker zou hebben.
Meer onderzoek is dus op zijn plaats.
De stof coumestrol is dus een plantaardig oestrogeen (phyto-oestrogeen).
Men vindt het ook in andere planten, waarvan de coumestrol in alfalfa het meest krachtig is van de plantaardige oestrogenen. Uit de zaadjes van alfalfa kweekt men, net zoals men dat met tuinkers doet, spruitgroente. Ook vindt men het in Witte klaver, erwten, bonen, spruitjes, kool, spinazie en soyabonen.
Omdat wetenschappers phyto-oestrogenen hebben teruggevonden in urine en bloed, weet men dat het in het menselijk lichaam wordt opgenomen.
Sommige studies in verschillende landen suggereren dat phyto-oestrogenen kunnen helpen beschermen tegen bepaalde vormen van kanker, zoals borst, uterus- en prostaatkanker.
Ook soja-eiwit, dat veel isoflavonen bevat zou bijdragen op vermindering van de kans op borstkanker. In Zuid-Oost Azië waar men dagelijks 50 tot 100 mg. isoflavonen met het eten binnenkrijgt, komt borstkanker minder voor. In onze streken krijgt men gemiddeld slechts 1 mg. van de isoflavonen binnen. Dit is geen bewijs, echter het wijst in de richting van een mogelijk verband. Door het intikken van +oestrogeen +borstkanker kan er via de zoekmachines allerlei informatie op dit gebied gevonden worden.
Terug naar de paardebloem.
De paardebloem kan men ook gewoon als gezonde voeding nuttigen. De blaadjes kun je in het voorjaar als sla gebruiken, die in deze periode minder bitter zijn, terwijl het vitaminegehalte hoog is in deze periode. Het werkt dan bloedreinigend en het stimuleert de bloedvorming. Zelfs de bloemen kunnen door de sla gegeten worden, en deze zijn rijk aan carotenoïden. Er bestaan wel 500 verschillende carotonoïden, en sommige daarvan worden als kleurstoffen in levensmiddelen verwerkt, de zogenaamde E-nummers, zoals in dit geval E160-161.
Beta-caroteen of ook wel pro-vitamine A is de grondstof voor vitamine A.
Het zijn de oranje-rode kleurstoffen in planten zoals paprika, tomaten, wortelen, meloen, abrikozen, kersen, pompoenen, maar men vindt het ook in broccoli, spinazie, groene kool en de paardebloem, welke laatste een zeer hoog gehalte aan beta-caroteen bevat.
Molsla noemt men de paardebloemen die onder een molshoop groeien en daardoor bleek van kleur blijven. Ook dit wordt als sla gegeten en in Frankrijk en Engeland zelfs gekweekt. We kennen allemaal Brussels lof, familie van de paardebloem, die op grote schaal in het donker wordt gekweekt en als groente wordt verkocht. Paardebloembladeren kan men als bloedzuiverende thee gebruiken en de wortels van de paardebloem kunnen in geroosterde vorm verwerkt worden als koffiesurrogaat.
Verder bevat het paardebloemblad vitamine B, C, en zelfs vitamine D en E. Dat paardebloem (zowel blad als wortel) vitamine D bevat, is best wel bijzonder, omdat het weinig voorkomt in planten. Men treft het ook nog aan in peterselie, alfalfa (spruitgroente !), avocado, paddestoelen en brandnetels.
Ook zijn er allerlei mineralen vertegenwoordigd in de paardebloem. In het blad en de wortel treft men vooral kalium aan, maar ook natrium, magnesium, silicium, ijzer, mangaan, zink, koper en fosfor. Ook treft men in de paardebloem een relatief hoog gehalte aan choline aan (onderdeel van vitamine B-complex).
Volgens het groot vitaminen boek van Mindell is choline één van de weinige stoffen die door de bloed-hersenbarrière heen kunnen dringen. Volgens Mindell helpt choline mee bij het onder controle houden van de cholesterolvorming, helpt mee met het verzenden van prikkels naar de hersenen (geheugen, Alzheimer), helpt bij het afbreken van giftige stoffen en geneesmiddelen in de lever, en heeft ook nog een kalmerend effect.
Dan heeft men nog het melksap, dat zich bevindt in het blad, de stengel en de wortel. Ook dit bevat weer bepaalde stoffen zoals o.a. suikers, vetten, bitterstoffen en inuline. Het melksap wordt vanouds wel uitwendig toegepast op wratten.
En de bloem bevat behalve pro-vitamine A nog wat monoterpenen (zie ook: sinaasappelschilletjes). Inuline is een koolhydraat dat ook in aardperen voorkomt. Bij de vertering van inuline komt geen glucose vrij en er is zodoende ook geen insuline nodig om dit koolhydraat te verwerken.
Een inventarisatie van de werking en toepassingen van de paardebloem:
antidiabeticum (ondersteuning bij suikerziekte)
aperativum (eetlustopwekkend)
cholagogum (galdrijvend)
cholereticum (galproduktie-bevorderend)
depurativum (bloed- en lymfezuiverend)
digestivum (spijsverteringsbevorderend)
diureticum (urinedrijvend)
stimulerend voor de alvleesklier (pancreas)
versterkend voor lever en gal
licht antiflogistisch (ontstekingsremmend)
mild laxerend.
De toepassingen van de paardebloem kunnen dan zijn:
Lever- en galaandoeningen (onvoldoende werking van de lever en gal, ter voorkoming van galstenen, galkoliek, leverstuwing, ter ondersteuning bij geelzucht, poortaderstuwing)
Klierziekten (bloedreinigend)
Reumatische aandoeningen, jicht, artritis (diuretisch en licht ontstekingsremmend)
Huidaandoeningen (wratten, eczeem, acne, bladeren als papje op de huid, vitamine D !)
Zweren, abcessen, eczeem (zie boven: papje op de huid aanbrengen)
Cellulitis
Slechte nierwerking en vochtophopingen/oedeem (urinedrijvend)
Bloedarmoede (via stimulering van de lever werkt het kruid normaliserend op de bloedvorming)
Voorjaarsmoeheid (bloedreinigend)
Constipatie(licht laxerend)
Slechte spijsvertering (spijsverteringsbevorderend i.v.m. de bitterstoffen)
Suikerziekte (inuline)
Stoornissen van de buikspeekselklieren en de milt.
Ook bij katten, honden en paarden e.a. kan men paardebloem toepassen. Ook voor dieren is het vochtafdrijvend, leverstimulerend, helpt bij gewrichtsaandoeningen, huidproblemen, leverkwalen en het geeft een glanzende vacht. Denk ook aan al die dieren die de paardebloem graag lusten.
Contra-indicaties zijn er niet, behalve dat er mensen zijn die bij aanraking allergisch reageren (contactdermatitis).
Vermeldenswaard is nog dat paardebloembladeren zo verschillend van vorm kunnen zijn.
Dit heeft te maken met de standplaats en de omstandigheden waarin de plant groeit.
Als de plant veel licht krijgt zijn de bladeren scherper ingesneden, terwijl de bladeren rond en gladder van vorm zijn, als de plant op een vochtige plaats groeit.
http://www.paradijsvogel.nl/paardebloem.htm
kamille erin
wittere tanden en ‘olieslurpen’
Goed ik heb weer eens een nieuwe alternatieve ‘geneeswijze’ gevonden (Zie voor mijn vorige alternatieve escapade mijn leverreinigingsverhaal met linkje onder aan post). Nadat ik wat problemen had met mijn verstandskies kreeg ik van de tandarts chloorhexidine geadviseerd zodat dit mijn ontstoken verstandskies zou reinigen. Ik volg dus de handleiding op en mijn verstandskies werd weer gezond. Ik heb alleen de gebruiksaanwijzing niet goed doorgelezen want bij de bijwerkingen stond namelijk dat je bruine aanslag op je tanden kon krijgen.
Gelukkig ben ik zo’n lucky bastard die een bruine vlek op zijn tanden kreeg (een flinke bruine streep op mijn voortand) naast een algehele gele verkleuring van mijn tanden. Nu ben ik niet heel ijdel, maar ik wil er liever niet uitzien als een verlepte heroine junk met rotte tanden.
Omdat ik geen tandartsverzekering heb, zocht ik naar alternatieve wijzen om mijn tanden witter te maken (bovendien denk ik ook niet dat een standaardverzekering het polijsten van de tanden dekt). Enfin ik heb lang op internet gezocht naar een alternatieve behandelingswijze voor wittere tanden en kwam op de zonnebloemkuur ofwel ‘olieslurpen/oilpulling’.
Wat is dit? Zie hier de link: http://www.plantaardigheden.nl/aardi…emoliekuur.htm
http://www.oilpulling.com/
Schijnbaar is de oliekuur/olieslurpen/oilpulling een hele oude traditionele kuur de het lichaam ‘ontgiftigd’ en als bijkomend voordeel wittere tanden belooft…right (heb inmiddels op enkele fora gezocht en mensen zijn laaiend enthousiast ). Nu geloof ik zelf niet in ontgiftigen maarja ik kan het altijd proberen. (enja het bleken van de tanden moet ook nog maar blijken). Enfin ik heb besloten om maar een gok te wagen. De benodigdheden:
– koudgeperste zonnebloemolie (deze is schijnbaar veel gezonder dan de standaard zonnebloemolie)
– een nuchtere maag
– wilskracht
Goed ik heb een fles koudgeperste olie bij zo’n reformwinkel gehaald en de proef op de som genomen.
Ik ben afgelopen vrijdag begonnen, en ik ‘slurp’ 1 keer per dag voor het ontbijt voor ongeveer 10 minuten 1 eetlepel olie. Ik laat het flink door mijn mond gaan en na die tien minuten is de olie compleet wit en zeer dun (precies naar behoren). Deze spuug ik vervolgens uit, om daarna zeer grondig mijn mond met water te spoelen.
Zondag en maandag heb ik overgeslagen, maar ik zit met vandaag meegerekend op mijn vierde dag.
Bevindingen tot dusver:
– de smaak is niet heel ranzig, en het spoelen is best vol te houden.
– mijn tanden en mijn mond voelt na het spoelen fris en glad aan
– ik heb niet echt het idee dat mijn tanden al veel bleker zijn. Misschien dat de bruine aanslag op mijn voortanden als iets minder is geworden maar dat kan bedrog zijn.
– Wat ik wel als bijeffect heb gemerkt is dat ik ineens behoorlijk moe ben. (inmiddels is dit al wat bijgetrokken) maar om onverklaarbare redenen was ik zaterdag, zondag, maandag helemaal kapot (terwijl ik absoluut niet actief geweest ben of ziek). DAarnaast is mijn maag tevens een beetje van streek. Ik had dit even opgezocht en het scheen normaal te zijn tijdens de ‘kuur’. Het betekent dat je lichaam de afvalstoffen eruit stoot . Ik betwijfel de wetenschappelijk onderbouwing van het laten verwijderen van slechte gifstoffen in je lichaam doormiddel van olie in je mond te laten rollen maargoed we zullen zien.
Iig de eerste vier dagen is wel aardig. Ik ben benieuwd wat de resultaten over een week zijn!
http://forum.dutchbodybuilding.com/f172/wittere-tanden-olieslurpen-207907/
Olie slurpen – ontgiftiging
Zoals je misschien weet zitten je mond en keel bomvol bacteriën en mogelijke ziekteverwekkers. Een zekere Dr. F. Karach komt met een zeer eenvoudige oplossing om je mond te ontgiften: olieslurpen.
Je neemt daarvoor koudgeperste zonnebloemolie uit de reform winkel en neemt een theelepel olie in je mond en laat deze 15-30 minuten in je mond spoelen. Je mag de olie absoluut niet doorslikken. De olie absorbeert bacteriën, ziekteverwekkers en toxische stoffen.
Na een tijdje spuug je de olie dan weer uit. Als deze nog geel is dan heb je de olie niet lang genoeg in je mond gehad. Als de olie wit als melk is betekent dat je veel afvalstoffen kwijt bent.
Een heel aparte theorie en de moeite waard als je kampt met chronische keel en mond klachten.
Uitgebreide informatie over olieslurpen vindt je hier
Enkele reakties van olie slurpers vind je op dit forum
Olie slurpen – aften
Er is op internet heel weinig te vinden over deze methode maar ik vond nog wel een gelijkwaardige tip van Monica Siebers:
Een mooie synergie is het rode Johanniskruid als dragerolie met 1% – 1,5 % essentiële olie van hetzelfde kruid. Dit is dan te gebruiken als spoelmiddel voor de mondholte bij aften. Het spoelen dient bij voorkeur op de nuchtere maag te gebeuren. Het spoelen en tussen de tanden doorpersen moet zo lang doorgaan tot de olie enigszins troebel en schuimend wordt. Daarna de olie uitspugen. Eventueel nog een keer herhalen. Het spoelen van de mond met olie is bovendien een uitstekende mondreiniging. Schadelijke stoffen en ontslakkingsstoffen die zich gedurende de nacht op de slijmvliezen van de mond hebben verzameld, worden erin opgenomen. Deze verwijdert u dan door de olie uit te spugen.
Ik vond ook nog deze Duitse tekst over de werking van het olie slurpen
Hoe is de werking van de olietherapie te verklaren?
Ik neem aan dat ziekteverwekkers (zoals bijv. pathogene gisten als Candida albicans, de oorzaak is van veel ziektes) door de in de mond rondgedraaide olie geabsorbeerd en afgevoerd worden.
Mogelijkerwijs wordt ook de in de zonnebloemolie opgeslagen informatie opgenomen door de slijmhuid. Zo wordt bijvoorbeeld zonne-energie opgeslagen in natuurlijke voedingsmiddelen. Albert Einstein noemde deze negatief geladen zonne-energie deeltjes (elektronen) in het kader van zijn Quantumtheorie ‘photonen’. Deze door de zon afgegeven photonen kunnen zich in planten aan onverzadigde vetzuren binden. Zo worden die vetzuren negatief geladen. Niet-levend voedsel zoals “fabrieksvoedsel’ of gekookte levensmiddelen bevatten deze elektro- actieve kracht niet en kunnen ze niet aanreiken aan onze lichaamscellen. Het is voedsel dat niet uitstraalt en het lichaam alleen maar belast. Kort gezegd: dood voedsel.
Hoe men die werking voelt? Nou, eenvoudig daardoor, dat men zich goed voelt. Ons lichaam is over het algemeen gezien een goede barometer en laat zien: dit doet mij goed. Afhankelijk van de constitutie kan dat natuurlijk per mens verschillen. Wij zijn door onze schepper als individuen en originelen geschapen. Alleen: een beetje geduld is noodzakelijk. In de natuur gaat alles erg langzaam. Hoeveel tijd heeft een zaadje alleen al nodig om zich tot een statige plant te ontwikkelen!
Deze eenvoudig uit te voeren ontgiftigingsmethode is zeer goed geschikt voor een algemene- en een zware metalen ontgifting. Het intensief ‘spoelen’ van de mond met koudgeperste, biologische zonnebloemolie geeft een grondige reiniging van het lichaam. De methode is ook erg goed geschikt voor patiënten met tandvleesproblemen. Maar pas op: de maatregelen zijn alleen dan werkzaam als men ze langere tijd toepast en regelmatig herhaalt. Meer informatie kunt u vinden in de boeken “Die Oelzieh-Kur” von Katharina Wolfram, ISBN Nr.3-442-13999-6 of “Pflanzenöle” von Ruth von Braunschweig, ISBN Nr.3-7742-4170-8.
(vertaling: het kruidenvrouwtje)
7 vitamins and minerals your mouth needs
Want healthy teeth and gums? Make sure your diet features these key ingredients. These nutritional building blocks are essential for your dental health.
Calcium
No surprises here — calcium is well known as a friend for teeth. Throughout the body, the mineral helps build bones and provide structural support. In your mouth, calcium helps harden your enamel and strengthen your jawbone.
What to eat: In addition to milk, good sources of calcium include cheese, yogurt, broccoli and salmon.
Vitamin D
Vitamin D helps the body absorb calcium while boosting bone mineral density, so it’s crucial to get an adequate amount of vitamin D to get the most out of your calcium intake.
What to eat: Your body naturally makes vitamin D when it’s exposed to sunlight, but the vitamin can also be found in fatty fish, canned tuna and portobello mushrooms. You can also look for foods and drinks that have been fortified with vitamin D, such as milk, orange juice and cereal.
Potassium
Like vitamin D, potassium improves bone mineral density. It also works with magnesium to prevent blood from becoming too acidic, which can leach calcium from your bones and teeth.
What to eat: Bananas are well known sources of potassium, but they’re not alone. Other fruits and vegetables with high levels of the mineral include lima beans, tomatoes, Swiss chard, potatoes, sweet potatoes, avocados and prunes.
Phosphorus
Phosphorus supports calcium in building strong bones and teeth.
What to eat: Luckily, phosphorus is found in a wide range of foods. Rich sources of the mineral include seafood, such as scallops, sardines, cod, shrimp, tuna and salmon. If you’re looking to get your phosphorus from plant-based foods, consider soybeans, lentils and pumpkin seeds. You can also find phosphorus in beef, pork and cheese.
Vitamin K
Think of this vitamin as a shield – it helps block substances that break down bone. It also helps your body produce osteocalcin, a protein that supports bone strength. A vitamin K deficiency can slow down your body’s healing process and make you more likely to bleed.
What to eat: Chowing down on leafy greens, such as kale, collards and spinach, can help you increase your vitamin K quota. Other great sources include parsley, broccoli and Brussel sprouts.
Since parsley is naturally antibacterial, it is excellent for your oral health. Along with brushing your teeth twice a day and flossing once a day, chewing parsley could help eliminate harmful bacteria in your mouth that can cause gum disease and tooth decay.
Oral Health Benefits That Come from Eating Parsley
Vitamin C
Vitamin C strengthen your gums and the soft tissue in your mouth. It can protect against gingivitis, the early stage of gum disease, and can prevent your teeth from loosening.
What to eat: You probably already know that citrus fruits are rich in vitamin C, but you can also find it in potatoes and leafy greens.
Vitamin A
This vitamin helps keep mucous membranes healthy. It prevents dry mouth and helps your mouth heal quickly.
What to eat: For strong gums and teeth, load up on fish, egg yolks and liver. You can also find it in leafy green vegetables like spinach, kale and collard greens, or in orange-colored fruits and oranges: think apricots, cantaloupe, pumpkin, carrots and sweet potatoes. These fruits and veggies contain high levels of beta-carotene, which your body converts into vitamin A.
https://www.deltadentalins.com/oral_health/vitamins-and-minerals.html
Oil pulling with a drop of clove and a drop of oregano in it:
Bijlage 18: Hoe tanden in elkaar zitten
Voor recept tv tandpasta, zie de g4dv op https://uvrm.wordpress.com/2013/07/22/gewoon-genietend-gifvrij-gezond-dieet-en-verzorging-g4dv/
By Dr. Mercola
It’s very difficult to achieve high-level physical health if your dental health isn’t effectively addressed. I’ve been involved with alternatives to regular dentistry for quite some time. I think many people fail to appreciate how important dentistry is to our total health.
Most tend to separate these two components, but both need to be considered as working in tandem.
Contrary to conventional dentistry, minimally invasive dentistry, like biological dentistry, is not about “drilling and filling;” creating an endless loop of revisits and retreating the same tooth again and again.
Instead, by using dietary prevention to create a healthy cavity-fighting bioflora in your mouth; dental prophylaxis such as brushing and irrigating with baking soda, and oil pulling; combined with minimally invasive restorations starting as early as possible, you can prevent about 80 percent of future dental problems.
Minimally Invasive Dentistry — A Valuable Aspect of Biological Dentistry
Dr. Tim Rainey is a true pioneer in biological dentistry, and is a big proponent of and leader in what’s termed “minimally invasive dentistry.”
“Basically, I knew that the way that we were preparing teeth back then was dead wrong; that you couldn’t go in and justify destroying massive amounts of tooth structure,” Dr. Rainey says. “…We need to be much more conservative.”
After dental school, the training and dogma of which he rebelled against, he began investigating alternatives to the standard “drill and fill” dogma. After reading a hallmark article by a Japanese researcher back in 1977, he began to put everything together:
How tooth decay actually occurs, what the tooth looks like on the inside, how the decay looks like, and finally, what could be done to minimize the damage being done to the tooth while trying to restore it.
“It took me about until 1983 to really understand what was really going on within the teeth. I’m talking several years there. I’m talking about dissecting hundreds, if not thousands, of teeth…
I realized two things. Number one, we did not even have a rudimentary understanding of the decay process in the teeth. Number two, everything that we’ve been taught about tooth structure and anatomy was just dead wrong.
By 1985, I had actually published the article on how to address 80 percent of all decay, which is in the chewing surface of the back teeth. That’s where most decay starts. We had a rather crude rudimentary way of going in and treating these teeth,” he says.
Minimally Invasive Restorations Can Last a Lifetime
The first patient he used his newly devised procedure on was the daughter of one of his class mates from dental school. The girl received these minimally invasive restorations in 1983 or ’84. Today, she is Dr. Rainey’s lead hygienist, and those restorations are still there, and those teeth have never decayed or broken down.
This is in stark contrast to what happens with most conventional fillings, especially if the dentist uses amalgam (about half of which is mercury, despite being deceptively referred to as “silver filling”). When you drill into the tooth with a high speed drill, and then stuff amalgam or other incompatible material in there, you can be almost certain that you will need additional work on that tooth down the road as the tooth begins to crack and the tooth structure fails.
“The average is somewhere around 14 to 15 years before the breakdown of the first restoration in the tooth and then somewhere around eight years for the second restoration,” Dr. Rainey says.
“Then you’re into the tooth has fractured, you start getting decay in between the teeth. That’s the root. That will destruct your teeth. Decay starts breaking down the teeth, and then you start getting into crowns and root canals. Here you have a whole series of manmade iatrogenic (dentistry-caused) ‘disasters,’ which fuels the future generations of dentists. It also fuels 80 percent of what all dental practice is about, that is repairing previous dentistry.”
By using early diagnosis and early intervention with minimally invasive dentistry, Dr. Rainey and other dentists trained in his techniques have eliminated 80 percent of future dentistry on the vast majority of their patients who are privileged to grow up in a practice such as theirs. As someone who has struggled with my own dental health, this sounds absolutely extraordinary. That equates to phenomenal savings in terms of money, pain, and emotional anguish, if you happen to be afraid of the dentist chair.
“Remember, there are several other people throughout the world who are now doing this. It has a very profound effect. We’re talking about something that the evidence of information has been out there approaching 30 years – three decades. Dental patients found out about it like they did in alternative medicine… They seek me out from all over. We have patients coming in from Canada. We haven’t even counted the number of states; I would say something around 30 states,” Dr. Rainey says.
“Of course, there are easier and simpler ways to do dentistry! You start these kids off very early. You eliminate the decay… and guess what? They don’t have much decay later on. We call it bulletproofing the teeth; where we go in, identify the defective pit, fissures, and grooves in the teeth, and clean those out.
There are several different types of materials that we can use. My preference is for glass ionomer cement… Not only do those chewing surfaces on those teeth never decay, but the interproximal areas are gaining some degree of protection because you’re removing the nidus of the infection, which is the bacteria within the teeth that are causing decay. You don’t have that bolus of xbowel bioactivity there to lead off into decay.”
Understanding Tooth Structure
The tooth is covered with a layer of lipoprotein, laden with calcium phosphate that comes and goes — eating and drinking, especially acidic foodstuffs and beverages, remove it, while saliva puts it back. Beneath that is an extremely hard and dense layer of enamel, which is about 0.2 millimeters, or 200-400 microns thick. Inside of that hard layer, the tooth structure becomes much softer. These parts all form the structural integrity of the tooth.
When you bite down on the tooth, the stress is transferred through the entire tooth down into the root, which deforms slightly. This is part of its natural stress-relieving mechanism. During the formation of the tooth can form little pits, fissures and grooves that may be hypocalcific — a defect that causes the enamel to be softer than normal and susceptible to decay.
“In the ideal world, you do not have decay start down in these pits and fissures, because you have a natural oil-based organic plug that seals that tooth,” Dr. Rainey explains. “However, in the real world what happens is as these teeth are finalizing development, you’ll get what we call ‘hypocalcified enamel.’ Now, if you put acid in that area, then you start getting a calcium deficit. That’s the beginning of decay in teeth.”
He identifies those areas, and using a miniature air abrasion tip that is very precise and focused, cleans out those pits, fissures and grooves. This removes the initial decay. Then he seals it with glass ionomer. The end result is that those teeth tend to not decay in the future.
Why Decay Occurs
Tooth decay is primarily driven by the symbiotic relationship between bacteria and acidity, which creates a pathogenic bioflora in your mouth. If you’re continually lowering the pH in your mouth, you start losing calcium, which is necessary for strong healthy teeth. Calcium deficiency leads to porosity in the teeth, which allows plaque that has turned pathogenic to attack the tooth more thoroughly. Once certain types of bacteria are able to penetrate the enamel, they put out enzymes that begin to break down the collagen of the inner structure of the tooth.
“That’s where you get cavitation, which is the loss of tooth structure to the point where you have a hole in that tooth,” Dr. Rainey explains.
One of the most important things Dr. Rainey instructs his patients to do is to use nothing but baking soda on their teeth at night.
“The pathogenic bacteria must have an acidic environment. Then you have the bacteria – the probiotic bacteria – that live in a neutral environment. You’re going to have X number of bacteria regardless of what you do. So, why not promote the non-pathogenic bacteria by neutralizing the acidity with baking soda at night, which has profound effects on the overall oral health of the individual?” Dr. Rainey says.
You can brush with it, use it as a mouth rinse, and even dissolve a little in the water you use in your WaterPik or HydroFloss.
- To brush: Wet your toothbrush and dip it into the baking soda. Brush as usual. Your teeth should feel smooth when finished
- To rinse: About a teaspoon in a small glass of water is sufficient. Just swish it around in your mouth and spit out
- To floss: Dissolve a small amount of baking soda in water and fill your irrigation instrument. Make sure not to let it dry inside your water pik as it will cause buildup and eventually render the tool useless. So, always keep water in your irrigation tool, and instead of storing it standing up, store it upside-down in a glass of baking soda and water, as the baking soda will prevent harmful bacteria from proliferating. Once a week, drain it all out and rinse it thoroughly with water
In the mornings, you could use toothpaste containing calcium and phosphate salts, or even hydroxyapatite, which can help remineralize your teeth.
“Since the Pro-Enamel [toothpaste], I’ve believed that almost all of the toothpastes out there now have calcium of some form in them. The magic is the calcium phosphate. You want those present, so they can precipitate back into the teeth as amorphous hydroxyapatite… You’re rebuilding an amorphous crystal of enamel, because of all the interactions of the enzymes, calcium, phosphate, and everything else that goes on within your mouth.
Where you really mess this up is by getting it too acidic. That’s where the baking soda comes in.
We use it in our cancer patients, where they have a real deficit of calcium and phosphate in their saliva – people who have problems. The brand name of it, as a prescription item, is called Caphoso®. You actually get it in a calcium solution, a phosphate salt solution. You mix those together, and then you rinse with them.” That;s the building block of enamel, and what it takes to remineralize enamel.
Promote Beneficial Oral Bacteria with Fermented Foods
To promote a beneficial oral bioflora he also recommends taking Evora tablets while you’re trying to change the bacterial balance in your mouth. Eating fermented foods, such as cultured yoghurt made from raw organic milk (AVOID store-bought yoghurts as they are worthless in terms of probiotics. Most are loaded with sugars and other detrimental ingredients, and all of them are pasteurized), or fermented vegetables, which you can easily and inexpensively make at home.
According to Dr. Rainey, any type of probiotics will naturally help get rid of harmful Strep mutans. This includes Lactobacillus and bacteria that are bioactive in high concentrations of lactic acid.
To Pull or Not to Pull…
Another interesting technique that can help improve your oral health is oil pulling. The technique is thousands of years old, and it’s an ancient Ayurvedic Indian tradition. To perform it, you vigorously swish an oil in your mouth, “pulling” it between your teeth for 20-30 minutes. You can use a number of oils for this, but sesame, sunflower or coconut oil are commonly used. Dr. Rainey is also working extensively with ozonated oils.
Oil pulling is thought to remove pathogenic bacteria, improve oral hygiene, and help detoxify your system. Dr. Rainey agrees the technique can be beneficial. A drawback is that it is time consuming. You need to go at it for quite some time in order to get results. It’s not like swishing with mouthwash for 30 seconds. Ideally, you’ll want to reach close to 30 minutes.
The Three Main Components of Minimally Invasive Dentistry
Contrary to conventional dentistry, minimally invasive dentistry, like biological dentistry, is not about “drilling and filling;” creating an endless loop of revisits and fixing old dental work until there’s nothing left to work with. It comprises three main components:
- Dietary prevention (creating a healthy bioflora in your mouth and body)
- Dental prophylaxis (baking soda; oil pulling)
- Minimally invasive restorations
As for dental prophylaxis, the simplest thing is just adding baking soda to your nightly oral hygiene. Ideally, add it to your dental irrigator, and brush with it. You can also use oil pulling in conjunction with this. They’re not mutually exclusive. You can combine the two, because it will provide a sort of organic matrix plug, which helps combat dental decay. And ultimately, you want to change the bioflora in your mouth, which is done through your diet. Fermented foods are key. A high-quality probiotic supplement may suffice if you really cannot stand fermented foods. I urge you to at least try some fermented veggies though, as they are, for most people, the most palatable. I think they’re delicious!
The next step, (where, ideally, you’d start your kids off) would be to see a dentist trained in minimally invasive dentistry. Kids treated with the NovaMin or baking soda air abrasion process to clean the pits and fissures and then seal them with glass ionomer, receive significant protection against future decay.
How to Find a Biological and Minimally Invasive Dentist
At present, there are a number of dentists trained in Dr. Rainey’s techniques. Several of them are in California and Florida. There’s also one in Beirut, Lebanon, and in New Zealand. To locate a qualified dentist, you can contact Dr. Rainey’s office at www.jtimrainey.com, or call 361-526-4695.
If there’s no minimally invasive dentistry practice in your area, or within reasonable travel distance, the following links can help you to find a mercury-free, biological dentist. These may not be trained in Dr. Rainey’s minimally invasive dentistry technique, but are trained to treat your oral and physical health as a cohesive whole. If you’re considering removing amalgam, you also need to make sure it’s done by biological dentist that’s been properly trained to do it safely, as removing amalgam can lead to severe and acute mercury poisoning:
- Consumers for Dental Choice
- International Academy of Biological Dentistry & Medicine (IABDM)
- Dental Amalgam Mercury Solutions (DAMS). E-mail them at: dams@usfamily.net or call 651-644-4572 for an information packet
- Huggins Applied Healing. You’ll need to fill out a form and they will connect with you to find a suitable dentist in your area
- Holistic Dental Association
- International Association of Mercury Safe Dentists
Ingrediënten Parodontax Fluoride Tandpasta:
Sodium Bicarbonate, Sodium Fluoride, Water, Glycerol, Cocamidopropyl Betaine, Rhatany Tincture (Ratanhia), Peppermint Oil (Pepermunt), Cornmint Oil (Akkermunt), Coneflower (Enchinacea), Xanthan Gum, Myrrh Tincture (Mirre), Chamomile Tincture (Kamille), Oil of Sage (Salie), Sodium Saccharin, Iron Oxide.
https://zolea.be/review-parodontax-fluoride-tandpasta/
De ratanhia (Krameria lappacea) is een struik van 20 tot 40 centimeter. Met een rechtopstaande stengel is hij te herkennen aan zijn talrijke harige en witachtige takken, zijn eenvoudige, langwerpige, harde en puntige bladeren, evenals zijn kleine rode bloemen en zijn bolvormige vruchten bedekt met stekels. Ten slotte vertoont de wortel, cilindrisch, kruipend en vertakt, een bast, bruin en vezelig.
Habitat en cultuur
De ratanhia komt oorspronkelijk uit Midden-Amerika, Peru en West-Indië, waar hij in hoogte groeit op droge en zanderige bodems (tussen 900 en 3000 meter hoogte op de westelijke hellingen van de Andes cordillera). Het wordt gekweekt voor zijn wortel die het hele jaar door wordt geoogst.
Eigendommen
Traditioneel wordt de wortel gebruikt vanwege zijn samentrekkende (het bevat tussen 10 en 20% tannines) en hemostatische eigenschappen als natuurlijke tandpasta. Dit is wat de Spaanse naam suggereert, raíz para los dientes (wortel voor tanden). Ratanhia is ook antimicrobieel en behandelt aandoeningen van het maagdarmkanaal.
De als zetpil geformuleerde droge extracten van ratanhia worden gebruikt bij de behandeling van aambeien en testiculaire disfuncties
https://fr.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ratanhia
Bestellen:
ratanhia
https://www.herboristerie.com/plantes-en-vrac-michel-pierre/1114-ratanhia-en-vrac.html
echinicea
https://www.pit-pit.com/echinacea-wortel.html
Six Simple Ways to Heal Tooth Decay and Reverse Cavities
by Altima Dental | May 18, 2018 | Patient Education
Like most people, when you discover you have a cavity or pain in your teeth, the first thing you do is make an appointment with your dentist as you think that fillings are the only way to fix cavities. However, what most people fail to realize is that tooth decay and cavities can be reversed and fillings aren’t the only option available.
This article will explain the basic principles behind how you can heal cavities naturally and prevent tooth decay.
- Change your diet and reduce your sugar intake. Studies in the British Medical Journal suggest that a change in diet can actually reverse tooth decay. Easy adjustments can be made to your diet immediately like:
- Consuming more calcium rich foods (i.e. kale, collards, broccoli rabe and dairy) which can help strengthen your bones and teeth.
- Avoid drinking pop, juice and drinks with high carbonation as the sugars cause excessive plaque and tartar build up which may result in cavities.
- If you want to protect your teeth from early decay or heal existing tooth decay, include the following steps in your oral care routine.
- Brush your teeth at least twice a day ensuring you reach all the surfaces, crevices, pockets and corners.
- Floss at least once daily. This helps remove any remaining food from underneath your gums and prevents bacteria from forming.
- Use mouthwash; it has antibacterial properties and helps you get rid of any remaining bacteria in your mouth.
- Add vitamins and supplements to your diet. Micro nutrients are essential to bone health and keep inflammation under control to prevent or reverse cavities. Certain vitamins help produce saliva which helps to prevent bacteria from staying on your teeth and certain vitamins make your teeth a lot stronger. Foods that help promote salivation include bananas, Brussels sprouts, and peas. Vitamins you should consume include Vitamin B, D, magnesium and iron. If you’re not interested in taking supplements, eat whole grain foods and seafood (i.e. salmon, canned tuna and sardines are all great sources of vitamin D).
- Eat foods with natural probiotics. Because bad bacteria associated with infection look for places to hide in the small areas between the teeth, consuming probiotics helps to offset the acidic pH. Foods rich in probiotics include kombucha, kefir and fermented foods like kimchee and sauerkraut. These foods stimulate the production of healthy bacteria in the mouth needed to prevent plaque buildup and dental decay.
- Be aware of the pH values in the foods/drink you consume. Imbalanced pH levels can create an environment for bacteria to thrive. Drinks such as coffee create pH imbalances (like some citrus fruits and sugars), and act as the perfect environment for harbouring infectious oral bacteria. If you’re a daily coffee drinker and suffering from tooth decay, a great alternative to coffee is green tea as it contains a polyphenol (known as catechins) which acts as a powerful antioxidant and has several anti-inflammatory properties which hinder the growth of harmful bacteria and improves oral health.
- Develop a new oral care regime. Have you heard of a technique called oil pulling? Oil pulling is believed to create a soap like cleansing on teeth with moisturizing and antiseptic capabilities. It consists of swishing an oil (i.e. sesame, sunflower or coconut oil) for about 10-20 minutes in the mouth to reduce plaque buildup. It’s important that you don’t swallow the oil and to brush your teeth afterwards. Oil pulling has been shown to reduce plaque and gingivitis in one month’s time.
Remember, if a cavity has already struck, a trip to the dentist may not be avoidable. However, you can limit the damage by following these simple steps and paying a little extra attention to your pearly whites.
If you need any further clarity, drop by one of our locations to speak to one of our dental team.
An Almost Foolproof Blueprint for Achieving Remineralized Teeth
February 6, 2018

Mineral loss. Not good for bones, definitely not good for teeth.
In the old understanding of how minerals are incorporated into the body, there was a notion that the minerals were there while we were growing as children and the bones and teeth were strong or they weren’t, dooming a person to a life of “soft bones” or “soft teeth.” A better understanding of how hard tissues, like bones and teeth, developed and led to a better understanding of the role of calcium in bone health and an awareness of how calcium-rich diets can improve bone health throughout an entire lifespan, not just the growing years. And yet, we were still told that teeth were only helped by minerals in childhood.
Happily, we have a much better understanding of mineral processes in the oral environment now than we have ever had before. We understand that lost minerals can be reintroduced to the teeth, and that remineralization strategies can make a huge difference for tooth health. While the enamel framework of a tooth is not naturally rebuilt by the body if it is lost, the minerals that fill out that framework can be replenished throughout daily life. Sure, the minerals can be lost, but they can also be replaced with stronger or weaker minerals based on what minerals are available.
There are more tools in the dental health kit than the dental drill. Using our understanding of how to strengthen weakened teeth has given us a blueprint for remineralizing teeth.
Hydroxyapatite – The Basic Building Block
Hydroxyapatite is a naturally occurring form of calcium that makes up as much as 70% bone and is the main mineral in tooth enamel. If you have demineralized enamel, the minerals lost are hydroxyapatite molecules. Improvements in the ability to synthesize bio-identical (just like that which occurs in your body) hydroxyapatite for medical use have greatly benefited people trying to treat early mineral loss in teeth. But, foods are not likely to have bioavailable hydroxyapatite in them.
So, use a toothpaste or tooth gel with bioavailable nano hydroxyapatite.
Fluoride – Mighty Mineral Glue
It was once believed that fluoride would only help bind calcium into teeth before erupted, which meant people thought fluoride would only benefit young children. Advances in our understanding of enamel and the oral environment have shown that topical fluoride can help teeth of all ages.
High pH – The Right Environment
There is a natural pH cycle in the mouth it drops after eating or drinking sweetened beverages, becoming more acidic, then the high acid environment dissolves minerals out of the teeth. In a healthy mouth, the pH rises with saliva after eating, allowing those minerals to redeposit on the teeth. If anything interrupts the rise in pH (frequent snacks, low saliva, etc.), there is a chance the minerals will be stripped away.
Xylitol – The Finishing Touches
Xylitol, a natural sweetener derived from birch trees or plant fiber, is a surprise champion for tooth health. It helps maintain oral health in multiple ways. In addition to killing cavity-causing bacteria by starving it to death, xylitol increases calcium absorption. It also helps raise saliva pH, making the oral environment more friendly for remineralization. Using products with clinically significant amounts of xylitol for oral care is the finishing touch to your building or good health.
Xylitol Gum | Neutralize pH (discontinued)
Hydroxyapatite.
https://www.nature.com/articles/sj.bdj.2017.1094
Hydroxyapatite
11 Ways to Remineralize Your Teeth and Stop Demineralization
- Brush teeth
- Fluoride toothpaste
- Cut sugar
- Chew gum
- Moderate fruit intake
- Add calcium
- Decrease dairy intake
- Probiotics
- Treat dry mouth
- Reduce starchy foods
- Drink more water
- Takeaway
Overview
Minerals such as calcium and phosphate help make up tooth enamel, along with bone and dentin. They also prevent tooth decay and subsequent cavities.
As you age, you lose the minerals in your teeth. This may be caused by eating sugary and acidic foods. It also occurs when bacteria accumulate in your mouth. Once the enamel or bone are gone, there’s no way to get them back without replacing the tooth entirely.
However, it is possible to help replenish these minerals with lifestyle changes and home remedies before tooth decay occurs. This process is known as remineralization. You can also stop demineralization in its tracks.
Talk to your dentist about the following treatment measures to help remineralize your teeth and help stop demineralization. Demineralization and remineralization are interrelated and in constant flux.
1. Brush your teeth
Brushing your teeth is important for removing bacteria. Cavities (also called dental caries) are primarily caused by the accumulation of Streptococcus mutans bacteria in your mouth.
According to a 2016 studyTrusted Source, these bacteria are transmitted via food and drink. Brushing your teeth regularly can remove the bacteria that may lead to mineral loss and cavities.
2. Use fluoride toothpaste
Not just any toothpaste will work against demineralization.
The American Dental Association (ADA) recommends fluoride toothpaste. In fact, toothpaste won’t get the ADA Seal of Acceptance unless it contains fluoride.
Fluoride toothpaste may prevent tooth decay and can also strengthen your teeth, making them less susceptible to future mineral loss.
3. Cut out sugar
Your dentist has likely warned you about sugar in the past, and for good reason. Sugar is highly acidic and interacts with bacteria in the mouth by breaking down tooth enamel.
More importantly, one studyTrusted Source found that a higher frequency in sugar consumption led to demineralization more than the amount of sugar consumed.
In other words, eating sugary foods in small amounts on a regular basis can do more harm than eating the occasional sugar-laden dessert.ADVERTENTIE
4. Chew sugarless gum
The role of gum in oral health has been debated for decades, but studies are showing that sugarless versions may actually promote tooth remineralization.
According to an older studyTrusted Source, sugar-free gum helps remove sugar, plaque, and carbs from teeth while also encouraging your salivary glands to produce more saliva.
Gum may also act as a barrier to block mineral loss. Xylitol and sorbitol appear to be the most promising sugar-free ingredients. To reap the remineralization benefits of sugarless gum, consider chewing after or between meals.
5. Consume fruit and fruit juices in moderation
While fruit is part of a healthy, balanced diet, it can also be highly acidic. Some of the worst culprits are citrus fruits, such as grapefruit and oranges.
Fruit acids create a process of calcium chelation on tooth enamel. This means that the acids bind to calcium and strip it away. Fruit juices are even worse, as these are highly acidic and often contain added sugars.
Your best bet is to stay away from juices and to eat acidic fruits only on occasion.HEALTHLINE RESOURCETRANSFORM: Health Equity
We believe in health equity—the equal opportunity for everyone to live their healthiest life. We are clarifying health inequities and creating a healthier world—for everyone.GO NOW
6. Get more calcium and vitamins
While calcium is produced within the teeth naturally, this important mineral is stripped by acids and bacteria over time. You can replace calcium by eating calcium-rich foods. For example, a 2003 studyTrusted Source found that eating calcium-rich cheese could counteract the effects of eating sugar.
If your diet is deficient in calcium, talk to your doctor about possible supplementation.
A 2012 study found that taking vitamin D supplements may help protect against cavities. Ask your doctor or dentist about taking vitamin D supplements.
You should also talk to them about daily multivitamins to be sure you’re getting other needed vitamins for healthy teeth.
7. Decrease dairy product consumption
While dairy products may be natural sources of calcium, the lactose in traditional milk products can increase acidity in your mouth. This is because lactose is a type of sugar.
You can still reap the benefits of calcium by choosing lactose-free milk, or by opting for a milk alternative like almond or soy milk.
8. Consider probiotics
When considering probiotics for remineralization, it’s important to choose strains that are naturally produced in the mouth. That way, you’re replacing the good bacteria without introducing potentially harmful strains.
The following probiotics are potentially helpful in oral health and remineralization:
- bifidobacterium
- reuteri
- rhamnosus
- salivarius
You can find probiotics in supplement form and certain yogurt brands also contain probiotics. You’ll need to take these daily for the best results.
9. Address your dry mouth
Dry mouth occurs when there isn’t enough saliva production. Saliva is not only important in keeping your mouth feeling comfortable, but it also helps prevent cavities.
According to 2016 researchTrusted Source, saliva is an integral part of remineralization. Saliva not only prevents dry mouth, but it also contains phosphate and calcium.
If you have dry mouth, talk to your dentist about chewing gums and rinses you can use to increase saliva activity.
10. Reduce starchy foods
Starchy foods, such as potatoes, rice, and bread, are loaded with simple carbohydrates. These increase the amount of fermentable sugars in the mouth, which can erode your teeth.
However, according to a 2003 studyTrusted Source, the risk of tooth decay tends to be higher when eating starchy foods combined with sugar. For example, sweetened rice is problematic for the teeth, but plain rice is not.
11. Drink more water
Water continues to be the preferred beverage of choice by doctors, nutritionists, and dentists. It’s not only naturally sugar-free, but it also helps remove harmful substances from the body.
Rinsing your mouth out with water may also help reduce demineralization when you don’t have a toothbrush on hand. This technique may be especially helpful after eating acidic or sugary foods.
While coffee and tea aren’t completely off-limits, they do little to remineralize your teeth. Plus, these substances can be acidic (especially coffee). Adding sugar can make these drinks even worse when it comes to oral health.
Sodas are also acidic, and often contain sugar, so they should be limited, too.
The bottom line
Mineral loss is inevitable because of the elements that teeth are exposed to every day. From food and drinks, to saliva and bacteria, your teeth are put through a lot of wear and tear. While your teeth are built to take on these elements, too much demineralization can eventually wear them down.
Taking steps to remineralize your teeth and stop any current demineralization, along with regular visits to your dentist, can help keep them healthy.
https://www.healthline.com/health/remineralizing-teeth
What Is the pH of Saliva?
What is pH?
The acronym pH stands for potential hydrogen. It’s used to describe the chemical acidity level vs. alkalinity level of a substance.
The pH level of 14 is the most alkaline, and the pH level of 0 is the most acidic. In the center of the spectrum is pH 7, the pH level for pure water.
For example, black coffee and vinegar are acidic and fall below pH 7. Seawater and antacids are alkaline and test above pH 7. With a pH just above 7, healthy human blood is just a little on the alkaline side.
What is the pH of saliva?
The normal pH range for saliva is 6.2 to 7.6.
Food and drink change the pH level of saliva. For example, bacteria in your mouth break down the carbohydrates you consume, releasing lactic acid, butyric acid, and aspartic acid. This lowers the pH level of your saliva.
Also, age may play a role. Adults tend to have more acidic saliva than children.
What is pH balance?
The human body is made up of about 60 percent water. It needs a pH close to water to sustain life.
Low pH
If there’s too much acid in the blood (low pH level), a metabolic acidosis occurs. This is associated with high blood pressure, kidney disease, diabetes and other conditions.
High pH
If there’s too much alkaline in the blood (high pH level), a metabolic alkalosis occurs. This is associated with adrenal disease and alcohol abuse.
Why should I care about the pH of my saliva?
Just like the rest of your body, your mouth needs a balanced pH. The pH level of your saliva can drop below 5.5 when you’re drinking acidic beverages. When this happens, the acids in your mouth start to demineralize (break down) tooth enamel.
If the tooth enamel becomes too thin, the dentin is exposed. This can lead to discomfort when consuming hot, cold, or sugary drinks.
Examples of acidic food and drink include:
- soft drinks (pH 3)
- white wine (pH 4)
- American cheese (pH 5)
- cherries (pH 4)
ADVERTENTIE

HEALTHLINE NEWSLETTERSign up for our daily nutrition tips and tricks
Healthier eating shouldn’t be a hassle. We’ll send you our evidence-based tips on meal planning and nutrition.Enter your emailGET STARTED
Your privacy is important to us. Any information you provide to us via this website may be placed by us on servers located in countries outside of the EU. If you do not agree to such placement, do not provide the information.
Symptoms of unbalanced saliva pH
Some indications that your saliva pH is out of balance include:
- persistent bad breath
- sensitivity to hot or cold food or beverages
- tooth cavities
How do I find out the pH of my saliva?
To test the pH of your saliva, you’ll need pH strips which are available at your drugstore or online. Once you have a pH strip, follow these steps:
- Do not eat or drink for a minimum of two hours before testing.
- Fill your mouth with saliva and then swallow or spit it out.
- Fill your mouth with saliva again and then place a small amount of it on a pH strip.
- The strip will change colors based on the acidity/alkalinity of your saliva. The outside of the box of pH strips will have a color chart. Match the color of your pH strip to the color chart to determine your saliva’s pH level.
How do I keep a balanced pH in my mouth?
To keep a balanced pH level in your mouth, you could consume only foods and beverages with a midrange pH. However, that would be pretty boring and most likely deprive you of important minerals and vitamins.
A more acceptable idea would be adjusting your behavior with certain foods and drinks, such as:
- Avoid sugary soft drinks. But if you can’t resist, drink them quickly and follow up with a drink of water. Try not to sip the sugary drinks over an extended period of time.
- Avoid black coffee. Adding dairy, not a sugary flavored creamer, can help counteract the acidity.
- Don’t brush. Avoid brushing your teeth after drinking high-acidity beverages such as soft drinks, fruit juices, cider, wine, or beer. High-acidity drinks soften your tooth enamel. Brushing too soon after consuming these drinks can further damage the enamel.
- Chew gum. After eating or drinking acidic foods or beverages, chew sugarless gum — preferably one with xylitol. Chewing gum encourages saliva production to help restore pH balance. It’s believed that xylitol will prevent bacteria from sticking to tooth enamel; it also encourages saliva production.
- Stay hydrated. Drink plenty of pH 7 water.
Saliva pH as a diagnostic tool
According to a 2013 study, your salivary pH can be used as a diagnostic biomarker. The study showed that the pH level of saliva changes based on the severity of a person’s periodontal disease.
The takeaway
Saliva that is properly pH balanced (6.2 to 7.6) helps maintain a healthy mouth and protect your teeth.
Testing your salivary pH with test strips is simple and there are number of easy lifestyle adjustments you can make to help keep your saliva pH properly balanced.
https://www.healthline.com/health/ph-of-saliva#takeaway
Should You Take Calcium Phosphate?
About calcium
Your body contains about 1.2 to 2.5 pounds of calcium. Most of it, 99 percentTrusted Source, is in your bones and teeth. The remaining 1 percent is distributed across your body in your cells, the membranes that encase your cells, your blood, and in other bodily fluids.
Most of us know that our bones and teeth are made primarily of calcium. But it’s not just any calcium. They’re made of calcium phosphate, a compound of calcium and phosphorous. Does this mean taking calcium phosphate supplements can give you healthier bones?
More than bones and teeth
Calcium does more than build strong bones and healthy teeth. This remarkable mineral also:
- helps blood vessels to regulate the flow of blood in your body
- assists in the contraction of your muscles
- aids in communication between nerve cells
- contributes to blood clotting
How much calcium do you need?
In general, both men and women need about 1,000 milligrams (mg) of calcium per day.
Women should up their intake to 1,200 mg at about 51 years old. This is because bone breakdown in postmenopausal women is greater than the amount of bone formation.
Men should up their intake to 1,200 mg at about 71 years old.
Infants, children, and pregnant women have the greatest need for calcium because of their exceptional rates of bone formation and growth.
According to the National Institutes of Health (NIH)Trusted Source, the recommended daily intake of calcium should be:
| infants, birth to 6 months | 200 mg |
| infants, 7 to 12 months | 260 mg |
| children, 1–3 years old | 700 mg |
| children, 4–8 years old | 1,000 mg |
| children, 9–18 years old | 1,300 mg |
| adult men, 19–70 years old | 1,000 mg |
| adult men, 71 years and older | 1,200 mg |
| adult women, 19–50 years old | 1,000 mg |
| adult women, 51 years and older | 1,200 mg |
HEALTHLINE NEWSLETTERGet our daily Nutrition email
To help you create your best meal plan, we’ll send you expert, evidence-based guidance on nutrition and weight loss.Enter your emailSIGN UP NOW
Your privacy is important to us. Any information you provide to us via this website may be placed by us on servers located in countries outside of the EU. If you do not agree to such placement, do not provide the information.
Where to get calcium
They say that milk can give you stronger bones and healthier teeth. But many other foods are good sources of calcium, too. Try adding more of these to your grocery list:
- cheese, yogurt, and other dairy products
- nuts and seeds
- beans
- broccoli
- greens, such as spinach, kale, arugula, and collard greens
- black-eyed peas
- figs
- oranges
- tofu
- salmon or sardines, canned, with bones
ADVERTENTIE
Types of calcium
There is no such thing as a nugget of pure, elemental calcium. In nature, calcium is found bound with other elements, such as carbon, oxygen, or phosphorous. When one of these calcium compounds is digested, it returns to its elemental state, and your body reaps the benefits.
Calcium from dolomite, bone meal, or oyster shells isn’t recommended because these sources may contain lead and other toxins. Your body absorbs calcium better when you take it in small doses (500 mg or less) with food.
Calcium phosphate — which you find as tricalcium phosphate in supplements — contains close to 39 percent elemental calcium. This is just a fraction below calcium carbonate (40 percent), but well above calcium citrate (21 percent), calcium lactate (13 percent), and calcium gluconate (9 percent).
Taking vitamin D will help your body absorb calcium better. Many calcium supplements also contain vitamin D.
Is calcium phosphate the answer?
“In most cases, calcium phosphate offers no advantage over calcium carbonate or calcium citrate,” said Dr. Roger Phipps, assistant professor at Husson University School of Pharmacy. “However, adequate phosphate is needed for bone health. So calcium phosphate may be a more appropriate supplement in someone with phosphate deficiency.”
Phosphate deficiency is more common in those with celiac disease, Crohn’s disease, kidney issues, alcohol use disorder, and those who take too many antacids. However, most people get enough phosphorus in the average American diet.
Most people who need calcium supplements need it because of vitamin D deficiency. In fact, excess phosphate linked to cola or soda consumption is a growing health concern because it’s associated with osteoporosis and problems with kidney function.Trusted Source
The verdict?
Stick to natural sources when it comes to calcium, unless a doctor recommends otherwise. If getting enough calcium is a concern for you, calcium carbonate and calcium citrate are likely your best options.https://www.myfinance.com/r/ssr/cde8c1fa-72c8-4070-9748-a3243bbc3a96?utm_campaign=hl-vms-multivitamin-widget-globalnous&utm_medium=embed&selector=%23__next+%3E+div%3Anth-of-type%285%29+%3E+div+%3E+div+%3E+div+%3E+div+%3E+article+%3E+div%3Anth-of-type%2810%29+%3E+div&csid=2aabbc01-7e37-4a0c-873b-7c2e8acdaddd&caid=3103ed07-b773-4580-a939-9dbcf26f242c&ciid=60c70cde-a34b-41c2-a2f2-0d645190ef48&tenant=wk_1Tqf7EYzOKyxm4Gvq042rU0Uky0&srckey=src_1Tqf7BF96WTbG5QbUndHWIgKoFo&mf_referrer=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.healthline.com%2Fhealth%2Ffood-nutrition%2Fshould-you-take-calcium-phosphate&_mfuuid_=9ff42965-de08-4c0b-a9a2-e0099660bbe3&width=750&subId=multivitaminwidget_hl_vms_bot_widget_globalnous_4605
https://www.healthline.com/health/food-nutrition/should-you-take-calcium-phosphate#takeaway
Xylitol is a naturally occurring alcohol found in most plant material, including many fruits and vegetables. It is extracted from birch wood to make medicine.
Xylitol is widely used as a sugar substitute and in “sugar-free” chewing gums, mints, and other candies. However, sorbitol is the most commonly used sweetener in sugarless gums because it is less expensive than xylitol and easier to make into commercial products.
People use xylitol to prevent cavities. It is also used to prevent tooth plaque and ear infection (otitis media), and for many other uses, but there is no good scientific evidence to support these uses.
Dog owners should know that xylitol can be toxic to dogs, even when the relatively small amounts from candies are eaten. If your dog eats a product that contains xylitol, it is important to take the dog to a veterinarian immediately.
How does it work ?
Xylitol tastes sweet but, unlike sugar, it is not converted in the mouth to acids that cause tooth decay. It reduces levels of decay-causing bacteria in saliva and also acts against some bacteria that cause ear infections.
https://www.webmd.com/vitamins/ai/ingredientmono-996/xylitol
Xylitol is a natural substance that can be found in a variety of fruits and vegetables. Some of the most common xylitol– rich foods include: berries, mushrooms, corns, and lettuces
http://www.golisdds.com/procedures/cleanings-prevention/xylitol-%E2%80%93-reducing-cavities/

CTx4 Gel 1100 .24%
4.8 star rating117 Reviews
CTx4 Gel 1100 is a low abrasion tooth gel that combines the proven anti-caries benefits of .24% neutral sodium fluoride with bio-available nano hydroxyapatite crystallites, xylitol, and CariFree’s unique, patented pH+ technology.
https://wellnessmama.com/3650/remineralize-teeth/

How to Protect Your Teeth If You’re Vegan
September 10, 2019
Whether your diet is vegan, vegetarian, or includes meat, science shows that eating plenty of plant-based foods is necessary for optimal health. But if you follow a vegan diet (or are considering doing so), which nutrients could you be missing? What do you need for a healthy mouth and teeth? Here’s what to know—and do.
Protect yourself against vitamin B12 deficiency
Insufficient amounts of vitamin B12 can result in gum disease and eventual tooth loss, but fruits and vegetables don’t provide this vital nutrient. There are B12-fortified cereals, yeasts, plant milks, and soy products available. However, these may not provide you enough B12, and you may need to take supplements to keep up your health. The Vegan Society has helpful information on recommended amounts.
Eat vegan sources of remineralizing foods
When you eat, acid erosion from certain foods (such as starches and sugars) may cause your teeth to begin losing the minerals that keep their enamel healthy and strong. But your teeth can gain back lost minerals if you’re also eating foods that supply them. Non-vegan remineralizing food suggestions frequently include dairy choices. For vegans, the best remineralizing foods are explained below.
 To get calcium, which strengthens tooth enamel and builds strong teeth, eat beans and legumes including black-eyed peas and lentils; leafy greens such as broccoli, collard greens, kale, and spinach; almonds; and calcium-added orange juice or vegan milks such as almond, rice, or soy milk.
To get calcium, which strengthens tooth enamel and builds strong teeth, eat beans and legumes including black-eyed peas and lentils; leafy greens such as broccoli, collard greens, kale, and spinach; almonds; and calcium-added orange juice or vegan milks such as almond, rice, or soy milk.
You can also keep your teeth strong by eating foods that contain potassium, which controls acid levels within your blood. Without this control, excess acid may deplete calcium levels within your bones and teeth. Good vegan sources of potassium include avocadoes, bananas, potatoes, prunes, sweet potatoes, swiss chard, and tomatoes.
For vitamin D, which helps your body absorb calcium (thus contributing to healthy teeth), good vegan sources are fortified cereal and portabella mushrooms. You can also help your body make vitamin D naturally when you go outside in the sun; just remember to wear sunscreen! You may also wish to consider taking vitamin D or combination calcium/vitamin D supplements.
Phosphorus rebuilds your tooth enamel, and you can get it from vegan foods such as lentils, pumpkin seeds, and soybeans.
Eat vegan sources of amino acids for plaque control
The amino acid arginine helps prevent cavities and gum disease, and also breaks down dental plaque. It’s frequently found in meat, poultry, fish, and dairy. Vegan sources of arginine include chickpeas, lentils, and soybeans; peanuts; and pumpkin seeds.

Prevent dry mouth with vegan sources of vitamin A
Vitamin A keeps your mucous membranes healthy and helps prevent dry mouth. Excellent sources of vitamin A are bright orange foods such as apricots, cantaloupe, carrots, pumpkin, and sweet potatoes. Leafy green foods including collard greens, kale, and spinach are also great sources of vitamin A.
Help your body heal with foods rich in vitamin K
Your body heals most easily when you have a sufficient intake of vitamin K. Without enough of this vitamin, you may bleed more easily and it can take longer to heal after an injury or surgery. You can boost your body’s healing processes by eating green vegetables including broccoli, Brussels sprouts, collard greens, kale, parsley, and spinach—all great sources of vitamin K.
Snack healthily and limit starches and sugars
If you’re eating a vegan diet with small amounts of protein and fat, you may find that you need snacks to keep up your energy during the day. Sugary and starchy foods (such as bread, cereal, crackers, muffins, pasta, and rice) can feed the bacteria in your mouth that cause tooth decay. Try instead to choose non-sugary snack foods that will replenish your energy, such as nuts, seeds, tofu, and vegetables.
Practice good oral hygiene and see your dentist regularly
After you eat, take 20 seconds to rinse your mouth vigorously with water to help eliminate leftover food particles and acid. Floss your teeth daily and brush them twice a day for two minutes each time—and of course, schedule regular teeth cleanings and dental checkups. Your oral health is part of your overall health!
References
4 Vitamins and Minerals That Help Strengthen Teeth. Pronamel. https://www.pronamel.us/healthy-living/nutrition-and-dental-health/natural-remedy-for-tooth-enamel-restoration/. Accessed April 26, 2019.
7 Vitamins and Minerals Your Mouth Needs. Delta Dental. https://www.deltadentalins.com/oral_health/vitamins-and-minerals.html. Published April 2016. Accessed April 26, 2019.
Amino acid found in some foods could improve oral health. Medical Xpress. https://medicalxpress.com/news/2015-05-amino-acid-foods-oral-health.html. Published May 7, 2015. Accessed September 4, 2019.
Diet and Oral Health. WebMD. https://www.webmd.com/oral-health/diet-oral-health#1. Published 2017. Accessed April 26, 2019.
Freeman A. Healthy Foods List: Seven Best Foods for Your Teeth. Colgate. https://www.colgate.com/en-us/oral-health/basics/nutrition-and-oral-health/healthy-foods-list-seven-best-foods-for-your-teeth-0214. Accessed April 23, 2019.
Goldman R. 10 Healthy High-Arginine Foods. Healthline. https://www.healthline.com/health/healthy-high-arginine-foods. Published 2019. Accessed September 4, 2019.
Winters C. Chew on This: 8 Foods for Healthy Teeth. LiveScience. https://www.livescience.com/44111-foods-healthy-teeth-bad-breath.html. Published March 14, 2014. Accessed April 23, 2019.
Remineralization occurs when vital minerals—like calcium—bond to the teeth to fill in the weakened areas of enamel.
These minerals need to be present in saliva to facilitate the process. You can get many of these minerals from the foods you eat, such as cheese and other dairy products, fiber-rich fruits and vegetables, or poultry and seafood.
However, modern diets are highly acidic, and your teeth may need some extra help to promote remineralization.
Find out more about how to actively repair tooth enamel.
6 Ways to Help Remineralize Teeth
1. Increase Saliva Production
One of the most effective ways to repair tooth enamel is to maximize the amount of saliva you produce. This is because essential components in your saliva – such as calcium and phosphate – can neutralize harmful acids and help restore minerals lost because of acids in your diet. Saliva is also your body’s natural defense against cavities.3, 6
2. Drink More Water
Tap water containing protective fluoride plays a crucial role in supporting remineralization by helping to replace some of the calcium present in the enamel. Rinsing your mouth with fluoridated tap water after eating or drinking acidic foods and drinks can also help to reduce the effects of acids on your teeth.3, 5, 6
3. Use a Toothpaste Designed for the Job
Opt for a toothpaste clinically proven to help rebuild enamel strength, like Pronamel. Pronamel is specially designed to penetrate deep and remineralize acid-weakened enamel, to help protect your enamel every time you brush. Discover how Pronamel toothpaste actively strengthens weakened tooth enamel.

4. Chew Sugar-Free Gum
Chewing sugar-free gum helps to keep that all-important saliva flow up, protecting your enamel from acid wear and demineralisation. Always look for gums with the American Dental Association Seal of Acceptance.2, 5
5. Eat a Remineralization Diet
Certain foods can help remineralize the spots in your teeth that acidic foods and drinks have weakened. For example, foods rich in calcium (dairy products like milk, cheese and yogurt) help put back minerals into the enamel, and fiber-rich fruits and vegetables encourage saliva flow.5
6. Dodge Acidic Drinks
Drinks that contribute to demineralization include sodas, sports drinks and fruit juices. In addition to their sugar content, these are all highly acidic and can wear down enamel – a combination that puts you at greater risk of demineralization and tooth decay.2
Take Steps to Remineralize Teeth
You can help remineralize your teeth by following the tips above and adopting a good dental hygiene routine with products like the Pronamel range that are designed to protect enamel. You should also pay regular visits to your dentist so that signs of demineralization can be spotted early.
Find out where to buy Pronamel and start your journey to healthier, stronger teeth.
SOURCES
By clicking any of the links below you will be taken to an external website that is independently operated and not managed by GSK. GSK assumes no responsibility for the content on the website. If you do not wish to leave this website, do not click on the links below.
- Tooth. Mouth Healthy. https://www.mouthhealthy.org/en/az-topics/t/tooth. Accessed on 30/03/20.
- Dietary acids and your teeth. Mouth Healthy. https://www.mouthhealthy.org/en/az-topics/e/dietary-acids-and-your-teeth. Accessed on 22/01/20.
- Demineralization–remineralization dynamics in teeth and bone. International Journal of Nanomedicine (2016). https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5034904/pdf/ijn-11-4743.pdf. Accessed 30/03/20.
- Determining the Effect of Calculus, Hypocalcification, and Stain on Using Optical Coherence Tomography and Polarized Raman Spectroscopy for Detecting White Spot Lesions. International Journal of Dentistry. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2905912/pdf/IJD2010-879252.pdf. Accessed on 22/01/20.
- The Best and Worst Foods for Your teeth. University of Rochester Medical School. https://www.urmc.rochester.edu/encyclopedia/content.aspx?ContentTypeID=1&ContentID=4062. Accessed 22/01/20.
- JADA. https://www.adha.org/resourcesdocs/7167_JADA_Saliva_Supplement.pdf. Accessed 22/01/20.
https://www.pronamel.us/tooth-enamel/enamel-remineralization/
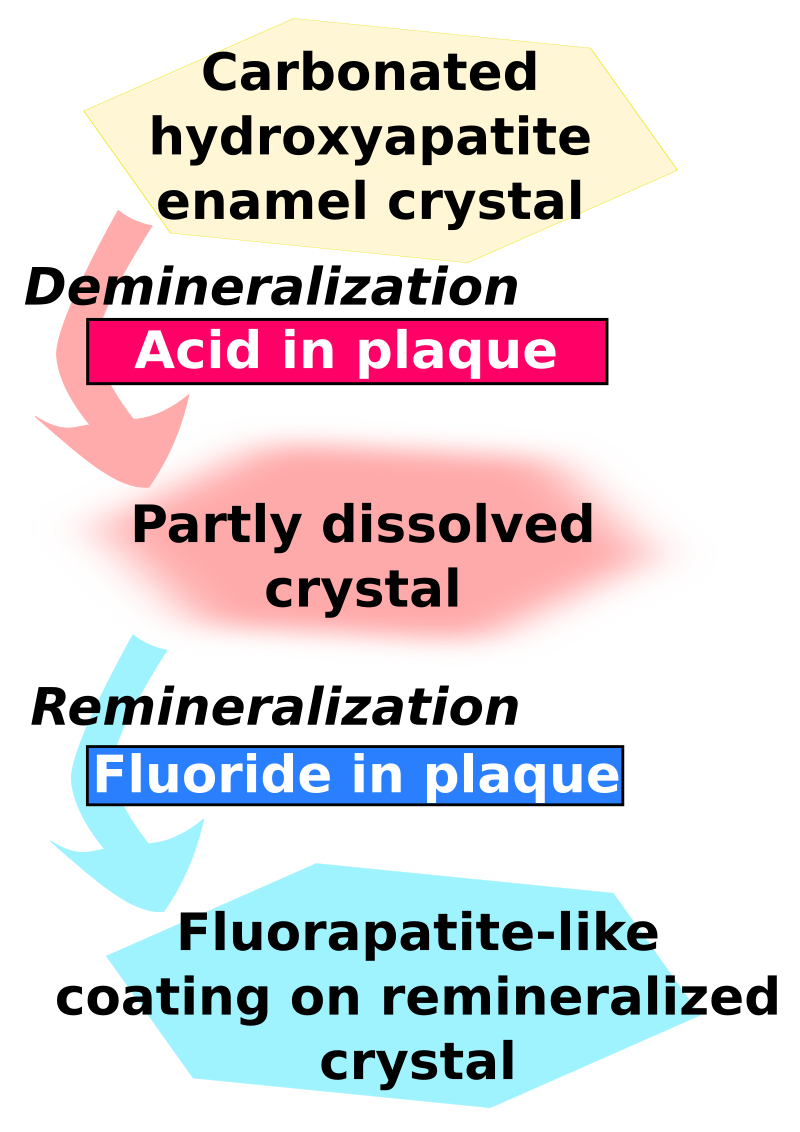
Tooth decay process[edit]
When food or drinks containing fermentable sugars enter the mouth, the bacteria in dental plaque rapidly feed on the sugars and produce organic acids as by-products.[1] The glucose produced from starch by salivary amylase, is also digested by the bacteria. When enough acid is produced so that the pH goes below 5.5, the acid dissolves carbonated hydroxyapatite, the main component of tooth enamel.[7] The plaque can hold the acids in contact with the tooth for up to two hours, before it is neutralised by saliva. Once the plaque acid has been neutralised, the minerals can return from the plaque and saliva to the enamel surface.
However, the capacity for remineralisation is limited, and if sugars enter the mouth too frequently a net loss of mineral from enamel produces a cavity, through which bacteria can infect the inner tooth and destroy the latticework. This process requires many months or years. [8][4]
Natural tooth remineralisation[edit]
Role of saliva[edit]
Remineralization occurs on a daily basis after attack by acids from food, through the presence of calcium, phosphate and fluoride found in saliva.[9][10]
Saliva also acts as a natural buffer to neutralise acid, preventing demineralisation in the first place. If there is reduced saliva flow or reduced saliva quality, this will increase the risk of demineralization and create the need for treatment in order to prevent demineralisation progression.[4]
Saliva function can be organised into five major categories that serve to maintain oral health and create an appropriate ecologic balance:
- Lubrication and protection
- Buffering action and clearance
- Maintenance of tooth integrity
- Antibacterial activity
- Taste and digestion.[4]
As the demineralisation process continues, the pH of the mouth becomes more acidic which promotes the development of cavities. Dissolved minerals then diffuse out of the tooth structure and into the saliva surrounding the tooth. The buffering capacity of saliva greatly impacts the pH of plaque surrounding the enamel, thereby inhibiting caries progression. Plaque thickness and the number of bacteria present determine the effectiveness of salivary buffers.[4] The high salivary concentrations of calcium and phosphate which are maintained by salivary proteins may account for the development and remineralisation of enamel. The presence of fluoride in saliva speeds up crystal precipitation forming a fluorapatite- like coating which will be more resistant to caries.[4]
Treatment and prevention[edit]
Besides professional dental care, there are other ways for promoting tooth remineralisation:
Fluoride[edit]
Fluoride therapy[edit]
Fluoride is a mineral found naturally in rock, air, soil, plants and water and may assist by:
- Potentially repairing early white spot lesions found on the tooth surface that may develop into cavities.[citation needed]
And a reduction in cavities may result in the following downstream benefits:
- Protecting children and adults against tooth decay [11]
- Helps prevent premature tooth loss of baby teeth due to decay and overall assists in guiding the adult teeth to correct tooth eruption.[citation needed]
- Aids in the prevention of invasive dental treatment therefore reducing the amount of money spent on dental treatment[citation needed]
- Provides an overall community advantage, especially individuals from low socioeconomic communities, who have less access to other forms of fluoride treatments[citation needed]
- Evidence confirms that water fluoridation is a safe and effective way to help protect teeth against decay[citation needed]
- The addition of fluoride to the water does not alter the taste or smell of the drinking water[citation needed]
Fluoride therapy is often used to promote remineralisation. This produces the stronger and more acid-resistant fluorapatite, rather than the natural hydroxyapatite. Both materials are made of calcium. In fluorapatite, fluoride takes the place of a hydroxide.[12]
Effect of fluoride[edit]
The presence of fluoride in saliva and plaque fluid interacts with remineralisation process in many ways and thus exerts a topical or surface effect. A person living in an area with fluoridated water may experience rises of fluoride concentration in saliva to about 0.04 mg/L several times during a day.[13] Technically, this fluoride does not prevent cavities but rather controls the rate at which they develop making them take a lot longer and making them easier to prevent via normal brushing as it will take a higher amount of acid, usually built up over a number of days, to destroy the created fluorapatite.[14] When fluoride ions are present in plaque fluid along with dissolved hydroxyapatite, and the pH is higher than 4.5,[15] a fluorapatite-like remineralised veneer is formed over the remaining surface of the enamel; this veneer is much more acid-resistant than the original hydroxyapatite, and is formed more quickly than ordinary remineralised enamel would be.[1] The cavity-prevention effect of fluoride is partly due to these surface effects, which occur during and after tooth eruption.[16] Fluoride interferes with the process of tooth decay as fluoride intake during the period of enamel development for up to 7 years of age; the fluoride alters the structure of the developing enamel making it more resistant to acid attack. In children and adults when teeth are subjected to the alternating stages of demineralisation and remineralisation, the presence of fluoride intake encourages remineralisation and ensures that the enamel crystals that are laid down are of improved quality.[17] Fluoride is commonly found in toothpastes. Fluoride can be delivered to many parts of the oral cavity during brushing, including the tooth surface, saliva, soft tissues and remaining plaque biofilm.[18] Some remineralisation methods may work for “white spot lesions” but not necessarily “intact tooth surfaces”.[19]
Fluoridated toothpaste[edit]
Regular use of a fluoridated toothpaste has been shown to provide a significant source of fluoride to the mouth by the means of direct fluoride contact to tooth structure.[20] The types of fluoride added to toothpaste include: sodium fluoride, sodium monofluorophosphate (MFP), and stannous fluoride.[21]
As stated previously, fluoride has been proven to positively affect the remineralisation process. Therefore, by using an adequately fluoridated toothpaste regularly, this assists the remineralisation process of any hard tooth tissues.
Fluoride varnish[edit]
Fluoride varnishes were developed late 1960s and early 1970s and since then they have been used both as a preventative agent in public health programs and as a specific treatment for patients at risk of caries by the 1980s, mostly in European countries.[20] Fluoride varnishes were developed primarily to overcome their shortcoming which is to prolong the contact time between fluoride and tooth surfaces.[20] Furthermore, when compared to other existing topical fluoride the advantages of fluoride varnishes application are being a quick and easy procedure for the clinicians, reduced discomfort for the receiving patients, and greater acceptability by the patients. Fluoride varnishes are a concentrated topical fluoride containing 5% sodium fluoride (NaF) except the Fluor protector which contains difluorosilane.[20] There are many types of fluoride varnishes and among them the popular brands are Duraphat and Fluor Protector. Currently, the anti-caries effect fluoride varnishes are backed up by Cochrane systematic reviews, 2002 which was updated in 2013 included 22 trials with 12,455 children aged 1–15 years old. The conclusion made is similar to its previous review, a 46% reduction in D(M)FS and 33% reduction in d (e/m)fs in permanent teeth and deciduous teeth respectively [20]
Water fluoridation[edit]
Community water fluoridation is the addition of fluoride in the drinking water with the aim of reducing tooth decay by adjusting the natural fluoride concentration of water to that recommended for improving oral health. The NHMRC released the public statement of efficacy and safety of fluoridation 2007 to set the recommended water fluoridation to the target range of 0.6 to 1.1 mg/L, depending on climate, to balance reduction of dental caries (tooth decay) and occurrence of dental fluorosis (mottling of teeth). Moreover the public statement states that the fluoridation of drinking water is an effective way to ensure the community is exposed to fluoride and can benefit from its preventative role in tooth decay.[22]
Plaque control[edit]
Oral hygiene practices involve the mechanical removal of plaque from hard tissue surfaces [23] Cariogenic bacteria levels in the plaque determine whether caries will occur or not, therefore, effective removal of plaque is paramount.[24] The removal of plaque inhibits demineralisation of teeth, and reversely increases opportunities for remineralisation.
Diet[edit]
Demineralization is caused by bacteria excreting acids as a product of their metabolism of carbohydrates. By reducing the intake frequency of carbohydrates in an individual’s diet, remineralization is increased and demineralization is decreased. Diet control is an important aspect in promoting remineralization to occur naturally. A loss of the tooth enamel structure and cavitation may occur if the demineralization phase continues for a long period of time. This disturbance of demineralisation caused by the presence of fermentable carbohydrates continues until the saliva has returned to a normal pH and had sufficient time to penetrate and neutralize the acids within any cariogenic biofilm present.[25]
Increased sugar consumption in the means of foods and drinks containing high levels of sugar are known to be associated with high rates of dental decay. As a result, members of the dental team routinely assess patients’ diets and highlight areas where this could be improved to reduce the risk of dental decay. A balanced diet is an important contributing factor towards oral health and general health. It is common knowledge that certain dietary habits contribute to disease, whether patients take note of advice which is given to them and change their diet as a result, is less certain.[26]
Recent studies on diet and caries have been confounded by the widespread use of fluoride toothpastes. Studies have argued that with greater exposure to fluoride, the sugar consumption/caries relationship may be weaker in the modern age than previously thought, with fluoride raising the threshold of sugar intake at which caries progresses to cavitation. It has been concluded in modern societies that a significant relationship between sugars and caries persists despite the regular widespread use of fluoride toothpaste.[27] Several reviews conclude that high sugar consumption continues to be the main threat for dental health of whole populations in some developed and many developing countries. Therefore, a key strategy to further reducing levels of caries in individuals as well as for populations, is by means of reducing the frequency of sugar intakes in the diet.
Foods high in refined carbohydrates, such as concentrated fruit snack bars, sweets, muesli bars, sweet biscuits, some breakfast cereals and sugary drinks including juices can contribute to dental decay, especially if eaten often and over long periods as the sugar nourishes the cariogenic bacteria in mouth. The bacteria produce acid, which destroys teeth. Highly refined packaged foods such as savory crackers and chips can also have high levels of carbohydrates. It is important to check the nutritional information panel on packaged foods to determine which foods and drinks have high carbohydrate concentrations.[28]
To prevent demineralisation in the mouth, it is important for an individual to ensure they have a well-balanced diet, including foods containing calcium and foods that are low in acids and sugars. The individual should have a diet high in fresh fruits and vegetables, wholegrain cereals, legumes, seeds and nuts. Sugary snacks including lollies, fruit bars, muesli bars, biscuits, dried fruit, cordials, juices and soft drinks should be limited as they contribute to dental decay and dental erosion. Additionally, excessive starchy foods (such as bread, pasta, and crackers), fruits and milk products consumed frequently can cause the growth of dental plaque and bacteria.[28] Therefore healthy eating[vague], healthy drinking[vague] and proper maintenance of oral hygiene is the best way to promote and maintain sound tooth structure for an individual.
Xylitol, Sorbitol, and Erythritol[edit]
Xylitol is a naturally-occurring sweetener that can be synthetically produced in bulk. It is classified as a sugar alcohol.[10] Xylitol inhibits acid production by oral bacteria and promotes remineralisation of the teeth.[10] It can be found in various products which include chewing gums and lozenges. Xylitol has been found to reduce mutans streptococci in plaque and saliva and reduce the binding of these to the acquired enamel pellicle.[10] This in turn leads to less adherent plaque and a decrease in acid production.[10] In addition, chewing xylitol gum will stimulate increased salivary flow which in turn increases the amount of calcium in the saliva and enhances the oral clearance.
Additional saliva flow which includes chewing products such as gums that contain no fermentable carbohydrates can aid in the modulation of plaque pH. Xylitol is a sugar alcohol which provides the sensation of tasting sweetness in foods, particularly chewing gum, without providing sucrose which is the only sugar that S.mutans are capable of using to produce the polyacrylamide adhesive which allows them bind to the teeth. Xylitol does not actively reduce or harm the presence or capacities of oral bacteria, but rather does not offer them the sustenance to propagate or function. There are often claims of significant dental benefits of Xylitol. These generally derive from the perspectives of; saliva production is increased during chewing and oral stimulation which can help to maintain a more adequate supply of saliva to support normal oral functioning. Also, the idea of Xylitol being a sweetener option which does not serve as fuel for oral bacteria is considered to be the healthier alternative than sucrose (table sugar), fructose, lactose, galactose products. While these considerations may not reverse any conditions in health, they are more so preventative, and do not further the consequential events such as dental caries, malodorous breath, excessive plaque and gingivitis conditions.
Erythritol may have greater protective action than xylitol and sorbitol.[29] However, this research is industry funded and not as comprehensive as the research on xylitol.
Biomimetic glass and ceramics[edit]
Further information: Biomimetic material § Biomimetic mineralization
Biomimetic glass and ceramic particles, including amorphous calcium sodium phosphosilicate (CSPS, NovaMin) and amorphous calcium phosphate (ACP, Recaldent), are used in some toothpastes and topical preparations to promote remineralisation of teeth.[30] These particles have a structure mimicking hydroxyapatite, providing new sites for mineralisation to occur.[31] Their binding to the teeth also occludes open dentin tubules, helping to reduce dentin hypersensitivity. Evidence is insufficient to recommend either for any indications, but the evidence for CSPS[30] is stronger than that for ACP.[32]
Oligopeptide P11-4[edit]
Main article: Oligopeptide P11-4
P11-4 (Ace-QQRFEWEFEQQ-NH2, Curolox) is a synthetic, pH controlled self-assembling peptide used for biomimetic mineralization e.g. for enamel regeneration or as an oral care agent.[33] It has a high affinity to tooth mineral.[34]
P11-4 is a self-assembling β-peptide. It builds a 3-D bio-matrix with binding sites for Calcium-ions serving as nucleation point for hydroxyapatite (tooth mineral) formation. The high affinity to tooth mineral is based on matching distances of Ca-ion binding sites on P11-4 and Ca spacing in the crystal lattice of hydroxyapatite. The matrix formation is pH controlled and thus allows control matrix activity and place of formation.[35]
Self assembling properties of P11-4 are used to regenerate early caries lesions. By application of P11-4 on the tooth surface, the peptide diffuse through the intact hypomineralized plate into the early caries lesion body and start, due to the low pH in such a lesion, to self-assemble generating a peptide scaffold mimicking the enamel matrix. Around the newly formed matrix de-novo enamel-crystals are formed from calcium phosphate present in saliva. Through the remineralization caries activity is significantly reduced in comparison with a fluoride treatment alone.[36] In aqueous oral care gels the peptide is present as matrix. It binds directly as matrix to the tooth mineral and forms a stable layer on the teeth.[37] This layer does protect the teeth from acid attacks. It also occludes open dentin tubule and thus reduces the dental sensitivity.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Remineralisation_of_teeth
What’s effective?
The most effectiveTrusted Source remineralizing toothpastes contain ingredients such as:
- stannous fluoride
- sodium fluoride
- calcium phosphate (hydroxyapatite)
These ingredients are able to bond to weakened tooth enamel, forming patches, much like patches sewn into worn-out fabric.
Even though these patches aren’t made from tooth enamel, they have the ability to strengthen and protect teeth.
Remineralizing toothpastes also help prevent additional tooth decay from occurring, especially when they’re combined with proactive oral care habits, such as brushing and flossing after meals.
What else helps?
Lifestyle and dietary choices, such as avoiding sugary substances like soda and candy, greatly impact the ability of teeth to remineralize and affect overall tooth health.
Calcium is one mineral that helps keep tooth enamel strong. Not enough calcium in teeth can sometimes be connected to a calcium deficiency.
If you are postmenopausal or have a condition such as hypocalcemia, your body might pull calcium from your teeth in order to support other vital functions.
Talk with your doctor about treatments that might help.https://77b02afa75134bb9862ae8cd05f478bf.safeframe.googlesyndication.com/safeframe/1-0-38/html/container.html
Choosing a remineralizing toothpaste
Ask a dentist
Talk with your dentist about remineralizing toothpastes and your specific needs.
In some instances, your dentist may recommend a prescription remineralizing toothpaste.
These typically have a higher fluoride content and may be designed to penetrate into the tooth’s root as well as into the enamel.
Look for the ADA seal
It’s good to choose a toothpaste with the American Dental Association’s (ADA) Seal of Acceptance. The seal indicates when a dental product has met ADA standards for safety and effectiveness.
You can always ask your dentist for their opinion on any product without the seal. You can even contact the company that makes the toothpaste to ask why it hasn’t received the seal.
Read the ingredients
Every toothpaste lists its active and inactive ingredients. Make sure to check the inactive ingredients to determine if you’re sensitive or allergic to them.
Potential allergens or irritants in toothpaste can include flavorings such as:
- mint
- cinnamon
- grape
- orange
Allergic reactions have also been linkedTrusted Source to ingredients such as:
- cocamidopropyl betaine (CAPB)
- propylene glycol
Know the brand
Look for a reputable brand name as well as transparency about the ingredients the product contains and the place where it’s manufactured.
Any product that promises to rebuild tooth enamel or that makes claims that seem too good to be true should probably be avoided.
Takeaway
Tooth enamel can’t be regenerated, but the mineral content within teeth can be increased.
Remineralizing toothpaste formulas, when combined with proper oral health and dietary choices, can help teeth become stronger, more comfortable, and less susceptible to cavities.
Last medically reviewed on March 29, 2021
Medically reviewed by Jennifer Archibald, DDS — Written by Corey Whelan — Updated on March 30, 2021https://77b02afa75134bb9862ae8cd05f478bf.safeframe.googlesyndication.com/safeframe/1-0-38/html/container.htmlhttps://77b02afa75134bb9862ae8cd05f478bf.safeframe.googlesyndication.com/safeframe/1-0-38/html/container.html
Donnez vie à vos concepts avec iStock.Les collections exclusives d’iStock offrent une série infinie de thèmes et les dernières tendances visuelles pour vos projets créatifs.SPONSORED BY ISTOCKSee More
https://wordpress.com/post/scentses4d.wordpress.com/3275
Natural hydroxyapatite is usually extracted from biological sources or wastes such as mammalian bone (e.g. bovine, camel, and horse), marine or aquatic sources (e.g. fish bone and fish scale), shell sources (e.g. cockle, clam, eggshell, and seashell), and plants and algae and also from mineral sources (e.g. limestone).
Abstract
Waste materials from natural sources are important resources for extraction and recovery of valuable compounds. Transformation of these waste materials into valuable materials requires specific techniques and approaches. Hydroxyapatite (HAp) is a biomaterial that can be extracted from natural wastes. HAp has been widely used in biomedical applications owing to its excellent bioactivity, high biocompatibility, and excellent osteoconduction characteristics. Thus, HAp is gaining prominence for applications as orthopaedic implants and dental materials. This review summarizes some of the recent methods for extraction of HAp from natural sources including mammalian, aquatic or marine sources, shell sources, plants and algae, and from mineral sources. The extraction methods used to obtain hydroxyapatite are also described. The effect of extraction process and natural waste source on the critical properties of the HAp such as Ca/P ratio, crystallinity and phase assemblage, particle sizes, and morphology are discussed herein
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2405844018368944
Silicon–hydroxyapatite bioactive coatings (Si–HA … – COREhttps://core.ac.uk › download › pdf
PDFby M López-Alvarez · 2009 · Cited by 63 — Diatomaceous earth and silica, together with commercial hydroxyapatite were respectively the silicon and HA sources used to produce the Si–HA coatings. … A new generation of bioactive coatings has emerged with the silicon substituted hydroxyapatite thin films (Si–HA).
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19089599/
Although xylitol does indeed kill bad bacteria in the mouth, Dr. Curatola explains that it disrupts the microbiome. … As this sugar alcohol remains in your gut, it is fermented and may cause bacterial overgrowth and yeast—resulting in bloating, cramping, gas, diarrhea, and acid reflux.Oct 23, 2018
DIY Remineralizing Tooth Powder that May Cure Tooth Decay
BY JOYBILEE FARM 262 COMMENTS
This post contains affiliate links. If you use these links to buy something we may earn a commission. Thanks.35.0kPinShareTweet
You can cure tooth decay with this DIY remineralizing toothpaste. It takes some commitment and a lifestyle change, but it’s doable with these steps.
Cure Tooth Decay
You really can cure tooth decay at home, according to Ramiel Nagel, author of Cure Tooth Decay. It takes some commitment and a lifestyle change, but it’s doable. It begins with a diet that is free of sugar and refined carbohydrates, the kind that raises your blood glucose levels. High blood glucose levels mean problems for bones and teeth. Keeping your blood sugar in balance is a key prescription for better health, including better dental health.
A traditional diet that is rich in organic fruits and vegetables, bone broth, fermented foods, grass-fed meat, and raw milk contains the vitamins and minerals necessary for bone health, according to Weston Price, a dentist who studied traditional diets and their effect on dental health.
Dr. Price found that people eating traditional diets not only had improved dental health, but their bone structure was also different and their teeth were stronger. But for those of us who didn’t grow up on a traditional diet, this remineralizing tooth powder can help bridge the gap, while we get our diets in order.

Living without a dentist
The book, Cure Tooth Decay by Ramiel Nagel, outlines a diet that will remineralize your teeth and stop new cavities from forming. It is based on research by Weston Price using bone broth, fermented grains, and raw milk products to stop the bad stuff from harming your teeth and encourage the good stuff to rebuild them.
The key takeaway from the book is that to cure tooth decay and remineralize your teeth, your teeth need to have direct contact with the building blocks that teeth are made of – calcium, phosphorous, and some trace minerals. Your teeth also need less contact with the things in the oral environment that inhibit the rebuilding process.
The good things that help rebuild your teeth are also the things that help rebuild your immune system and help you conquer chronic diseases like cancer. There is a critical connection between the state of your teeth and the state of your health.

The bad stuff:
The oral environment that prevents cavities from healing and destroys dental enamel
- Uncontrolled blood sugar spikes
- Sugary food and drink
- Commercial toothpaste – the glycerin (#ad) and fluoride inhibit the remineralization of tooth enamel
- Artificial sweeteners – increase blood sugar, acidify the mouth
- Fluoridated water – binds to tooth enamel making it weak and preventing mineralization with calcium and phosphorous.
- Unfermented grains – inhibit the absorption of minerals due to anti-nutrients
- Bacteria that form biofilms in the mouth preventing the remineralization of tooth enamel and destroying tooth enamel
- Acidic oral environment – eats away at tooth enamel causing cavities
- Dental drilling destroys tooth enamel and prevents the remineralization of teeth.
- Glycerine, found in commercial toothpaste coats teeth and prevents the remineralization of tooth enamel

The good stuff:
An oral environment that strengthens and builds tooth health
- Is rich in calcium — calcium and phosphorous are the building blocks that your teeth need to rebuild. You have to supply them.
- Maintains neutral pH, not overly acidic. The toothpowder is alkaline and should act as a pH buffer — so brush at least twice a day.
- Is free of bad-bacterial biofilms – has a predominance of good bacteria in the microbiome – lactic acid bacteria is one of the good guys that helps keep the bad guys in check. You’ll need to brush your tongue when you brush your teeth, and floss at least once a day to get rid of the biofilms. Bacterial biofilms will prevent the minerals from adhering to your teeth.
- Is without dental treatments that destroy tooth enamel and oral integrity such as dental fillings and root canals. Once the dentist has drilled your teeth and removed the enamel, that tooth is compromised. Root canals remove the nerve and blood supply from a tooth which allows bacteria to proliferate in the dead tissue. Ideally, avoid both if you can, by catching potential problems before they require emergency management.
- Even if you are like me, with mercury fillings and a root canal, this remineralizing tooth powder recipe will still help, but if you can avoid the invasive dental treatments you’ll repair your teeth more easily. But don’t take my word for it. Do your own research.
- Diet high in fruits and vegetables and calcium-rich bone broths, low in sugar, processed foods, and fermented grains will both rebuild tooth enamel and rebuild your overall health and wellness. There is a connection between the health of your teeth and the overall health of your body.

How to cure tooth decay
According to Cure Tooth Decay, you can cure tooth decay. Healing your cavities involves not just tooth brushing and oral hygiene but also a change in lifestyle and diet. You can’t just change from commercial toothpaste and keep eating crap and expect to rebuild your tooth enamel and heal your cavities.
Your body deserves better.
My personal experience
My daughter was heading overseas for 2 years to serve as a full-time writer with a Christian Aid Organization. Before she left for her trip we tried to get her in to see the dentist. She had a shadow on one of her teeth that we thought might be a cavity. But we don’t have a dental plan. The three dentists in our area aren’t taking new patients, and they couldn’t fit her in anytime in the next six months. So instead Sarah kept an eye on her diet and started using this remineralizing tooth powder.
Today Sarah’s cavities are completely gone. She cut out quite a bit of the sugary treats she was eating and I made her this remineralizing tooth powder to brush her teeth with twice a day. She brushes her teeth and then holds the mixture at the back of her mouth for a minute, while she combs her hair, and then spits it out and rinses with plain water. She’s had very yellow teeth since she was young, attributed to the fluoridation treatments that our dentist gave her. She brushed and brushed and her teeth have remained yellow.
However, after two months of using this remineralizing tooth powder, her teeth are regaining their whiteness.
And finally, her gums have bled after flossing for over a decade. She said to me this morning, “My gums are no longer bleeding. It’s the first time in my life that my gums aren’t bleeding when I brush my teeth and floss.” It makes me feel happy to improve my baby’s oral health with such a simple step as making my own remineralizing tooth powder.
But even better, I’ve had a toothache since I had the “flu” last Spring. I’ve had a biofilm in my mouth that I couldn’t seem to shake. The pain was in a tooth that I had an unnecessary, botched root canal over 20 years ago. It was so severe that I couldn’t chew anything on that side of my mouth. Since the dentists in town aren’t taking any new patients I hadn’t been able to have it looked at. It was a blessing in disguise.
I started using the same remineralizing tooth powder that I made for Sarah and the pain disappeared after the first day of using the tooth powder and it never came back. Robin is also using it and his teeth have changed from yellow to a much whiter and healthier look.
So while it won’t by itself cure tooth decay, it is one piece of the solution.
15 years of experimenting with DIY natural toothpaste
15 years of experimenting with DIY natural toothpaste
I haven’t used commercial toothpaste in over 15 years and I haven’t been to the dentist since 2003. I’ve experimented with different recipes and kept the good and tossed the bad. I’ve tried plain baking soda – it worked but was a little soapy tasting, 1/1 baking soda, and Himalayan salt – it hurt my mouth, a bit too abrasive. I’ve tried both of these plain and with added peppermint essential oil – the peppermint oil is nicer. I’ve added coconut oil to make it more like a toothpaste rather than a tooth powder – it was harder to get a uniform amount out of the jar, and it became solid in our cold house. If we lived somewhere warmer, we might choose the coconut oil recipe instead of this one.
Here’s my recipe for remineralizing tooth powder for sensitive teeth. It has been perfected after 15 years of trial and error. It’s going to get the toxins of regular fluoride toothpaste out of your mouth and you’ll even save money — actually a lot of money — by making your own toothpaste at home, and it may actually cure tooth decay as it remineralizes your teeth. So forget paying $4 a tube for toothpaste that’s fluoride-free and SLS free — make your own with these easy to find ingredients.
Note: If you are sensitive to scents use the essential oils in this recipe sparingly. Try 10 drops of the peppermint essential oil instead of 1 tsp. The following recipe is the one I use exactly. But it may not be suitable for you if you are sensitive to essential oils. Feel free to experiment and adapt it to your needs.
If this is for a child under five, skip the peppermint essential oil and add 2 tablespoons of cinnamon powder, from the spice rack, in place of the peppermint essential oil.
DIY Tooth Powder Recipe that:
- Whitens teeth
- Freshens breath
- Remineralizes tooth enamel
- Repairs cavities
- Antibacterial
- Pain-relieving
- Prevents cavities by strengthening tooth enamel, removing bacteria, and changing pH
Cure tooth decay with remineralizing tooth powder for sensitive teeth
DIY Remineralizing Toothpaste (makes 1 cup with no fillers)
Ingredients:
- 3 tbsp. calcium carbonate
- 2 tbsp. bentonite clay
- 1/2 cup baking soda
- 1/4 cup Himalayan salt, whirled in your spice grinder until a fine powder
- 1 tsp. peppermint EO
- 10 drops myrrh EO,
- 10 drops clove EO
Directions:
This tooth powder has no fillers. Every part is essential. Initially buying the ingredients may seem expensive, but it will give you many months of tooth powder for your efforts.
Mix calcium, clay, baking soda, and Himalayan salt in a glass bowl. Whisk it to blend it thoroughly. Add peppermint EO (#ad) (reduce the amount to your personal preference), myrrh EO, and clove EO. Divide between two ½ cup jelly jars. Cap tightly. Store this in an 8 ounce Mason jar.
How to use this remineralizing tooth powder to cure tooth decay:
Package the toothpowder into smaller jars for use. In our family, each family member has their own one-ounce jar of tooth powder. We clean and refill these jars as necessary from an 8-ounce mason jar, pictured at the top of the article. Alternatively, use a spice bottle with a shaker top and sprinkle the tooth powder on the toothbrush. You only need the smallest amount of tooth powder.
Moisten the toothbrush under the tap. Use plain, non-fluoridated water. If your water is fluoridated it’s better to use filtered water to brush your teeth. Fluoride will bind to your teeth preventing remineralization with calcium. Fluoride is also harmful to the thyroid, filling the iodine receptors, and inhibiting iodine uptake.
Shake off any excess water from the toothbrush.
Stick your moistened toothbrush in the jar and take up a tiny amount of the tooth powder on the brush.
Brush teeth as normal. If you are remineralizing your teeth to cure tooth decay, hold the goop in your mouth for 60 seconds while you do something else. This allows your tooth enamel to be in contact with the remineralizing calcium and clay. Spit. Do not swallow. The spit will be grey. That’s the clay removing toxins from your mouth. It’s normal. Rinse your mouth with clear water.
Brush at least twice a day. Floss once a day.
Turn this into remineralizing toothpaste:
If your family is used to toothpaste and would find it easier to use a paste rather than a powder, simply add ½ cup to ¾ cup of coconut oil to the above recipe. It will remain soft and paste-like if your ambient temperature is between 60 and 70 degrees F. Organic virgin coconut oil is known to prevent cavities.
What does each ingredient in the recipe do?
If any of the ingredients in my personal tooth powder recipe bother you or a family member, just leave them out. This is a folk recipe, not a prescription. So that you can make wise decisions for your own family here is what each of the ingredients does in the recipe.
If you are making this recipe for a child you can leave out the essential oils. Or make this herbal tooth powder recipe instead which uses the whole herbs instead of the essential oils.
Calcium carbonate – supports healthy enamel
Bentonite clay trace minerals that support oral health
Baking soda – supports oral health, changes pH, mildly abrasive
Himalayan salt, trace minerals that support oral health,
Peppermint eo – refreshing, traditionally used for oral health
Myrrh eo – refreshing, traditionally used for oral health,
Clove eo – traditionally used for oral health
Cure Tooth Decay
Get the bad stuff out of your mouth. Put the good stuff in your mouth. Make this remineralizing tooth powder today and you’ll be on your way to not just better dental health, but also better overall health. Your teeth are a window to your overall health.
And grab the book, Cure Tooth Decay to learn the full protocol for holistic dental health.
Disclaimer:
Does this replace seeing your dentist? Of course not. This is a book review, not dental advice. As always, consult with your health professional for personalized advice in your own circumstance. And please don’t ingest essential oils, always spit the toothpowder out when you are finished brushing your teeth.
If you are using this toothpowder with children try this DIY herbal tooth powder with less essential oils, or even leave the essential oils out completely.
https://joybileefarm.com/cure-tooth-decay/
FDA has determined that the product contains elevated lead levels and may pose a lead poisoning risk. … FDA laboratories have found elevated levels of lead in “Best Bentonite Clay.” Exposure to lead can cause serious damage to the central nervous system, kidneys, and immune system.
Periodontal disease is an immune-inflammatory disease which consists of connective tissue breakdown, loss of attachment, and alveolar bone loss.In normal physiology, there is an equilibrium maintained between reactive oxygen species (ROS) activity and antioxidant defence capacity. when this equilibrium changes and shifts in favour of ROS, it will result in oxidative stress (OS). Increased levels of acute phase proteins have been associated with gingival inflammation and periodontitis, which reflected the locally stressed environment. it has been well established that in chronic inflammation sites there is over-production of ROS. The human body consists of an array of antioxidant defense mechanisms (non-enzymatic and enzymatic antioxidants) which removes harmful ROS as soon as they are formed and prevent their deleterious effects. Superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT), and glutathione peroxidase are the enzymatic antioxidants, while the nonenzymatic antioxidants include vitamins E and C, and reduced glutathione. C – reactive protein (CRP) is a plasma protein that reflects a measure of the acute phase response to inflammation and is one of the markers of choice in monitoring this response. Changes in peripheral blood cellular and molecular components can be seen in patients with periodontitis, as periodontitis includes inflammatory changes of the periodontal tissues. Ashwagandha is also known as Indian ginseng and winter cherry. It consists of dried roots of Withania Somnifera (Family: Solanaceae).6 The Sanskrit words ashva meaning horse, and gandha meaning smell together form the name Ashwagandha. Ashwagandha possessed marked anti-inflammatory effect against denaturation of protein in vitro. the effect was plausibly due to the alkaloid and withanolide contents of ashwagandha. It is a multipurpose herb, which acts as adaptogenic, antioxidant, anticancer, anxiolytic, antidepressant, cardio protective, thyroid modulating, immunomodulating, antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, neuroprotective, cognitive enhancing and hematopoietic agent.So, this study is carried out to assess SOD & CRP levels with or without Ashwagandha supplementation as an adjunct to scaling and root planing(SRP) in chronic periodontitis(CP) patients.
https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03533972
J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2015 Apr; 7(Suppl 1): S255–S259.doi: 10.4103/0975-7406.155943PMCID: PMC4439686PMID: 26015726
Benefits of Aloe vera in dentistry
S. P. Mangaiyarkarasi,T. Manigandan,1M. Elumalai,2Priyanka K. Cholan, and Roopam Pal Kaur2Author informationArticle notesCopyright and License informationDisclaimerThis article has been cited by other articles in PMC.Go to:
Abstract
Aloe vera (Aloe barbadensis) is a plant that belongs to Liliaceae family. The name Aloe derives from the Arabic word “Alloeh” meaning shining bitter substance while “vera” in Latin means true. It contains various minerals and vitamins. It has got various properties such as immunomodulatory, antiviral and antiinflammatory in nature. A. vera can play a significant role in dentistry in treatment of lichen planus, oral submucous fibrosis, recurrent aphthous stomatitis, alveolar osteitis, periodontitis, etc.KEY WORDS: Aloe vera, dentistry, gel
Aloe vera (Aloe barbadensis) is a succulent plant that belongs to Liliaceae family. The name Aloe derives from the Arabic word “Alloeh” meaning shining bitter substance while “vera” in Latin means true. There are more than 300 species of the aloe-plant, but the Aloe barbadensis species exhibits the best medicinal properties. It grows mainly in the dry areas of Africa, Asia, Europe, and America.[1] Ideal environment to grow this plant is a tropical climate and low rainfall areas.Go to:
Aloe-plant Description
The outermost layer is a hard rind that is 15 cells thick. This rind is very important because this is where the syntheses of all 75 nutrients that are contained within the plant occurs. Below this lawyer is the sap. This is a circulation system that basically moves materials up to the leaves and down to the roots. The sap is very rich in anthraquinones, which are powerful laxatives.
The mucilage layer basically holds the plant together. It also acts as a barrier and keeps the inner gel very sterile. The mucilage layer is very high in polysaccharides including the immunomodulator, acemannan. The gel that is below this, also known as parenchyma, is where the leaf stores all its nutrients. The gel is fileted out at the mucilage layer. This retains all the sterile gel with its nutrients, the mucilage layer with its valuable polysaccharides and just the right amount of anthraquinones from the sap layer. Too much sap in the final product would increase the laxative effect.Go to:
Contents of Aloe vera Gel
Until date, 75 nutrients have been identified in stabilized A. vera gel.
The most important are: Lignin is a cellulose-based substance found in the gel with no known specific medicinal properties although its presence in topical aloe preparations is thought to provide the ability to penetrate the human skin.
Saponins are glycosides which are thought to comprise about 3% of A. vera gel. They are soapy substances, containing antiseptic properties, which are capable of cleansing.Go to:
Minerals
Vitamins
Aloe vera contains many vitamins, including Vitamin A, C, E, B1, B2, B3 (niacin), B6, choline, folic acid, alpha-tocopherol, beta-carotene. A. vera is also one of the few plants that contain vitamin B12.
Vitamins A, C and E are important antioxidant vitamins, essential in the fight against damaging free radicals. All three positively influence the immune system and Vitamin C in particular assists in wound healing. It also makes collagen, keeping bones skin and joints firm and strong. Vitamin A is essential to maintain normal night vision. Vitamin E helps the body utilize oxygen, prevents blood clots, thrombosis, and atherosclerosis. It also improves wound healing and fertility.
Antiinflammatories
In addition to vitamins and minerals, [Table 1] A. vera has ingredients that act as antiinflammatories. Bradykinase is an A. vera enzyme, which reduces skin inflammation. A. vera has 12 anthraquinones, also known as laxatives. It has fatty acids, salicylic acid and hormones called auxins and gibberellins, all of which result in inflammation reversal. These anti-inflammatories work most often by stimulating immune system function and collagen growth, or by blocking the paths of irritants.
Table 1
Role of minerals

Amino acids
The human body requires 20 amino acids for good health to be maintained, and all but eight can be manufactured in the body. The others called essential amino acids need to be taken as food. Together they form the building blocks of proteins from which we manufacture and repair muscles.
Aloe vera provides 19 of the 20 required amino acids and seven of the eight essential ones. The missing amino acid is tryptophan, although Bill Coates, an American pharmacist and Aloe expert, claims it has this one too. The evidence is not conclusive yet, although providing seven out of the eight required is good going.
Enzymes
Aloe vera contains many enzymes, which can be divided into two groups, those that aid digestion and those that are anti-inflammatory. Of the ones that aid digestion some, like amylase, break down starch and sugar, while others, such as lipase, help break down fats.
Sugars
Aloe vera contains two sorts of sugars, monosaccharides, such as glucose and fructose, and long chain sugars called polysaccharides, the main one being a glucomannose often referred to as Acemannan.
Acemannan has been shown to have several actions:
- Immunomodulating properties – it helps to return immunity to normal by boosting the level of antibodies
- Antiviral – particularly against tumor producing viruses, such as feline leukemia
- Reduces secondary infections
- Increase the activity of T-lymphocytes by up to 50%
- Increase the activity of large white blood cells (macrophages) leading to increased wound healing.
Sterols
- The plant sterols are important anti-inflammatory agents. Of the three ones, lupeol, acts as an antiseptic and analgesic agent.
Salicylic acid
- Also found in A. vera, is metabolized in the body to an aspirin-like compound which, together with lupeol, provide some of its painkilling properties.
Applications in Dentistry
Oral lichen planus
Choonhakarn et al.[2] conducted a randomized controlled trial study to check the efficacy of A. vera gel in the treatment of oral lichen planus (OLP). He concluded that A. vera gel is statistically significantly more effective than placebo in inducing clinical and symptomatological improvement of OLP. Therefore, A. vera gel can be considered a safe alternative treatment for patients with OLP.
Oral submucous fibrosis
Sudarshan et al.[3] carried out a preliminary study to compare the efficacy of A. vera with antioxidants in the treatment of oral submucous fibrosis (OSMF). In this study, 20 subjects with OSMF were included. Patients are divided into two groups, Group A received 5 mg of A. vera gel 3 times daily for 3 months, and Group B received antioxidant capsules twice daily for 3 months. He concluded that A. vera group showed a better treatment response (reduced burning sensation and enhanced mouth opening) than the antioxidants group. Hence, it can be applied topically and effective in the treatment of OSMF.
Recurrent aphthous stomatitis
Babaee et al.[4] conducted a double-blind clinical trial to evaluate the topically administered A. vera gel on oral cavity minor aphthous. It was concluded that A. vera 2% oral gel is not only effective in decreasing the patient’s pain score and wound size, but also decreased the aphthous wound healing period.
Radiation-induced oral mucositis
Ahmadi[5] postulated that oral A. vera mouthwash may not only prevent radiation-induced mucositis by its wound healing and antiinflammatory mechanism, but also reduce oral candidiasis of patients undergoing head and neck radiotherapy due to its antifungal and immunomodulatory properties. Hence, A. vera mouthwash is an alternative agent for treating radiation-induced oral mucositis and candidiasis in patients with head and neck cancers.
Gingivitis
Ajmera[6] et al. conducted a study to evaluate the antiinflammatory property of A. vera mouthwash on plaque-induced gingivitis. Forty-five patients who were diagnosed with plaque-induced gingivitis were included in the study. They were divided into three groups with fifteen patients in each group. Group 1 was asked to rinse with 10 ml of A. vera mouthwash twice daily for 3 months. Group 2 were treated with scaling only. Group 3 patients were asked to rinse with A. vera mouthwash and scaling was done. The result suggested reduction in gingival inflammation in all the three groups, but it was more reduction in the A. vera mouthwash and scaling group. Davis et al.[7] tested the anti-inflammatory and wound healing activity of A. vera due to the presence of growth substance mannose-6 phosphate. Hence, it was concluded that A. vera had a significant anti-inflammatory property. Thus, it can be used as an adjunct to mechanical therapy for treating plaque-induced gingivitis. Bovik in 1966[8] used A. vera for the gingivectomy sites and showed that healing was better and fast.
Periodontitis
Bhat[9] et al. evaluated the clinical effects of subgingival application of A. vera gel in periodontal pockets of adult periodontitis patients after mechanical debridement. In this study, 15 subjects were evaluated for clinical parameters such as plaque index, gingival index, probing pocket depth at baseline, followed by scaling and root planning (SRP). Test site comprised of SRP, followed by intra-pocket placement of A. vera gel, which was compared with the control site in which only SRP was done, and clinical parameters were compared between the two sites at 1-month and 3 months from baseline. Results exhibited encouraging findings in clinical parameters of the role of A. vera gel as a drug for local delivery and it was concluded that subgingival administration of A. vera gel results in improvement of periodontal condition. A. vera gel can be used as a local drug delivery system in periodontal pockets.
Tooth gel
Aloe vera tooth gel is effective in controlling bacteria that causes cavities than other commercially available toothpaste. A. vera gel’s ability to kill and remove harmful microorganisms is due to compounds called anthraquinones, which are antiinflammatory. A. vera gel does not contain the abrasives found in most toothpastes, hence less harsh on teeth and it is a better alternative for people with sensitive teeth.
George et al.[10] conducted an in vitro evaluation regarding the antimicrobial activity of an A. vera tooth gel (forever bright tooth gel) and two commercially popular tooth pastes (Colgate, Palmolive) and concluded that A. vera tooth gel was effective than two commercially popular toothpastes in controlling all the organisms that is, Streptococcus mutans, Candida albicans, Lactobacillus acidophilus, Streptococcus mitis, Enterococcus faecalis, Prevotella intermedia, and Peptostreptococcus anaerobius. In addition, the A. vera gel demonstrated superior antibacterial effect against Streptococcus mitis despite the absence of additional fluoride.[11]
Alveolar osteitis
Poor et al.[12] compared the incidence of alveolar osteitis (AO) in patients treated with either clindamycin-soaked Gelfoam or SaliCept Patches. The SaliCept Patch is a freeze-dried pledget that contains Acemannan Hydrogel (Carrington Laboratories, USA) obtained from the clear inner gel of A. vera. The results suggested that the SaliCept Patch significantly reduced the incidence of AO compared with clindamycin-soaked Gelfoam.Go to:
Denture Cleanser and Adhesive
Denture patients with sore ridges and ill-fitting dentures and partials can benefit as fungises and bacterial contamination reduce the inflammatory irritations.[13]
The sticky and viscous nature of acemannan, aprototype acemannan was formulated into a denture adhesive and evaluated for adhesive strength in both wet and dry conditions; the adhesive also was used to evaluate cytotoxicity to human gingival fibroblasts. An optimal formula with a high and relatively stable adhesive bond strength and minimum cytotoxicity was observed.[14]
Dental Implants
Aloe vera can also be used around dental implants to control inflammation from bacteria contamination.[13]
Storage of Gutta Percha Cones
Prakash P Athiban et al.[15] concluded that A. vera is indeed effective as a GP decontaminant and it holds a promising future as a medium for storage of GP cones.Go to:
Root Canal Filling Material in Primary Teeth
Kriplani et al.[16] conducted to evaluate the antimicrobial effectiveness of A. vera with sterile water zinc oxide and eugenol, zinc oxide-eugenol (ZOE) with A. vera, calcium hydroxide and sterile water, calcium hydroxide with sterile water and A. vera, calcium hydroxide and iodoform (metapex) and vaseline (control) against 18 strains of bacteria isolated from infected root canals of primary molar teeth using agar diffusion assay. It was concluded that A. vera + sterile water was found to have superior antimicrobial activity against most of the microorganisms, followed by ZOE + A. vera, calcium hydroxide + A. vera, ZOE, calcium hydroxide, Metapex in the descending order and Vaseline showed no inhibition.
Advantages
Aloe vera can be used as a local drug delivery system because of its various benefits[9]
- Easily available
- Easily applicable with minimal equipments
- Cheap
- No adverse effects.
Contra indications
- Contraindicated in cases of known allergy to plants in the Liliaceae family, pregnancy and breastfeeding[17]
- Oral aloe is not recommended during pregnancy due to theoretical stimulation of uterine contractions, and in breastfeeding mothers, it may sometime cause gastrointestinal distress in the nursing infant.
Side Effects
Topical
It may cause redness, burning and stinging sensation. Allergic reactions are mostly due to anthraquinones, such as aloin and barbaloin. It is best to apply in a small area first to test for possible allergic reaction.[17]
Systemic
Abdominal cramps, diarrhea, red urine, hepatitis, dependency or worsening of constipation. Prolonged use has been reported to increase the risk of colorectal cancer. Laxative effect may cause electrolyte imbalances (low potassium levels).Go to:
Conclusion
In contrast with traditional medicine modalities, A. vera is quite economical; it will markedly reduce both medical cost and invalidity. Dentistry is varying with induction of modern science to practice dentistry. The studies available in literature are short-term studies. Long-term studies are required with larger sample size. More research on its healing properties, antibacterial, antiinflammatory properties and releasing pattern as a local drug delivery system is required.Go to:
Footnotes
Source of Support: Nil
Conflict of Interest: None declared.Go to:
References
1. Surjushe A, Vasani R, Saple DG. Aloe vera: A short review. Indian J Dermatol. 2008;53:163–6. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]2. Choonhakarn C, Busaracome P, Sripanidkulchai B, Sarakarn P. The efficacy of Aloe vera gel in the treatment of oral lichen planus: A randomized controlled trial. Br J Dermatol. 2008;158:573–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]3. Sudarshan R, Annigeri RG, Sree Vijayabala G. Aloe vera in the treatment for oral submucous fibrosis – A preliminary study. J Oral Pathol Med. 2012;41:755–61. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]4. Babaee N, Zabihi E, Mohseni S, Moghadamnia AA. Evaluation of the therapeutic effects of Aloe vera gel on minor recurrent aphthous stomatitis. Dent Res J (Isfahan) 2012;9:381–5. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]5. Ahmadi A. Potential prevention: Aloe vera mouthwash may reduce radiation-induced oral mucositis in head and neck cancer patients. Chin J Integr Med. 2012;18:635–40. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]6. Ajmera N, Chatterjee A, Goyal V. Aloe vera: It’s effect on gingivitis. J Indian Soc Periodontol. 2013;17:435–8. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]7. Davis RH, Donato JJ, Hartman GM, Haas RC. Anti-inflammatory and wound healing activity of a growth substance in Aloe vera. J Am Podiatr Med Assoc. 1994;84:77–81. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]8. Bovik EG. Aloe vera: Panacea or old wives tales? Tex Dent J. 1966;84:13–6. [Google Scholar]9. Bhat G, Kudva P, Dodwad V. Aloe vera: Nature’s soothing healer to periodontal disease. J Indian Soc Periodontol. 2011;15:205–9. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]10. George D, Bhat SS, Antony B. Comparative evaluation of the antimicrobial efficacy of Aloe vera tooth gel and two popular commercial toothpastes: An in vitro study. Gen Dent. 2009;57:238–41. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]11. Academy of General Dentistry. Tooth Gel: Healing Power of Aloe vera Proves Beneficial for Teeth and Gums. ScienceDaily, 28 Jul. 2009. Web. 22 Oct. 2011 [Google Scholar]12. Poor MR, Hall JE, Poor AS. Reduction in the incidence of alveolar osteitis in patients treated with the SaliCept patch, containing Acemannan hydrogel. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2002;60:374–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]13. Moore TE. Aloe vera: Its Potential Use in Wound Healing and Disease Control in Oral Conditions. [Last accessed on 2012 Jun 25]. Available from: www.iasc.org/moore.html .14. Tello CG, Ford P, Iacopino AM. In vitro evaluation of complex carbohydrate denture adhesive formulations. Quintessence Int. 1998;29:585–93. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]15. Athiban PP, Borthakur BJ, Ganesan S, Swathika B. Evaluation of antimicrobial efficacy of Aloe vera and its effectiveness in decontaminating gutta percha cones. J Conserv Dent. 2012;15:246–8. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]16. Kriplani R, Thosar N, Baliga MS, Kulkarni P, Shah N, Yeluri R. Comparative evaluation of antimicrobial efficacy of various root canal filling materials along with aloevera used in primary teeth: A microbiological study. J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2013;37:257–62. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]17. Moore TE. The M and M’s of Aloe vera – Is it for dentistry? J Okla Dent Assoc. 2001;91:30–1. 36. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4439686/
Ratio of n–6 to n–3 fatty acids and bone mineral density in older adults: the Rancho Bernardo Study
Lauren A Weiss, Elizabeth Barrett-Connor, Denise von MühlenThe American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, Volume 81, Issue 4, April 2005, Pages 934–938, https://doi.org/10.1093/ajcn/81.4.934Published: 01 April 2005 Article history
ABSTRACT
Background: Several lines of evidence suggest that n–3 fatty acids reduce the risk of some chronic diseases, including heart disease, diabetes, and cancer. Other research, mainly in animals, also suggests a role in bone health.
Objective: We aimed to investigate the association between the ratio of dietary n–6 to n–3 fatty acids and bone mineral density (BMD) in 1532 community-dwelling men and women aged 45–90 y.
Design: Between 1988 and 1992, dietary data were obtained through self-administered food-frequency questionnaires, and BMD was measured at the hip and spine with the use of dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry. A medical history was obtained and current medication use was validated. Age- and multiple-adjusted linear regression analyses were performed.
Results: There was a significant inverse association between the ratio of dietary linoleic acid to α-linolenic acid and BMD at the hip in 642 men, 564 women not using hormone therapy, and 326 women using hormone therapy; these results were independent of age, body mass index, and lifestyle factors. An increasing ratio of total dietary n–6 to n–3 fatty acids was also significantly and independently associated with lower BMD at the hip in all women and at the spine in women not using hormone therapy.
Conclusions: A higher ratio of n–6 to n–3 fatty acids is associated with lower BMD at the hip in both sexes. These findings suggest that the relative amounts of dietary polyunsaturated fatty acids may play a vital role in preserving skeletal integrity in older age.n–3 Fatty acids, n–6 fatty acids, bone mineral density, Rancho Bernardo, osteoporosis, older adultsTopic:
- omega-6 fatty acids
- hormone replacement therapy
- omega-3 fatty acids
- polyunsaturated fatty acids
- bone mineral density
- diet
- food
- hip region
- hip joint
- endocrine therapy
- older adult
Issue Section: Bone metabolism
INTRODUCTION
Diet plays a vital role in the risk of chronic disease. Two types of polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs), n–6 and n–3, have received attention with regard to health and disease (1). PUFAs are incorporated into cellular membranes in the body, and the composition of fatty acids plays a key role in the behavior of the membrane proteins and cell-cell communication (2). In observational and experimental studies, higher intakes of n–3 fatty acids appear to reduce the risk of coronary artery disease, hypertension, type 2 diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, autoimmune disorders, and cancer (1). Other studies have shown that diets rich in n–6 fatty acids create an inflammatory environment that may increase the risk of disease (3). Recent evidence suggests that a balanced ratio of these 2 types of fatty acids may be necessary for optimal health, normal development, and prevention of chronic disease (3, 4).
Foods rich in n–3 fatty acids include cold-water fish (eg, salmon, albacore tuna, mackerel, and herring), some vegetable oils (eg, soybean and canola), nuts (eg, walnuts), and seeds (eg, flaxseed). Small amounts of n–3 fatty acids are also found in various vegetables, fruit, eggs, poultry, and meat. Foods that contain n–6 fatty acids include other vegetable oils (eg, corn, safflower, sunflower, and sesame), cereal grains, poultry, meat, milk, eggs, and most processed foods. In the usual American diet, n–6 fatty acids are consumed in much larger quantities than are n–3 fatty acids (4).
Four reviews support the thesis that PUFAs influence bone metabolism (2, 5–7). In animals, a higher ratio of n–6 to n–3 fatty acids is associated with detrimental effects on bone health, and a lower ratio is associated with healthy bone properties (5). Results from a small number of experimental studies of the effects of PUFA supplementation on bone in humans are inconclusive (8–10). The results of a recent investigation by MacDonald et al (11) suggest that PUFAs are harmful to bone in women. No large epidemiologic studies have reported the association between ratios of PUFAs and bone mineral density (BMD) in both sexes. We report here the association between the ratio of dietary n–6 to n–3 fatty acids and BMD in community-dwelling older men and women.
SUBJECTS AND METHODS
Study population
Subjects were participants in the Rancho Bernardo Study, a population-based cohort of older, middle to upper-middle class, white residents of a southern California community. Between 1988 and 1992, all surviving community-dwelling members of this cohort were invited to participate in a study of osteoporosis. At this visit, BMD was measured and a food-frequency questionnaire was administered. All participants gave written informed consent. The Institutional Review Board of the University of California, San Diego, approved the protocol.
Assessment of diet
Information on usual dietary intake was obtained from 643 men and 903 postmenopausal women by using the self-administered semiquantitative Harvard-Willett Diet Assessment Questionnaire (12). Self-reported foods were converted into nutrients by using the food-composition database of the US Department of Agriculture. This food-frequency questionnaire was designed to quantify individual fatty acids, essential parent compounds, linoleic acid (LA; 18:2n–6) and α-linolenic acid (ALA; 18:3n–3), and the corresponding long-chain fatty acids, arachidonic acid (20:4n–6), eicosapentaenoic acid (20:5n–3), and docosahexaenoic acid (22:6n–3). PUFA ratios were entered into the model separately: LA:ALA and total n–6 (LA + arachidonic acid):total n–3 (ALA + eicosapentaenoic acid + docosahexaenoic acid). Information on smoking habits, alcohol intake, exercise frequency, reproductive history, and use of vitamins, thiazides, thyroid hormones, steroids, and estrogen was also obtained through standard questionnaires. All pills and prescriptions were brought to the study center for confirmation of current supplement and medication use by a specially trained nurse. Height and weight were measured while the participants wore light clothing and no shoes.
Measurement of bone mineral density
Baseline BMD was measured at the total hip and lumbar spine in g/cm2 by dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (QDR model 1000; Hologic Inc, Waltham, MA). Total hip BMD was obtained by summing the bone mineral content at the femoral neck, intertrochanter, and greater trochanter and dividing by the composite area of the 3 sites. Spine BMD was defined as the average BMD of lumbar vertebrae L1–L4. Instruments were calibrated daily and had measurement precisions of ≤1% for the spine and ≤1.5% for the hip.
Data analysis
Complete dietary variables and BMD measurements from the same visit between 1988 and 1992 were available for 642 men and 890 women. Statistical analyses were performed by using SPSS (SPSS for WINDOWS 11.5; SPSS Inc, Chicago, IL). Data from men and women were analyzed separately, and women were further stratified according to hormone therapy (HT) status, after preliminary analyses showed a significant interaction between PUFAs and HT on BMD. Total calcium intake was log transformed to meet the assumptions of statistical tests. Comparisons between men and women and between women receiving or not receiving HT were Bonferroni-corrected for multiple comparisons.
The association between total hip or lumbar spine BMD and PUFA ratios was assessed by multiple regression analysis. Regression models were adjusted for age and were fully adjusted for standard osteoporosis covariates, including age, body mass index, calcium intake (diet plus supplements), current exercise (≥3 times per week), smoking status (never, past, or current), alcohol intake, use of thiazides, and use of thyroid hormones. Body mass index was used as a covariate instead of energy intake to adjust for the greater caloric intakes of heavier individuals, because actual energy intake from the FFQ is difficult to capture (12). Increasing age, smoking, alcohol intake, and calcium deficiency have previously been found to affect the metabolism of fatty acids and bone (13). The linearity of the relation between PUFAs and bone was tested by including a quadratic term in the adjusted regression models. There was no evidence for nonlinearity; therefore, linear models were used. Total vitamin C intake was negatively associated with a lower PUFA ratio. Regression analyses that included antioxidant intake (total vitamin E, vitamin C, and retinol) were performed separately, with no significant effect on the observed associations. Regression models were also performed excluding users of fish-oil supplements (n = 24), with no change in the results. Supplement users were included in all models. All statistical tests were significant at the P < 0.05 level.
RESULTS
The baseline characteristics of the study population are shown in Table 1. The mean age of the men was 72.9 y and that of the women was 72.5 y. The groups were compared with the use of independent t tests. The men were heavier than the women and had higher BMD. Women using HT were significantly younger, were taller, and had higher BMD at the hip and lumbar spine than did nonusers. The mean dietary intakes of PUFA variables in men and women are shown in Table 2. Men had a significantly higher ratio of n–6 to n–3 fatty acids than did women. Dietary PUFA intake did not vary significantly by hormone use (Table 2).
Descriptive characteristics of the study population1
| Women | |||
| Men (n = 642) | −HT n = 564) | +HT (n = 326) | |
| Characteristic | |||
| Age (y) | 72.9 ± 9.32 | 74.0 ± 9.23 | 69.4 ± 8.6 |
| Height (cm) | 173.9 ± 6.34 | 159.1 ± 6.23 | 160.2 ± 5.8 |
| Weight (kg) | 79.0 ± 11.74 | 62.8 ± 11.6 | 62.8 ± 10.4 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 26.1 ± 3.44 | 24.8 ± 4.1 | 24.5 ± 3.8 |
| Dietary variables | |||
| Total calcium intake (mg/d)5 | 757.1 ± 426.44 | 914.7 ± 535.43 | 1088.6 ± 580.7 |
| Alcohol intake (g/d) | 14.6 ± 17.54 | 8.2 ± 12.4 | 8.9 ± 12.1 |
| Bone mineral density (g/cm2) | |||
| Total hip | 0.944 ± 0.1544 | 0.761 ± 0.1384 | 0.833 ± 0.138 |
| Lumbar spine | 1.064 ± 0.1964 | 0.868 ± 0.1703 | 0.948 ± 0.178 |
| Categorical variables (%) | |||
| Smoking history | |||
| Never | 31.7 | 53.1 | 43.3 |
| Past | 59.6 | 37.6 | 45.5 |
| Current | 8.8 | 9.3 | 11.1 |
| Physical activity (≥3 times/wk) | 74.9 | 63.1 | 73.0 |
| Thiazide medication use | 7.2 | 7.9 | 8.7 |
| Thyroid medication use | 6.1 | 24.0 | 31.6 |
| Fish-oil supplement use | 1.9 | 1.1 | 1.8 |
1
−HT, women not currently using hormone therapy; +HT, women currently using hormone therapy. Participant numbers may vary slightly at different bone sites because of problems of positioning, hip replacement, and participant fatigue.2
x̄ ± SD (all such values).3
Significantly different from HT users, P < 0.05 (independent t test and Bonferroni correction).4
Significantly different from all women, P < 0.05 (independent t test and Bonferroni correction).5
Diet plus supplements.Open in new tab
Dietary intake of polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA) in men and women1
| Women | |||
| PUFA variable | Men (n = 642) | −HT (n = 564) | +HT (n = 326) |
| Total PUFA (g/d) | 12.1 ± 5.2 | 11.7 ± 5.1 | 12.1 ± 5.2 |
| ALA (g/d) | 1.1 ± 0.5 | 1.1 ± 0.5 | 1.1 ± 0.5 |
| EPA + DHA (g/d) | 0.2 ± 0.2 | 0.2 ± 0.3 | 0.2 ± 0.2 |
| Total n–3 fatty acids (g/d) | 1.3 ± 0.5 | 1.3 ± 0.6 | 1.4 ± 0.6 |
| LA (g/d) | 10.5 ± 4.7 | 10.1 ± 4.5 | 10.5 ± 4.6 |
| AA (g/d) | 0.1 ± 0.1 | 0.1 ± 0.1 | 0.1 ± 0.1 |
| Total n–6 fatty acids (g/d) | 10.7 ± 4.7 | 10.2 ± 4.5 | 10.6 ± 4.6 |
| LA:ALA | 10.0 ± 2.62 | 9.4 ± 2.3 | 9.3 ± 2.0 |
| Total n–6:total n–3 fatty acids | 8.4 ± 2.52 | 7.9 ± 2.2 | 7.8 ± 1.9 |
1
All values are x̄ ± SD. −HT; women not currently using hormone therapy; +HT, women currently using hormone therapy; ALA, α-linolenic acid (18:3n–3); EPA, eicosapentaenoic acid (20:5 n–3); DHA, docosahexaenoic acid (22:6 n–3); total n–3, ALA + EPA + DHA; LA, linoleic acid (18:2n–6); AA, arachidonic acid (20:4n − 6); total n − 6, LA+AA.2
Significantly different from all women, P < 0.05 (independent t test).Open in new tab
Both the age-adjusted and the fully adjusted linear regression analyses for PUFA ratios and BMD at the hip and lumbar spine are shown in Table 3. In the age-adjusted models, the ratios were significantly and negatively associated with hip BMD in all groups and with lumbar spine BMD in women not using HT only (P < 0.05). After adjustment for all covariates, an increasing ratio of LA:ALA remained significantly associated with lower BMD at the hip in men (P < 0.05), women using HT (P < 0.05), and women not using HT (P = 0.05); in this last group, this ratio was also inversely associated with BMD at the spine (P < 0.05). In women with and without HT, the total ratio of n–6 to n–3 fatty acids was inversely associated with hip BMD and was additionally associated with BMD at the spine in women not using HT (P < 0.05).
Linear regression analysis of the ratio of n–6 to n–3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and bone mineral density in men and women1
| Total hip | Lumbar spine | |||
| Variable | β (95% CI) | P | β (95% CI) | P |
| Men (n = 642) | ||||
| LA:ALA | ||||
| Age-adjusted | −0.007 (−0.011, −0.003) | < 0.01 | −0.003 (−0.008, 0.003) | 0.38 |
| Full model2 | −0.005 (−0.009, −0.001) | 0.02 | 0.001 (−0.005, 0.006) | 0.96 |
| Total n–6:total n–3 fatty acids | ||||
| Age-adjusted | −0.006 (−0.010, 0.001) | 0.02 | −0.003 (−0.010, 0.003) | 0.31 |
| Full model | −0.003 (−0.007, 0.001) | 0.16 | −0.001 (−0.006, 0.005) | 0.86 |
| Women | ||||
| −HT (n = 564) | ||||
| LA:ALA | ||||
| Age-adjusted | −0.005 (−0.010, −0.001) | 0.02 | −0.007 (−0.013, −0.001) | 0.02 |
| Full model | −0.004 (−0.008, 0.001) | 0.05 | −0.006 (−0.012, −0.001) | 0.04 |
| Total n–6:total n–3 fatty acids | ||||
| Age-adjusted | −0.008 (−0.012, −0.003) | < 0.01 | −0.009 (−0.015, −0.003) | < 0.01 |
| Full model | −0.006 (−0.010, −0.001) | 0.01 | −0.007 (−0.013, −0.001) | 0.02 |
| +HT (n = 326) | ||||
| LA:ALA | ||||
| Age-adjusted | −0.010 (−0.017, −0.003) | < 0.01 | −0.006 (−0.016, 0.004) | 0.21 |
| Full model | −0.008 (−0.014, −0.001) | 0.03 | −0.004 (−0.013, 0.006) | 0.43 |
| Total n–6:total n–3 Fatty acids | ||||
| Age-adjusted | −0.010 (−0.017, −0.003) | < 0.01 | −0.004 (−0.014, 0.006) | 0.46 |
| Full model | −0.008 (−0.015, −0.001) | 0.03 | −0.002 (−0.013, 0.008) | 0.63 |
1
Participant numbers may vary slightly at different bone sites because of problems of positioning, hip replacement, and participant fatigue. −HT, women not currently using hormone therapy; +HT, women currently using hormone therapy; LA, linoleic acid; ALA, α-linolenic acid; total n–6, LA + arachidonic acid; total n–3, ALA + eicosapentaenoic acid + docosahexaenoic acid. β is the unstandardized regression coefficient.2
Adjusted for age, BMI, total calcium intake, exercise, smoking, alcohol intake, use of thiazides, and use of thyroid hormones.Open in new tab
DISCUSSION
In this cohort, an increasing ratio of dietary n–6 to n–3 fatty acids was significantly associated with lower BMD. The most consistent association was seen with the ratio of LA, the predominant n–6 fatty acid, to ALA, the predominant n–3 fatty acid, where an increasing ratio of n–6 to n–3 fatty acids was associated with lower BMD at the hip in men and in women regardless of HT status and at the lumbar spine in women not using HT. In addition, the ratio of total n–6 to n–3 fatty acids was inversely associated with BMD at the hip in both groups of women and at the lumbar spine in women not using HT. These associations were independent of other bone-related variables, such as age, lifestyle, and medication use.
The average intake of total n–3 fatty acids by the men and women in the current study was 1.3 g/d. This is slightly lower than the average US intake of ≈1.6 g/d. The average ratio of total n–6 to n–3 fatty acids in the present study was 8.4 in men and 7.9 in women. This is also lower than the average ratio of all n–6 to n–3 PUFAs of ≈9.8:1 (4). Although the “optimal” ratio of n–6 to n–3 fatty acids is unknown, Paleolithic nutrition studies show that hunter-gatherer populations consumed nearly equal amounts of n–6 and n–3 fatty acids (14). Modern agricultural practices and changes in food processing have been blamed for the increased consumption of n–6 fatty acids through increased intake of corn, sunflower, and sesame oils. At the same time, the intake of n–3 fatty acids decreased as the result of reduced consumption of cold-water fish, changes in animal production practices, and loss of cereal germ in processed grains. Overall, these changes led to an increase in the ratio of n–6 to n–3 fatty acids (4, 14).
Only a few studies have reported the association between PUFAs and bone density in humans, with inconsistent findings. In a cross-sectional study, Terano (15) compared the BMD of 132 men and women aged 38–80 y living in a fishing village in Japan with that of 332 age-matched urban control subjects and found that the women living in the fishing village, who consumed larger amounts of n–3 fatty acids, had greater radial BMD than did the controls. In a recent investigation, MacDonald et al (11) found that PUFA intake was associated with bone loss at the femoral neck in 891 women who consumed low amounts of calcium. In a randomized clinical trial that included 85 pre- and postmenopausal women, Bassey et al (10) found no significant difference in the effect on bone or bone biomarkers of supplementation with n–6 to n–3 fatty acids in a ratio of ≈10:1 plus calcium versus calcium alone. In an 18-mo clinical trial in 65 postmenopausal women with low bone mass, Kruger et al (9) found that supplementation with a 10:1 ratio of n–6 to n–3 fatty acids preserved BMD at the spine and increased BMD at the femoral neck, whereas the placebo group experienced bone loss. In 21 of these women, continued supplementation for another 18 mo resulted in significant BMD increases at the lumbar spine and further increases at the femoral neck. Van Papendorp et al (8) found that supplementation with both fish oil and a mixture of fish oil plus evening primrose oil in a ratio of ≈10:1 for 16 wk increased bone formation and calcium absorption in 40 osteoporotic women. In a clinical trial in 33 postmenopausal women with a mean age of 58.2 y, Terano (15) found that n–3 fatty acid supplementation increased bone density and bone formation compared with placebo.
In many animal studies, n–3 fatty acids or a low ratio of n–6 to n–3 fatty acids has shown a positive influence on bone (7). Studies have shown that differing ratios of n–6 to n–3 fatty acids alter the synthesis of prostaglandin and insulin-like growth factor I (2), that high levels of n–6 fatty acids increase prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) production (16, 17), and that supplementation with n–3 fatty acids or lower ratios of n–6 to n–3 fatty acids increase calcium transport (18) and calcium absorption (13). PUFA-deficient rats were shown to develop severe osteoporosis (13), and a recent study found that n–3 fatty acid repletion re-establishes the ratio of n–6 to n–3 fatty acids in bone compartments and reverses the compromised bone structural properties in n–3–deficient rats (19). In contrast, 3 animal studies showed adverse effects or no effect of n–3 fatty acids or a low ratio of n–6 to n–3 fatty acids on bone in growing rats (20), pigs (21), and rabbits (22).
There are a plethora of biologically plausible pathways whereby PUFAs may regulate the factors involved in bone metabolism, such as prostaglandins, cytokines, insulin-like growth factor I, and calcium. Reviewers have suggested that one or a combination of these factors may have an effect on bone (5, 6, 13, 23). For example, PGE2, the major prostaglandin involved in bone metabolism, is synthesized from n–6 fatty acids, whereas n–3 fatty acids inhibit its production (1, 13). Normal or moderate concentrations of PGE2 support bone formation, whereas greater quantities promote bone resorption (5). Fatty acids are also involved in calcium metabolism. Higher n–3 fatty acid intake enhances calcium absorption, decreases calcium loss, and increases bone calcium (13, 20,23). In addition, the inhibition of cytokine production has been implicated as a potential mechanism of the favorable effects of fatty acids on bone, with higher intakes of n–3 fatty acids inhibiting the synthesis of proinflammatory cytokines, such as interleukin 6, interleukin 1, and tumor necrosis factor α (24, 25). Kettler (6) suggested that bone loss is mediated by cytokines, and n–3 fatty acid supplementation in animals and humans reduces cytokine synthesis and increases calcium absorption.
In the present study, there was a significant interaction between hormone use and the ratio of dietary n–6 to n–3 fatty acids on BMD at the hip and spine. Fatty acids could potentiate the effect of HT on bone through increasing calcium absorption (26). A study in ovariectomized rats showed that estrogen plus a combination of n–6 and n–3 fatty acids increases bone formation and decreases bone resorption, whereas estrogen alone only increases bone formation (27).
To our knowledge, this is the first large epidemiologic investigation of the association between PUFAs and BMD in older, community-dwelling white men and women who had a wide range of dietary n–6 and n–3 fatty acid intake. The latest longitudinal study by Macdonald et al (11) investigated the association between total PUFAs and bone in women only and did not differentiate between various types of PUFAs (eg, n–3 versus n–6). Previous experimental studies had limited ability to assess a range of fatty acid intakes because of study design and small sample sizes.
Although the food-frequency questionnaire is useful for ranking individuals on the basis of their annual dietary intakes, it is semiquantitative and subject to recall bias, particularly for seasonal foods (12, 28). Nevertheless, the reliability of the food-frequency questionnaire for the dietary assessment of PUFAs was validated previously by studies showing a good agreement between fatty acid intake estimated from a food-frequency questionnaire and biological markers of intake (29, 30). In another study, fat biopsies in postmenopausal women paralleled intake of dietary PUFAs from the semiquantitative Harvard-Willett Diet Assessment Questionnaire (31) used in the present study.
Observational studies of diet-disease associations cannot address lifetime dietary intake or dietary change and cannot completely exclude confounding if higher intakes of n–3 fatty acids or a low ratio of n–6 to n–3 fatty acids covaries with a more healthy diet (eg, more calcium) or another healthy lifestyle pattern (eg, more exercise). In this study, calcium intake and physical activity were higher in individuals with more favorable PUFA ratios, but adjustment for these differences did not materially change the associations.
In conclusion, PUFAs in the diet appear to be a modifiable risk factor that may be related to the development of osteoporosis (32). Experts suggest that 2 concomitant changes need to occur in fatty acid consumption to reduce the risk of chronic disease: an increased intake of n–3–rich foods and a decrease in the consumption of animal and vegetable foods that contain large amounts of n–6 fatty acids (3, 4). Randomized clinical trials are needed to test whether fatty acids have an effect on bone. If fatty acid supplementation is effective, it could offer a safe, relatively inexpensive approach to the prevention of osteoporosis.
LAW, EB-C, and DvM were responsible for the study concept and design, acquisition of data, analysis and interpretation of data, critical revision of the manuscript for important intellectual content, and statistical analysis. LAW was responsible for drafting the manuscript. EB-C obtained the funding for the study. None of the authors had any conflicts of interest in connection with this study.
FOOTNOTES
2
Supported by research grants from the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (DK 31801) and the National Institute on Aging (AG 07181).
REFERENCES
1.Simopoulos AP. Essential fatty acids in health and chronic disease. Am J Clin Nutr 1999;70 (suppl):560S–9S.
2.Albertazzi P, Coupland K. Polyunsaturated fatty acids. Is there a role in postmenopausal osteoporosis prevention? Maturitas 2002;42:13–22.
3.Simopoulos AP. The importance of the ratio of omega-6/omega-3 essential fatty acids. Biomed Pharmacother 2002;56:365–79.
4.Kris-Etherton PM, Taylor DS, Yu-Poth S, et al. Polyunsaturated fatty acids in the food chain in the United States. Am J Clin Nutr 2000;71 (suppl):179S–88S.
5.Watkins BA, Li Y, Lippman HE, Seifert MF. Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and skeletal health. Exp Biol Med (Maywood) 2001;226:485–97.
6.Kettler DB. Can manipulation of the ratios of essential fatty acids slow the rapid rate of postmenopausal bone loss? Altern Med Rev 2001;6:61–77.
7.Watkins BA, Li Y, Lippman HE, Feng S. Modulatory effect of omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids on osteoblast function and bone metabolism. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids 2003;68:387–98.
8.Van Papendorp DH, Coezter H, Kruger MC. Biochemical profile of osteoporotic patients on essential fatty acid supplementation. Nutr Res 1995;15:325–34.
9.Kruger MC, Coetzer H, de Winter R, Gericke G, van Papendorp DH. Calcium, gamma-linolenic acid and eicosapentaenoic acid supplementation in senile osteoporosis. Aging (Milano) 1998;10:385–94.
10.Bassey EJ, Littlewood JJ, Rothwell MC, Pye DW. Lack of effect of supplementation with essential fatty acids on bone mineral density in healthy pre- and postmenopausal women: two randomized controlled trials of Efacal v. calcium alone. Br J Nutr 2000;83:629–35.
11.Macdonald HM, New SA, Golden MH, Campbell MK, Reid DM. Nutritional associations with bone loss during the menopausal transition: evidence of a beneficial effect of calcium, alcohol, and fruit and vegetable nutrients and of a detrimental effect of fatty acids. Am J Clin Nutr 2004;79:155–65.
12.Willett WC, Sampson L, Stampfer MJ, et al. Reproducibility and validity of a semiquantitative food frequency questionnaire. Am J Epidemiol 1985;122:51–65.
13.Kruger MC, Horrobin DF. Calcium metabolism, osteoporosis and essential fatty acids: a review. Prog Lipid Res 1997;36:131–51.
14.Simopoulos AP. Evolutionary aspects of omega-3 fatty acids in the food supply. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids 1999;60:421–9.
15.Terano T. Effect of omega 3 polyunsaturated fatty acid ingestion on bone metabolism and osteoporosis. World Rev Nutr Diet 2001;88:141–7.
16.Watkins BA, Shen CL, Allen KG, Seifert MF. Dietary (n–3) and (n–6) polyunsaturates and acetylsalicylic acid alter ex vivo PGE2 biosynthesis, tissue IGF-I levels, and bone morphometry in chicks. J Bone Miner Res 1996;11:1321–32.
17.Marshall LA, Johnston PV. Modulation of tissue prostaglandin synthesizing capacity by increased ratios of dietary alpha-linolenic acid to linoleic acid. Lipids 1982;17:905–13.
18.Coetzer H, Claassen N, van Papendorp DH, Kruger MC. Calcium transport by isolated brush border and basolateral membrane vesicles: role of essential fatty acid supplementation. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids 1994;50:257–66.
19.Reinwald S, Li Y, Moriguchi T, Salem NJr., Watkins BA. Repletion with (n–3) fatty acids reverses bone structural deficits in (n–3)-deficient rats. J Nutr 2004;134:388–94.
20.Claassen N, Coetzer H, Steinmann CM, Kruger MC. The effect of different n–6/n–3 essential fatty acid ratios on calcium balance and bone in rats. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids 1995;53:13–9.
21.Judex S, Wohl GR, Wolff RB, Leng W, Gillis AM, Zernicke RF. Dietary fish oil supplementation adversely affects cortical bone morphology and biomechanics in growing rabbits. Calcif Tissue Int 2000;66:443–8.
22.Weiler HA, Fitzpatrick-Wong SC. Modulation of essential (n–6):(n–3) fatty acid ratios alters fatty acid status but not bone mass in piglets. J Nutr 2002;132:2667–72.
23.Das UN. Essential fatty acids and osteoporosis. Nutrition 2000;16:386–90.
24.Endres S, Ghorbani R, Kelley VE, et al. The effect of dietary supplementation with n–3 polyunsaturated fatty acids on the synthesis of interleukin-1 and tumor necrosis factor by mononuclear cells. N Engl J Med 1989;320:265–71.
25.Meydani SN, Endres S, Woods MM, et al. Oral (n–3) fatty acid supplementation suppresses cytokine production and lymphocyte proliferation: comparison between young and older women. J Nutr 1991;121:547–55.
26.McKane WR, Khosla S, Burritt MF, et al. Mechanism of renal calcium conservation with estrogen replacement therapy in women in early postmenopause–a clinical research center study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1995;80:3458–64.
27.Schlemmer CK, Coetzer H, Claassen N, Kruger MC. Oestrogen and essential fatty acid supplementation corrects bone loss due to ovariectomy in the female Sprague Dawley rat. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids 1999;61:381–90.
28.Subar AF, Frey CM, Harlan LC, Kahle L. Differences in reported food frequency by season of questionnaire administration: the 1987 National Health Interview Survey. Epidemiology 1994;5:226–33.
29.Hunter DJ, Rimm EB, Sacks FM, et al. Comparison of measures of fatty acid intake by subcutaneous fat aspirate, food frequency questionnaire, and diet records in a free-living population of US men. Am J Epidemiol 1992;135:418–27.
30.Garland M, Sacks FM, Colditz GA, et al. The relation between dietary intake and adipose tissue composition of selected fatty acids in US women. Am J Clin Nutr 1998;67:25–30.
31.London SJ, Sacks FM, Caesar J, Stampfer MJ, Siguel E, Willett WC. Fatty acid composition of subcutaneous adipose tissue and diet in postmenopausal US women. Am J Clin Nutr 1991;54:340–5.
32.Ilich JZ, Kerstetter JE. Nutrition in bone health revisited: a story beyond calcium. J Am Coll Nutr 2000;19:715–37.
Google ScholarCrossrefPubMed © 2005 American Society for Clinical Nutrition
Email alerts
Article activity alertAdvance article alertsNew issue alertReceive exclusive offers and updates from Oxford Academic
Related articles
- Protective effects of fish intake and interactive effects of long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acid intakes on hip bone mineral density in older adults: the Framingham Osteoporosis StudyFarina et al., The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 2011
- Lean Body Mass, Not Estrogen or Progesterone, Predicts Peak Bone Mineral Density in Premenopausal WomenLee-Jane W. Lu et al., The Journal of Nutrition, 2008
- n−3 Fatty acids are positively associated with peak bone mineral density and bone accrual in healthy men: the NO2 StudyHögström et al., The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 2007
- Osteoporosis: association of recent fractures with quantitative US findings.C C Glüer et al., Radiology, 1996
- Male OsteoporosisSeena Zierler-Brown et al., US Pharmacist, 2007
- Bone disease in monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance: results from a screened population-based studySigrun Thorsteinsdottir et al., Blood Advances, 2017
Powered byI consent to the use of Google Analytics and related cookies across the TrendMD network (widget, website, blog). Learn moreYes No
Dose-response effects of fish-oil supplementation in healthy volunteersDietary fatty acids and cancerAlpha-linolenic acid deficiency in patients on long-term gastric-tube feeding: estimation of linolenic acid and long-chain unsaturated n-3 fatty acid requirement in manOmega-6 fatty acids and risk of heart failure in the Physicians’ Health Study
Related articles in
Related articles in PubMed
Dairy foods, calcium, and risk of breast cancer overall and for subtypes defined by estrogen receptor status: a pooled analysis of 21 cohort studies.Post-diagnostic reliance on plant-compared with animal-based foods and all-cause mortality in omnivorous long-term colorectal cancer survivors.Genetic variants modify the associations of concentrations of methylmalonic acid, vitamin B-12, vitamin B-6, and folate with bone mineral density.Association of food insecurity with dietary intakes and nutritional biomarkers among US children, National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) 2011-2016.
Citing articles via
Web of Science (170)Google ScholarCrossref
https://academic.oup.com/ajcn/article/81/4/934/4649143
The takeaway
Aloe vera has powerful properties. It works as an antibacterial and anti-inflammatory agent.
Active components with its properties: Aloe vera contains 75 potentially active constituents: vitamins, enzymes, minerals, sugars, lignin, saponins, salicylic acids and amino acids.4–6
- Vitamins: It contains vitamins A (beta-carotene), C and E, which are antioxidants. It also contains vitamin B12, folic acid, and choline. Antioxidant neutralizes free radicals.
- Enzymes: It contains 8 enzymes: aliiase, alkaline phosphatase, amylase, bradykinase, carboxypeptidase, catalase, cellulase, lipase, and peroxidase. Bradykinase helps to reduce excessive inflammation when applied to the skin topically, while others help in the breakdown of sugars and fats.
- Minerals: It provides calcium, chromium, copper, selenium, magnesium, manganese, potassium, sodium and zinc. They are essential for the proper functioning of various enzyme systems in different metabolic pathways and few are antioxidants.
- Sugars: It provides monosaccharides (glucose and fructose) and polysaccharides: (glucomannans/polymannose). These are derived from the mucilage layer of the plant and are known as mucopolysaccharides. The most prominent monosaccharide is mannose-6-phosphate, and the most common polysaccharides are called glucomannans [beta-(1,4)-acetylated mannan]. Acemannan, a prominent glucomannan has also been found. Recently, a glycoprotein with antiallergic properties, called alprogen and novel anti-inflammatory compound, C-glucosyl chromone, has been isolated from Aloe vera gel.7,8
- Anthraquinones: It provides 12 anthraquinones, which are phenolic compounds traditionally known as laxatives. Aloin and emodin act as analgesics, antibacterials and antivirals.
- Fatty acids: It provides 4 plant steroids; cholesterol, campesterol, β-sisosterol and lupeol. All these have anti-inflammatory action and lupeol also possesses antiseptic and analgesic properties.
- Hormones: Auxins and gibberellins that help in wound healing and have anti-inflammatory action.
- Others: It provides 20 of the 22 human required amino acids and 7 of the 8 essential amino acids. It also contains salicylic acid that possesses anti-inflammatory and antibacterial properties. Lignin, an inert substance, when included in topical preparations, enhances penetrative effect of the other ingredients into the skin. Saponins that are the soapy substances form about 3% of the gel and have cleansing and antiseptic properties.
Mechanism of actions
- Healing properties: Glucomannan, a mannose-rich polysaccharide, and gibberellin, a growth hormone, interacts with growth factor receptors on the fibroblast, thereby stimulating its activity and proliferation, which in turn significantly increases collagen synthesis after topical and oral Aloe vera.9 Aloe gel not only increased collagen content of the wound but also changed collagen composition (more type III) and increased the degree of collagen cross linking. Due to this, it accelerated wound contraction and increased the breaking strength of resulting scar tissue.10 An increased synthesis of hyaluronic acid and dermatan sulfate in the granulation tissue of a healing wound following oral or topical treatment has been reported.11
- Effects on skin exposure to UV and gamma radiation: Aloe vera gel has been reported to have a protective effect against radiation damage to the skin.12,13 Exact role is not known, but following the administration of aloe vera gel, an antioxidant protein, metallothionein, is generated in the skin, which scavenges hydroxyl radicals and prevents suppression of superoxide dismutase and glutathione peroxidase in the skin. It reduces the production and release of skin keratinocyte-derived immunosuppressive cytokines such as interleukin-10 (IL-10) and hence prevents UV-induced suppression of delayed type hypersensitivity.14
- Anti-inflammatory action: Aloe vera inhibits the cyclooxygenase pathway and reduces prostaglandin E2 production from arachidonic acid. Recently, the novel anti-inflammatory compound called C-glucosyl chromone was isolated from gel extracts.8
- Effects on the immune system: Alprogen inhibit calcium influx into mast cells, thereby inhibiting the antigen-antibody-mediated release of histamine and leukotriene from mast cells.7 In a study on mice that had previously been implanted with murine sarcoma cells, acemannan stimulates the synthesis and release of interleukin-1 (IL-1) and tumor necrosis factor from macrophages in mice, which in turn initiated an immune attack that resulted in necrosis and regression of the cancerous cells.15 Several low-molecular-weight compounds are also capable of inhibiting the release of reactive oxygen free radicals from activated human neutrophils.16
- Laxative effects: Anthraquinones present in latex are a potent laxative. It increases intestinal water content, stimulates mucus secretion and increases intestinal peristalsis.17
- Antiviral and antitumor activity: These actions may be due to indirect or direct effects. Indirect effect is due to stimulation of the immune system and direct effect is due to anthraquinones. The anthraquinone aloin inactivates various enveloped viruses such as herpes simplex, varicella zoster and influenza.18 In recent studies, a polysaccharide fraction has shown to inhibit the binding of benzopyrene to primary rat hepatocytes, thereby preventing the formation of potentially cancer-initiating benzopyrene-DNA adducts. An induction of glutathione S-transferase and an inhibition of the tumor-promoting effects of phorbol myristic acetate has also been reported which suggest a possible benefit of using aloe gel in cancer chemoprevention.19,20
- Moisturizing and anti-aging effect: Mucopolysaccharides help in binding moisture into the skin. Aloe stimulates fibroblast which produces the collagen and elastin fibers making the skin more elastic and less wrinkled. It also has cohesive effects on the superficial flaking epidermal cells by sticking them together, which softens the skin. The amino acids also soften hardened skin cells and zinc acts as an astringent to tighten pores. Its moisturizing effects has also been studied in treatment of dry skin associated with occupational exposure where aloe vera gel gloves improved the skin integrity, decreases appearance of fine wrinkle and decreases erythema.21 It also has anti-acne effect.
- Antiseptic effect: Aloe vera contains 6 antiseptic agents: Lupeol, salicylic acid, urea nitrogen, cinnamonic acid, phenols and sulfur. They all have inhibitory action on fungi, bacteria and viruses.
Clinical uses: The clinical use of aloe vera is supported mostly by anecdotal data. Though most of these uses are interesting, controlled trials are essential to determine its effectiveness in all the following diseases.22,23
A. Uses based on scientific evidence: These uses have been tested in humans or animals. Safety and effectiveness have not always been proven.
Conditions: Seborrheic dermatitis,24 psoriasis vulgaris,25,26 genital herpes,27,28 skin burns,5,29 diabetes (type 2),30 HIV infection,31 cancer prevention,32,33 ulcerative colitis34 wound healing (results of aloe on wound healing are mixed with some studies reporting positive results35 and others showing no benefit36 or potential worsening37,38 ), pressure ulcers,36 mucositis,39 radiation dermatitis,40 acne vulgaris,41 lichen planus,42 frostbite,43 aphthous stomatitis,44 and constipation.17
B. Uses based on tradition or theory: The below uses are based on tradition or scientific theories. They often have not been thoroughly tested in humans, and safety and effectiveness have not always been proven.
Conditions: Alopecia, bacterial and fungal skin infections, chronic leg wounds, parasitic infections, systemic lupus erythematosus, arthritis and tic douloureux.
Side effects
Topical: It may cause redness, burning, stinging sensation and rarely generalized dermatitis in sensitive individuals. Allergic reactions are mostly due to anthraquinones, such as aloin and barbaloin. It is best to apply it to a small area first to test for possible allergic reaction.
Oral: Abdominal cramps, diarrhea, red urine, hepatitis, dependency or worsening of constipation. Prolonged use has been reported to increase the risk of colorectal cancer. Laxative effect may cause electrolyte imbalances (low potassium levels).
Contraindication: Contraindicated in cases of known allergy to plants in the Liliaceae family.
Sources
https://www.healthline.com/health/aloe-vera-for-gums#takeaway
FoodNDTV Food DeskUpdated: November 15, 2018 5:56 pm IST

Our elders often plucked mint leaves after having food; it was a common belief that these leaves act as mouth-fresheners and digestive aid. Turns out, mint leaves may also keep your oral health in check. The essential oil present in peppermint is most effective in killing what are called anaerobic bacteria, which tend to live in low-oxygen environment. These bacteria tend to cause gum diseases and other oral health problems. Menthol, a compound that is present in peppermint, causes the cooling sensation, which is similar to that of brushing your teeth with toothpaste or using a mouthwash. So, here’s everything you need to know about how peppermint makes for an amazing aid for your oral health.
Peppermint for oral health | Mint for teeth and gums
- Its natural anti-inflammatory and anti-bacterial properties help curb the growth of bacteria in the mouth, further preventing infections.
- It is an amazing treatment for post tooth-extraction. It helps prevent the swelling in connective tissues and reduces bleeding too.
- The presence of potassium, magnesium, calcium, iron and phosphorus in mint leaves is essential for maintenance and formation of bone-density in tooth and jaw.
- The vitamins and minerals work together to fortify enamel and ensure strengthening teeth and gums.
- It acts as an alkaline food that contradicts the effects of the acidic environment that is responsible for gum diseases and tooth decay.
- Chewing on mint leaves can help keep your mouth moist and fresh. It stimulates the production of saliva and the enzymes that are important for digestion.
How to use peppermint for oral health?
Chewing on fresh mint leaves is considered a great way to keep your oral health in check. Another way is to make your own mouthwash using peppermint essential oil and baking soda mixed in water. Drinking peppermint tea after meals is an efficient way to kill bacteria in the mouth and stimulate the digestion process.
10 Herbs For Healthy Teeth & Gums
If you aren’t growing your own herbs, any of these may be found at either Mountain Rose Herbs or Bulk Herb Store.
Finally, to make any of these herbs into a tincture, check out How To Make An Herbal Tincture (aka Herbal Extract) or if you’d rather not use alcohol, How To Make A Non-Alcoholic Herbal Extract {Herbal Glycerite}.
Herb #1 — Myrrh
It also heals and tightens gums, cures bleeding gums, and fights bacteria that would otherwise cause gum disease and tooth decay. I use it daily as a preventative.
Herb #2 — Neem
Modern research attests its ability to reduce plaque, prevent cavities and gum disease, and freshen breath. You can easily add powdered neem to your usual toothpaste.
And remember, the bark is more potent than the leaf.
Herb #3 — Echinacea
Herb #4 — Goldenseal
This herb is especially helpful for healing gums. It’s antibiotic, antiviral, and anti-inflammatory.
Herb #5 — Oregon Grape Root
Antimicrobial and an astringent, Oregon grape root also soothes and tightens swollen gums.
Herb #6 — Propolis
Herb #7 — Plantain
You probably already have this herb growing in your yard! It heals wounds and draws out infections (for more information, check out this post).
Herb #8 — Sage
Herb #9 — White Oak Bark
This herb soothes and reduces swelling.
Herb #10 — Peppermint

Make Your Own Natural Mouthwash!
You can combine any of your favorite herbal tinctures into a natural, healing mouthwash! If you don’t want to make your own tinctures (see instructions here and here), you can easily buy some ready-made, too.
This is my favorite blend of healing herbal tinctures:
Sources:
12 Proven Health Benefits of Ashwagandha
We include products we think are useful for our readers. If you buy through links on this page, we may earn a small commission. Here’s our process.
Ashwagandha is an ancient medicinal herb.
It’s classified as an adaptogen, meaning that it can help your body manage stress.
Ashwagandha also provides numerous other benefits for your body and brain.
For example, it can boost brain function, lower blood sugar and cortisol levels, and help fight symptoms of anxiety and depression.
Here are 12 benefits of ashwagandha that are supported by science.
1. Is an ancient medicinal herb
Ashwagandha is one of the most important herbs in Ayurveda, a form of alternative medicine based on Indian principles of natural healing.
It has been used for over 3,000 years to relieve stress, increase energy levels, and improve concentration (1Trusted Source).
Ashwagandha is Sanskrit for smell of the horse, which refers to both its unique smell and ability to increase strength.
Its botanical name is Withania somnifera, and it’s also known by several other names, including Indian ginseng and winter cherry.
The ashwagandha plant is a small shrub with yellow flowers that’s native to India and North Africa. Extracts or powder from the plant’s root or leaves are used to treat a variety of conditions.
Many of its health benefits are attributed to its high concentration of withanolides, which have been shown to fight inflammation and tumor growth (1Trusted Source).
SUMMARY
Ashwagandha is a prominent herb in Indian Ayurvedic medicine and has become a popular supplement due to its health benefits.
2. Can reduce blood sugar levels
In several studies, ashwagandha has been shown to lower blood sugar levels.
One test-tube study found that it increased insulin secretion and improved insulin sensitivity in muscle cells (2Trusted Source).
Also, several human studies have suggested that it can reduce blood sugar levels in both healthy people and those with diabetes (3, 4Trusted Source, 5Trusted Source, 6Trusted Source).
Additionally, in a 4-week study in people with schizophrenia, those treated with ashwagandha had an average reduction in fasting blood sugar levels of 13.5 mg/dL, compared with 4.5 mg/dL in those who received a placebo (5Trusted Source).
What’s more, in a small study in 6 people with type 2 diabetes, supplementing with ashwagandha for 30 days lowered fasting blood sugar levels. However, the study didn’t include a control group, making the results questionable (6Trusted Source).
SUMMARY
Limited evidence suggests that ashwagandha reduces blood sugar levels through its effects on insulin secretion and sensitivity.
ADVERTENTIE
3. Might have anticancer properties
Animal and test-tube studies have found that withaferin — a compound in ashwagandha — helps induce apoptosis, which is the programmed death of cancer cells (7Trusted Source).
It also impedes the growth of new cancer cells in several ways (7Trusted Source).
First, withaferin is believed to promote the formation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) inside cancer cells, disrupting their function. Second, it may cause cancer cells to become less resistant to apoptosis (8Trusted Source).
Animal studies suggest that it may help treat several types of cancer, including breast, lung, colon, brain, and ovarian cancer (9Trusted Source, 10Trusted Source, 11Trusted Source, 12Trusted Source, 13Trusted Source).
In one study, mice with ovarian tumors treated with withaferin alone or in combination with an anti-cancer drug showed a 70–80% reduction in tumor growth. The treatment also prevented the spread of cancer to other organs (13Trusted Source).
Although no evidence suggests that ashwagandha exerts similar effects in humans, the current research is encouraging.
SUMMARY
Animal and test-tube studies have shown that withaferin, a bioactive compound in ashwagandha, promotes the death of tumor cells and may be effective against several types of cancer.
4. Can reduce cortisol levels
Cortisol is known as a stress hormone given that your adrenal glands release it in response to stress, as well as when your blood sugar levels get too low.
Unfortunately, in some cases, cortisol levels may become chronically elevated, which can lead to high blood sugar levels and increased fat storage in the abdomen.
Studies have shown that ashwagandha may help reduce cortisol levels (3, 14Trusted Source, 15Trusted Source).
In one study in chronically stressed adults, those who supplemented with ashwagandha had significantly greater reductions in cortisol, compared with the control group. Those taking the highest dose experienced a 30% reduction, on average (3).
SUMMARY
Ashwagandha supplements may help lower cortisol levels in chronically stressed individuals.
5. May help reduce stress and anxiety
Ashwagandha is perhaps best known for its ability to reduce stress.
Researchers have reported that it blocked the stress pathway in the brains of rats by regulating chemical signaling in the nervous system (16Trusted Source).
Also, several controlled human studies have shown that it can reduce symptoms in people with stress and anxiety disorders (14Trusted Source, 17Trusted Source, 18Trusted Source).
In a 60-day study in 64 people with chronic stress, those in the group that supplemented with ashwagandha reported a 69% reduction in anxiety and insomnia, on average, compared with 11% in the placebo group (14Trusted Source).
In another 6-week study, 88% of people who took ashwagandha reported a reduction in anxiety, compared with 50% of those who took a placebo (18Trusted Source).
SUMMARY
Ashwagandha has been shown to reduce stress and anxiety in both animal and human studies.
Fight off inflammation with high-quality, natural ingredients — at a low price. Amazon Elements Turmeric Complex provides an affordable way to support your immune system.SHOP ON AMAZON
6. May reduce symptoms of depression
Although it hasn’t been thoroughly studied, a few studies suggest ashwagandha may help alleviate depression (14Trusted Source, 18Trusted Source).
In one controlled 60-day study in 64 stressed adults, those who took 600 mg of high-concentration ashwagandha extract per day reported a 79% reduction in severe depression, while the placebo group reported a 10% increase (14Trusted Source).
However, only one of the participants in this study had a history of depression. For this reason, the relevance of the results is unclear.
SUMMARY
The limited research available suggests that ashwagandha may help reduce depression.
7. Can boost testosterone and increase fertility in men
Ashwagandha supplements may have powerful effects on testosterone levels and reproductive health (15Trusted Source, 19Trusted Source, 20Trusted Source, 21Trusted Source).
In one study in 75 infertile men, the group treated with ashwagandha showed increased sperm count and motility.
What’s more, the treatment led to a significant increase in testosterone levels (21Trusted Source).
The researchers also reported that the group who took the herb had increased antioxidant levels in their blood.
In another study, men who received ashwagandha for stress experienced higher antioxidant levels and better sperm quality. After 3 months of treatment, 14% of the men’s partners had become pregnant (15Trusted Source).
SUMMARY
Ashwagandha helps increase testosterone levels and significantly boosts sperm quality and fertility in men.
8. May increase muscle mass and strength
Research has shown that ashwagandha may improve body composition and increase strength (4Trusted Source, 20Trusted Source, 22Trusted Source).
In a study to determine a safe and effective dosage for ashwagandha, healthy men who took 750–1,250 mg of pulverized ashwagandha root per day gained muscle strength after 30 days (4Trusted Source).
In another study, those who took ashwagandha had significantly greater gains in muscle strength and size. It also more than doubled their reductions in body fat percentage, compared with the placebo group (20Trusted Source).
Ashwagandha has been shown to increase muscle mass, reduce body fat, and increase strength in men.
9. May reduce inflammation
Several animal studies have shown that ashwagandha helps decrease inflammation (23Trusted Source, 24Trusted Source, 25Trusted Source).
Studies in humans have found that it increases the activity of natural killer cells, which are immune cells that fight infection and help you stay healthy (26Trusted Source, 27Trusted Source).
It has also been shown to decrease markers of inflammation, such as C-reactive protein (CRP). This marker is linked to an increased risk of heart disease.
In one controlled study, the group who took 250 mg of standardized ashwagandha extract daily had a 36% decrease in CRP, on average, compared with a 6% decrease in the placebo group (3).
10. May lower cholesterol and triglycerides
In addition to its anti-inflammatory effects, ashwagandha may help improve heart health by reducing cholesterol and triglyceride levels.
Animal studies have found that it significantly decreases levels of these blood fats.
One study in rats found that it lowered total cholesterol and triglyceride levels by 53% and nearly 45%, respectively (28Trusted Source).
While controlled human studies have reported less dramatic results, they have observed some impressive improvements in these markers (3, 4Trusted Source, 5Trusted Source, 6Trusted Source).
In a 60-day study in chronically stressed adults, the group taking the highest dosage of standardized ashwagandha extract experienced a 17% decrease in LDL (bad) cholesterol and an 11% decrease in triglycerides, on average (3).
SUMMARY
Ashwagandha may help reduce the risk of heart disease by decreasing cholesterol and triglyceride levels.
11. May improve brain function, including memory
Test-tube and animal studies suggest that ashwagandha may mitigate memory and brain function problems caused by injury or disease (29Trusted Source, 30Trusted Source, 31Trusted Source, 32Trusted Source).
In one study, rats with epilepsy that were treated with ashwagandha had nearly a complete reversal of spatial memory impairment. This was likely caused by a reduction in oxidative stress (32Trusted Source).
Although ashwagandha has traditionally been used to boost memory in Ayurvedic medicine, only a small amount of human research has been conducted in this area.
In one controlled study, healthy men who took 500 mg of standardized extract daily reported significant improvements in their reaction time and task performance, compared with men who received a placebo (33Trusted Source).
Another 8-week study in 50 adults showed that taking 300 mg of ashwagandha root extract twice daily significantly improved general memory, task performance, and attention (34Trusted Source).
12. Is safe for most people and widely available
Ashwagandha is a safe supplement for most people, although its long-term effects are unknown.
However, certain individuals should not take it, including pregnant and breastfeeding women.
There’s also a great selection of high-quality supplements available online.
The bottom line
Ashwagandha is an ancient medicinal herb with multiple health benefits.
Sources
a teaspoon of ashwaganda powder Many of its health benefits are attributed to its high concentration of withanolides, which have been shown to fight inflammation and tumor growthIt has also been shown to decrease markers of inflammation, such as C-reactive protein (CRP). This marker is linked to an increased risk of heart disease.
Echinicea (reduces inflammation, boosts the immune system, and helps fight infection in the mouth.)
Trace Minerals for Your Teeth

A nutrient-rich diet, on the other hand, supports healthy, ongoing remineralization.
And it’s not just about calcium, although that indeed is a critical mineral for keeping teeth strong and sturdy. It’s not just about vitamin D or K or phosphorous. What we really need is a mixed mineral and vitamin cocktail in our diet, as many nutrients require the presence of others to work effectively.
Like all essential nutrients, minerals are best supplied through plants – which absorb them from the soil – or through the meat, milk, cheese, butter and eggs of animals that feed on those plants. Excellent whole food sources of minerals include dark, leafy greens and other vegetables, nuts, and seeds, whole grains, legumes and meat. (Whole food matters, as the more our food is processed, the more nutrients it loses.) Foods that deplete minerals include coffee, soda, sugar and alcohol.
Many herbs and spices contain minerals, too, and one in particular stands out as an excellent source of many of the nutrients critical to enamel integrity: stinging nettle.

The herb Urtica dioica, commonly known as nettle, is probably one of the most useful plants available to mankind. Though it’s prickly nature makes it hard to harvest (a sting from a nettle plant can cause swelling and itching like a bug bite), it’s rich in protein, fiber, vitamins and, most importantly, minerals.
Humans have been braving nettle’s sting for centuries. With its spinachy-cucumbery flavor, it is found in many delectable recipes all over the world and was once prized by the Native Americans as a nutrient source in the spring when other food sources were scarce.
Medicinally, nettles have been used throughout history to treat allergies, kidney and urinary tract disorders, digestive disorders, musculoskeletal issues, skin irritation, hemorrhage, flu, arthritis and gout. In the old days, it was common practice to flog oneself with nettle branches to relieve joint pain!
https://beyondbiodent.com/trace-minerals-teeth/
Essential Oils – The Potentially Unhealthy Ingredient in your “Healthy” Toothpaste
Think swapping toxic chemicals for an essential oils toothpaste is a safe bet? Think again! Your healthy and natural toothpaste may be just as harmful.
Updated on July 3, 2020
- Essential oils can match the effectiveness of manmade chemicals such as Chlorhexidine.
- Essential oils are highly concentrated
- Essential oils in the mouth kill beneficial bacteria
- Essential oils to avoid during pregnancy
- Factors that contribute to essential oil safety
- Should your toothpaste contain essential oils?
- The concern behind essential oils toothpaste is warranted
- Chocolate lover’s DIY toothpaste without essential oils
Without a doubt, natural alternatives to mainstream commercial toothpastes are usually a better choice for your oral health. However an all natural solution is not always what it seems.
Our mouths are similar to our guts in that they house a living, breathing microbiome of bacteria. Our oral microbiomes contain both good and bad bacteria. The key to a healthy mouth, teeth, and fresh breath is finding the best balance of these bacteria. This is not accomplished by continuously and indiscriminately killing bacteria in your mouth with mouthwashes and toothpastes.
Contrary to what most of us have been told for the majority of our lives, it isn’t a good idea to blast the bacteria in your mouth with products such as Listerine mouthwash, which claims to ‘kill 99% of germs.’ When you use products that kill bad bacteria, those same products can also harm good bacteria.
Being the health-conscious person you are, you’d probably prefer to see ‘peppermint oil’ on a tube of toothpaste over ‘sulfuric acid monododecyl ester sodium salts.’ While I’m going to have to agree with you on that one, this does NOT mean the safer sounding ingredient isn’t powerful and capable of leaving a lasting negative impact on your health.
In fact, some essential oils have been found to be as powerful as chlorhexidine – the flagship ingredient in many prescription mouthwashes – well-known for its ability to crush your oral microbiome.
Additionally, high amounts of essential oils can damage gum tissues – similar to chlorhexidine. Studies have found mouth rinses with some essential oils to be damaging to healthy gums and in some cases, they can prevent gums from functioning normally.
Essential oils can match the effectiveness of manmade chemicals such as Chlorhexidine.
We tend to think because an ingredient comes from a natural source (and we can pronounce their names!) they are safer than the manmade, mystery ingredients inside so many of our products. But essential oils have been used for hundreds of years for their powerfully antibacterial properties.
Essential oils have long been used in cleaning products, to disinfect wounds, and to treat infections precisely due to their effectiveness in killing microbes. Some believe essential oils may be the next ‘antibiotics’ as many bacterial strains have become more and more antibiotic resistant.
So, why then would we think it’s a good idea to add essential oils to our toothpastes?
I’ve seen many an article explain the importance of the oral microbiome and beneficial bacteria, only to immediately recommend using toothpastes containing powerfully antibacterial essential oils.
Are essential oils beneficial in toothpaste and other oral care products? Or have we overlooked the strength of this important natural ingredient?
Essential oils are highly concentrated
There’s a reason that tiny bottle is so expensive.
Essential oils are highly concentrated derivatives of their respective plant. Here’s how much plant life you need to make a standard 15 ml bottle of your favorite essential oil:
- 315 pounds of rose petals
- 30 pounds of lavender flowers
- 75 lemons
- 1 pound of peppermint plant
Many essential oils carry serious warnings due to their potency. They should be considered pharmaceutical grade and used with the same care you would use a drug.
I’m not trying to scare you away from essential oils at all here, I love my essential oils. I just want you to be aware that they are powerful and need to be used responsibly. As a general rule of thumb, any time you’re using essential oils they should always be diluted and you usually only need a couple of drops.
Essential oils in the mouth kill beneficial bacteria
The problem with many natural products is there isn’t nearly as much funding for research when compared to pharmaceuticals. Most of the studies on the effects of essential oils on the oral microbiome are examining their ability to kill oral pathogens or how effective they are in comparison to conventional ingredients (such as chlorhexidine).
One study found that tea tree mouth rinses were effective at killing bacteria and volatile sulphur compound, known to cause bad breath. It seems like good news until the same study concluded that tea tree oil was as effective as chlorhexidine.
Remember nasty chlorhexidine? It’s a disinfectant that kills both beneficial and harmful bacteria of the mouth. Tea tree oil has long been used for its antibacterial properties and is probably not great for your oral microbiome.
That being said, many of the conclusions of available studies tend to consider essential oils effective if they kill bacterial or fungal infections. The better studies, measure the effectiveness of various essential oils in a variety of concentrations and their effect on specific organisms in the mouth.
While we are hearing more about the gut microbiome and the delicate balance needed among the bacteria there – the oral microbiome, inextricably linked to the gut microbiome, is not being discussed.
There are claims that some essential oils are capable of killing only the bad bacteria and leaving the beneficial. However, there is a serious lack of research comparing the effects of essential oils on beneficial and harmful bacteria. What research does exist on the subject, does not support this claim. Essential oils can damage healthy gum tissue and kill microbes indiscriminately.
I do think that in the case of harmful bacterial or fungal overgrowth, such as candidiasis, essential oils could be an effective and safe as a short term option. My concern with essential oils in oral products is daily exposure that could lead to a disrupted microbiome.
Essential oils to avoid during pregnancy
Using essential oils during pregnancy is a topic of contentious debate and in need of more research all around. Due to their therapeutic potency, there are valid concerns for essential oil use during pregnancy. There are a few essential oils that carry warnings from ancient folklore but due to the delicate nature of pregnancy, a better ‘safe than sorry’ attitude has been adopted for many essential oils (peppermint and clary sage are two of these).
The National Association for Holistic Aromatherapy (NAHA) recommends pregnant women avoid the following essential oils:
- Aniseed
- Basil
- Birch
- Camphor
- Mugwort
- Parsley seed
- Pennyroyal
- Sage
- Tansy
- Tarragon
- Thuja
- Wintergreen
- Wormwood
I bring up essential oils and pregnancy mostly because toothpastes are a source of essential oils that many pregnant mothers don’t consider and the concerns demonstrate the medicinal power and efficacy of essential oils.
Factors that contribute to essential oil safety
‘Essential oils’ is a blanket term that can be misleading when discussing safety and effectiveness. There are thousands of essential oils available on the market. Additionally, the production of essential oils is not regulated by the FDA and so therefore they vary in purity. With these variables in mind, there are four important considerations when it comes to essential oil safety.
- Species of the plant and its therapeutic use – Some oils are great for certain health factors but terrible for others. An example of this is fennel oil is great for improving colic in infants but can cause seizures in people with epilepsy – two dramatically opposing effects of the same oil.
- Quality of the essential oil – This should be a given. I urge you to only use high-quality essential oils from trusted sources. When it comes to your natural toothpaste, sticking with a better brand is usually a better bet.
- Application method – How you use an essential oil will influence how much you should use. Using essential oils in a diffuser is generally safe and there aren’t as many limits. Once you start applying oils to your skin, your mouth or begin consuming them, the amount you should use significantly decreases. In fact, using essential oils orally (such as in toothpaste) has the lowest recommended dosage when compared to dermal or internal use.
- Chemical composition – For many oils, the compounds contained in the oil are what give it its therapeutic properties. Many of the compounds have been isolated and studied while others could use more research.
Should your toothpaste contain essential oils?
It’s important that the sources of your essential oils are always high-quality. When it comes to your toothpaste ingredients, it’s tough to know where their essential oils are coming from. Also, most of the essential oils toothpastes are antibacterial, such as:
- Peppermint
- Tea tree
- Wintergreen
- Spearmint
- Clove
But this isn’t always the case.
Some essential oils found in toothpastes are not very antibacterial and totally acceptable, such as Aniseed (anise). Surprisingly Cinnamon oil has the most potential bactericidal properties and is found in many toothpastes.
The biggest concern I have for essential oils in toothpastes is how potentially powerfully destructive the antibacterial properties can be in a toothpaste.
The concern behind essential oils toothpaste is warranted
What’s confusing for consumers is that we don’t know the exact concentration of the essential oil, the therapeutic dose of the essential oil nor how much essential oil is used per tube of toothpaste, but we know that just one drop can pack a major antibacterial punch.
Check your toothpaste ingredients to see where on this list essential oils falls – the lower on the list the better. While this isn’t a hard and fast rule for knowing exactly how much essential oils are in your toothpaste, it can help you when you’re making a decision between two tubes.
I want to add that if you’re using a brand of toothpaste where the worst ingredient is essential oils, you’re doing much better at taking care of your mouth than most of the country. Commercial toothpastes like Crest and Colgate are packed with all sorts of nasty chemicals. I’m constantly telling my patients, “Oral health is about progress, not perfection.”
That being said, the concern behind essential oils in toothpaste is warranted. In an effort to improve your oral microbiome and dental health, you may have chosen and equally damaging product.
Chocolate lover’s DIY toothpaste without essential oils
I’ve seen many dental health success stories in patients who focus on diet and lifestyle over quick fixes. Through focusing on a nutrient dense diet, reducing inflammation, and promoting good oral microbiome health, you’ll have better oral and overall health.
I’ve created a DIY toothpaste with all this information in mind and it has been wildly successful – I’m excited to share it with you!
My Chocolate Lover’s DIY Toothpaste combines all the essential elements for cultivating a healthy oral microbiome and mouth.
I first designed this toothpaste for my family and patients but I was hearing such great feedback, I just had to share it with you. This toothpaste:
- Promotes remineralization of your teeth
- Includes cacao which contains compounds that reduce cavities and strengthen enamel
- Nourishes your beneficial bacteria with probiotics and prebiotics
- Gives your mouth a neutral pH, which will leave a wonderful aftertaste
- Plus, it tastes amazing!
I’d love to hear how you like this toothpaste – share a photo of you and your family using it with the hashtag #ChocolatesLoversDIYToothpaste and tag me @askthedentist on Instagram, Facebook, or Twitter.
DIY Probiotic Toothpaste
Updated on July 3, 2020
Looking for an alternative to commercial toothpastes containing toxic ingredients that are harmful to your health? Here’s a natural and effective toothpaste you won’t have to call your doctor for in case you accidentally swallow some!
This homemade toothpaste may look more like dessert, but don’t be fooled!
Coconut oil and bentonite clay are the perfect foundation for toothpaste, creating a delightful taste and texture along with superior effectiveness.
Coconut oil supports the gut microbiome (remember that oral health is connected to gut health and that your mouth is part of your digestive tract).
Bentonite clay cleans your teeth without being too abrasive, while its high mineral content helps to remineralize your teeth.
The addition of probiotics and prebiotics help to create a healthy mouth flora. And as for the cacao…believe it or not it’s not just about the taste! (Although we here at Ask the Dentist do indeed love some high quality chocolate). Compounds found in cacao lower your chance of cavities and also harden tooth enamel.
Indulge in the naturally delicious flavor and satisfaction of brushing your teeth with healthy, non-toxic toothpaste that you made yourself!
https://askthedentist.com/diy-probiotic-toothpaste/
Key Oral Health Benefits of Ginger
Consuming ginger can help you…
- Remove plaque.
- Keep cavities away.
- Strengthen your gum tissue.
- Temporarily relieve toothaches and oral pain.
- Prevent inflammatory oral diseases.
- Reduce your risk of gingivitis and gum disease.
- Protect you from serious oral infections, diseases, and cancers.
Ginger Can Help Fight Against Gingivitis and Gum Disease
Now you know ginger can protect you from serious oral health issues.
But, how exactly does it do this?
Active Ingredient #1: Raffinose for Plaque Defense
Raffinose, one of the key active ingredients in ginger, helps prevent bacterial buildup around your teeth and gums.
This robust ingredient found in ginger fights sugar formation around the teeth, therefore keeping biofilm from developing. A biofilm is a stubborn form of bacteria that sticks to surfaces. It is the primary cause of plaque accumulation and can ultimately lead to cavities and overall decay.
The ingredient, Raffinose, further:
- Relieves pain, swelling, and infections related to toothaches.
- Reduces biofilm and other bacterial accumulation on teeth and gums.
- Prevents inflammatory diseases like periodontal disease, which diminishes bone and tissue in your mouth.
And much, much more.
Active Ingredient #2: Gingerol for Fighting Infection
Gingerol is the main ingredient that gives ginger its spice.
In fact, this super ingredient actually stopped cancerous cells from metastasizing. The same ingredient that adds spice to your meals can possibly also stop cancer from spreading.
Olive leaf
Olive Leaf Extract Attenuates Inflammatory Activation and DNA Damage in Human Arterial Endothelial Cells. Olive leaf extract (OLE) is used in traditional medicine as a food supplement and as an over-the-counter drug for a variety of its effects, including anti–inflammatory and anti-atherosclerotic ones.
9 Impressive Health Benefits of Onions
Though all vegetables are important for health, certain kinds offer unique benefits.
Onions are members of the Allium genus of flowering plants that also includes garlic, shallots, leeks and chives.
These vegetables contain various vitamins, minerals and potent plant compounds that have been shown to promote health in many ways.
In fact, the medicinal properties of onions have been recognized since ancient times, when they were used to treat ailments like headaches, heart disease and mouth sores (1Trusted Source).
Here are 9 impressive health benefits of onions.

1. Packed With Nutrients
Onions are nutrient-dense, meaning they’re low in calories but high in vitamins and minerals.
One medium onion has just 44 calories but delivers a considerable dose of vitamins, minerals and fiber (2Trusted Source).
This vegetable is particularly high in vitamin C, a nutrient involved in regulating immune health, collagen production, tissue repair and iron absorption.
Vitamin C also acts as a powerful antioxidant in your body, protecting your cells against damage caused by unstable molecules called free radicals (3Trusted Source).
Onions are also rich in B vitamins, including folate (B9) and pyridoxine (B6) — which play key roles in metabolism, red blood cell production and nerve function (4Trusted Source).
Lastly, they’re a good source of potassium, a mineral in which many people are lacking.
In fact, the average potassium intake of Americans is just over half the recommended daily value (DV) of 4,700 mg (5Trusted Source).
Normal cellular function, fluid balance, nerve transmission, kidney function and muscle contraction all require potassium (6Trusted Source).
SUMMARYOnions are low in calories yet high in nutrients, including vitamin C, B vitamins and potassium.
2. May Benefit Heart Health
Onions contain antioxidants and compounds that fight inflammation, decrease triglycerides and reduce cholesterol levels — all of which may lower heart disease risk.
Their potent anti-inflammatory properties may also help reduce high blood pressure and protect against blood clots.
Quercetin is a flavonoid antioxidant that’s highly concentrated in onions. Since it’s a potent anti-inflammatory, it may help decrease heart disease risk factors, such as high blood pressure.
A study in 70 overweight people with high blood pressure found that a dose of 162 mg per day of quercetin-rich onion extract significantly reduced systolic blood pressure by 3–6 mmHg compared to a placebo (7Trusted Source).
Onions have also been shown to decrease cholesterol levels.
A study in 54 women with polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS) found that consuming large amounts of raw red onions (40–50 grams/day if overweight and 50–60 grams/day if obese) for eight weeks reduced total and “bad” LDL cholesterol compared to a control group (8Trusted Source).
Additionally, evidence from animal studies supports that onion consumption may reduce risk factors for heart disease, including inflammation, high triglyceride levels and blood clot formation (9Trusted Source, 10Trusted Source, 11Trusted Source).
SUMMARYResearch shows that eating onions may help reduce heart disease risk factors, such as high blood pressure, elevated triglyceride levels and inflammation.
3. Loaded With Antioxidants
Antioxidants are compounds that inhibit oxidation, a process that leads to cellular damage and contributes to diseases like cancer, diabetes and heart disease.
Onions are an excellent source of antioxidants. In fact, they contain over 25 different varieties of flavonoid antioxidants (12Trusted Source).
Red onions, in particular, contain anthocyanins — special plant pigments in the flavonoid family that give red onions their deep color.
Multiple population studies have found that people who consume more foods rich in anthocyanins have a reduced risk of heart disease.
For example, a study in 43,880 men showed that habitual intakes as high as 613 mg per day of anthocyanins were correlated to a 14% lower risk of nonfatal heart attacks (13Trusted Source).
Similarly, a study in 93,600 women observed that those with the highest intake of anthocyanin-rich foods were 32% less likely to experience a heart attack than women with the lowest intake 14Trusted Source).
Additionally, anthocyanins have been found to protect against certain types of cancer and diabetes (15Trusted Source, 16Trusted Source).
SUMMARYRed onions are rich in anthocyanins, which are powerful plant pigments that may protect against heart disease, certain cancers and diabetes.
ADVERTENTIE
4. Contain Cancer-Fighting Compounds
Eating vegetables of the Allium genus like garlic and onions has been linked to a lower risk of certain cancers, including stomach and colorectal.
A review of 26 studies showed that people who consumed the highest amount of allium vegetables were 22% less likely to be diagnosed with stomach cancer than those who consumed the least amount (17Trusted Source).
Moreover, a review of 16 studies in 13,333 people demonstrated that participants with the highest onion intake had a 15% reduced risk of colorectal cancer compared to those with the lowest intake (18Trusted Source).
These cancer-fighting properties have been linked to the sulfur compounds and flavonoid antioxidants found in allium vegetables.
For example, onions provide onionin A, a sulfur-containing compound that has been shown to decrease tumor development and slow the spread of ovarian and lung cancer in test-tube studies (19Trusted Source, 20Trusted Source).
Onions also contain fisetin and quercetin, flavonoid antioxidants that may inhibit tumor growth (21Trusted Source, 22Trusted Source).
SUMMARYA diet rich in allium vegetables like onions may have a protective effect against certain cancers.
5. Help Control Blood Sugar
Eating onions may help control blood sugar, which is especially significant for people with diabetes or prediabetes.
A study in 42 people with type 2 diabetes demonstrated that eating 3.5 ounces (100 grams) of fresh red onion reduced fasting blood sugar levels by about 40 mg/dl after four hours (23Trusted Source).
Additionally, multiple animal studies have shown that onion consumption may benefit blood sugar control.
A study showed that diabetic rats fed food containing 5% onion extract for 28 days experienced decreased fasting blood sugar and had substantially lower body fat than the control group (24Trusted Source).
Specific compounds found in onions, such as quercetin and sulfur compounds, possess antidiabetic effects.
For example, quercetin has been shown to interact with cells in the small intestine, pancreas, skeletal muscle, fat tissue and liver to control whole-body blood sugar regulation (25Trusted Source).
SUMMARYDue to the many beneficial compounds found in onions, consuming them may help reduce high blood sugar.
6. May Boost Bone Density
Though dairy gets much of the credit for boosting bone health, many other foods, including onions, may help support strong bones.
A study in 24 middle-aged and postmenopausal women showed that those who consumed 3.4 ounces (100 ml) of onion juice daily for eight weeks had improved bone mineral density and antioxidant activity compared to a control group (26Trusted Source).
Another study in 507 perimenopausal and postmenopausal women found that those who ate onions at least once a day had a 5% greater overall bone density than individuals who ate them once a month or less (27Trusted Source).
Plus, the study demonstrated that older women who most frequently ate onions decreased their risk of hip fracture by more than 20% compared to those who never ate them (27Trusted Source).
It’s believed that onions help reduce oxidative stress, boost antioxidant levels and decrease bone loss, which may prevent osteoporosis and boost bone density (28Trusted Source).
SUMMARYStudies show that onion consumption is associated with improved bone mineral density.
7. Have Antibacterial Properties
Onions can fight potentially dangerous bacteria, such as Escherichia coli (E. coli), Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) and Bacillus cereus (29Trusted Source).
Furthermore, onion extract has been shown to inhibit the growth of Vibrio cholerae, a bacteria that is a major public health concern in the developing world (30Trusted Source).
Quercetin extracted from onions seems to be a particularly powerful way to fight bacteria.
A test-tube study demonstrated that quercetin extracted from yellow onion skin successfully inhibited the growth of Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) and Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) (31Trusted Source).
H. pylori is a bacteria associated with stomach ulcers and certain digestive cancers, while MRSA is an antibiotic-resistant bacteria that causes infections in different parts of the body (32Trusted Source, 33Trusted Source).
Another test-tube study found that quercetin damaged the cell walls and membranes of E. coli and S. aureus (34Trusted Source).
SUMMARYOnions have been shown to inhibit the growth of potentially harmful bacteria like E. coli and S. aureus.
8. May Boost Digestive Health
Onions are a rich source of fiber and prebiotics, which are necessary for optimal gut health.
Prebiotics are nondigestible types of fiber that are broken down by beneficial gut bacteria.
Gut bacteria feed on prebiotics and create short-chain fatty acids — including acetate, propionate and butyrate.
Research has shown that these short-chain fatty acids strengthen gut health, boost immunity, reduce inflammation and enhance digestion (35Trusted Source, 36Trusted Source).
Additionally, consuming foods rich in prebiotics helps increase probiotics, such as Lactobacillus and bifidobacteria strains, which benefit digestive health (37Trusted Source).
A diet rich in prebiotics may help improve the absorption of important minerals like calcium, which may improve bone health (38Trusted Source).
Onions are particularly rich in the prebiotics inulin and fructooligosaccharides. These help increase the number of friendly bacteria in your gut and improve immune function (39Trusted Source).
SUMMARYOnions are a rich source of prebiotics, which help boost digestive health, improve bacterial balance in your gut and benefit your immune system.
9. Easy to Add to Your Diet
Onions are a staple in kitchens around the world.
They give flavor to savory dishes and can be enjoyed either raw or cooked.
Not to mention, they can boost your intake of fiber, vitamins and minerals.
Here are some tips on how to add onions to your diet:
- Use raw onions to add a kick of flavor to your guacamole recipe.
- Add caramelized onions to savory baked goods.
- Combine cooked onions with other vegetables for a healthy side dish.
- Try adding cooked onions to egg dishes, such as omelets, frittatas or quiches.
- Top meat, chicken or tofu with sauteed onions.
- Add thinly sliced red onions to your favorite salad.
- Make a fiber-rich salad with chickpeas, chopped onions and red peppers.
- Use onion and garlic as a base for stocks and soups.
- Throw onions into stir-fry dishes.
- Top tacos, fajitas and other Mexican dishes with chopped raw onions.
- Make a homemade salsa with onions, tomatoes and fresh cilantro.
- Prepare a hearty onion and vegetable soup.
- Add onions to chili recipes for a flavor boost.
- Blend raw onions with fresh herbs, vinegar and olive oil for a tasty homemade salad dressing.
SUMMARYOnions can easily be added to savory dishes, including eggs, guacamole, meat dishes, soups and baked goods.
The Bottom Line
The health benefits related to onions are quite impressive.
What’s more, they’re versatile and can be used to heighten the flavor of any savory dish.
Adding more onions to your diet is an easy way to benefit your overall health.
https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/onion-benefits\
I adapted this article a little bit:
1. USE EITHER ORGANIC non deodorized cold pressed COCONUT OIl (anti inflammation, anti bacterial), Organic coldpressed olive oil (fights inflammation).
2. USE 1 TABLESPOON OF THE OIL, TWO TIMES A DAY.
3. SWISH THIS IN YOUR MOUTH FOR 20 MINUTES, MAKE SURE YOU BRUSH YOUR TEETH FIRST.
4. SPIT IT OUT WHEN YOU ARE THROUGH. DON’T SWALLOW IT!
According to my findings, this protocol helps to whiten and repair teeth and improve receding gums. I myself am practicing this protocol, so I will let you know what and how it does for me.
Now let’s talk about your cavities, tooth enamel, and general tooth health. From what I have found out tooth decay comes from a deficiency of fat-soluble vitamins; namely Bèta Carotene, D, E, and K. So, to replace these missing nutrients you have to eat foods that are rich in these vitamins. Also, you can use supplements but they have to be whole food organic supplements such as Standard Process. Keep in mind, supplements should be something you can use until you can improve your diet enough to eliminate the need for them. Sometimes this is not possible and you may need some supplements ongoing.
If you would like my personal help you can always make an appointment for Nutrition Response Testing.
Note: Always use a toothpaste with no fluoride and no chemicals. Be as natural as you can. I suggest making your own with a little coconut oil .
https://www.pronamel.us/tooth-enamel/enamel-remineralization/
The results of the present study concluded that oil pulling using coconut oil and sesame oil is effective in reducing the severity of gingivitis. Coconut oil pulling practice is more effective in reducing the severity of gingivitis and thereby the gingival health status compared to oil pulling using sesame oil.
Comparative evaluation of 6% cranberry, 10% green tea, 50% aloe vera and 10% sodium ascorbate on reversing the immediate bond strength of bleached enamel: In vitro study
From one hundred and twenty extracted maxillary central incisors enamel blocks of 5 × 5 mm were prepared and arbitrarily divided into six experimental groups (n = 20): Group A: no bleaching, Group B: only bleaching protocol, Group C – bleaching + 6% cranberry extract solution, Group D – bleaching +10% Green Tea extract, Group E − bleaching + 50% aloe vera extract, Group F – bleaching + 10% Sodium Ascorbate. After bleaching antioxidants were applied for 10 min and were subjected to bonding procedures. The specimens were sectioned into 120 small strips of size (1 × 1 × 8 mm). Sixty sticks were analyzed to micro tensile bond strength using Universal testing machine and fractured segment were observed for failure modes (Adhesive, Cohesive and Mixed) under stereomicroscope. Remaining 60 sticks were observed for interface gap between tooth and composite resin under SEM. The %AA (antioxidant activity) was assessed with spectrophotometric analysis.
Results
Data was statistically analyzed using ANOVA and Post Hoc Tukey’s test. Group A (91.68 ± 2.24 Mpa) showed higher mean micro tensile bond strength versus group D (82.14 ± 1.45 Mpa), followed by group E (75.26 ± 1.92Mpa), group F (63.89 ± 1.95Mpa), group C (57.58 ± 1.96 Mpa) and least in group B (31.5 ± 1.27 Mpa). The %failure mode inferred maximum adhesive mode of failure (86.25%).
Conclusion
All the four antioxidants were able to reverse the compromised bond strength comparatively after bleaching maximum being green tea followed by aloe vera, sodium ascorbate, and minimum in cranberry.
Rahman H, Ansari MI, Khangwal M, Solanki R, Mansoori S. Comparative evaluation of 6% cranberry, 10% green tea, 50% aloe vera and 10% sodium ascorbate on reversing the immediate bond strength of bleached enamel: In vitro study. J Oral Biol Craniofac Res. 2021 Apr-Jun;11(2):107-112. doi: 10.1016/j.jobcr.2020.12.007. Epub 2021 Jan 7. PMID: 33532195; PMCID: PMC7829262.Hena Rahman,a,∗ Mohd Irfan Ansari,b Monika Khangwal,c Ravindra Solanki,d and Shahnaz Mansoorie
aDentistry Department, Government Medical College, Jalaun, India
bDept. of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics, FOD, JMI, New Delhi, India
cDentistry Department, BPS GMC for Women, Khanpur Kalan, India
dDept of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, PGIDS Rohtak, India
eFaculty of Dentistry, JMI, New Delhi, India
Hena Rahman: moc.liamg@snvaneh
∗Corresponding author. moc.liamg@snvaneh
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7829262/
The investing and supporting structures of the teeth, termed Periodontium is responsive to endogenous hormones of our body. Among the endogenous hormone Estrogen and Progesterone have direct influence on oral tissues. The periodontal status at a given time is a cumulative effect of sex hormone levels, their regulatory impact, and the effects of int…
Sources
https://www.shermanoaksdentistry.com/is-chocolate-better-for-your-teeth-than-flouride/


4 thoughts on “Research for Oils & Herbs Teeth Nourishing Toxin-free Toothpaste”